🍡 Market Integration
Learn Market Integration
- Kohis and Uhl have defined “Market integration as process which refers to the expansion of firms by consolidating additional marketing functions and activities under a single management”.
- Eg:
- Setting up of milk processing plant by animal husbandry farmer.
- Establishment of wholesale facilities by retailers.
- Integration shows the relationship of firms in a market.
- Integration influences market conduct of firms and consequently their marketing efficiency.
- Markets differ in the extent of integration.
Types of market integration
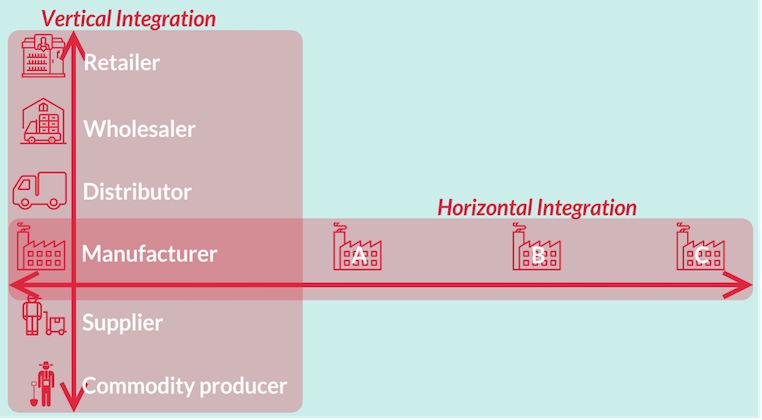
1. Horizontal integration:
- When a firm gains control over other firms, performing
similar marketing functions. - Some marketing agencies (say, sellers) combine to form a union with a view to reducing their effective number and the extent of competition in the market.
- Horizontal integration is advantageous for the members who join the group.
- If farmers join hands and form cooperatives, they are able to sell their produce in bulk and reduce their cost of marketing.
- Horizontal integration of selling firms is not in the interests of consumers or buyers.
2. Vertical integration
- Occurs when a firm performs
more than one activityin the sequence of the marketing process. - It is linking together of two or more functions within a single firm or under a single ownership.
- Eg:
- If a firm assumes the functions of the commission agent as well as retailing.
- Floor mill which engages in retailing activity as well.
- Vertical integration leads to some economies in the cost of marketing.
- Enjoys greater market power while reducing the number of middlemen.
- There are two types of vertical integration:
- a) Forward Integration: Eg: Wholesaler assuming the function of retailing i.e. assuming another function.
- b) Backward Integration: Eg: Processing firm assumes the function of assembling / purchasing the produce from villages.
- Firms often expand both vertically and horizontally. Eg: Modern retail stocks.
- Horizontal: Expanding either retail stores or number of commodities they deal.
- Vertical: Operate their own wholesale, purchasing and processing establishment.
3. Conglomeration:
- A combination of agencies or activities
not directly related to each other, may when it operates under a united management, be termed a conglomeration. - Eg: Hindustan Lever Ltd. Delhi cloth and General mill (cloth & vanaspati).
- Kohis and Uhl have defined “Market integration as process which refers to the expansion of firms by consolidating additional marketing functions and activities under a single management”.
- Eg:
- Setting up of milk processing plant by animal husbandry farmer.
- Establishment of wholesale facilities by retailers.
- Integration shows the relationship of firms in a market.
- Integration influences market conduct of firms and consequently their marketing efficiency.
- Markets differ in the extent of integration.
Types of market integration

1. Horizontal integration:
- When a firm gains control over other firms, performing
similar marketing functions. - Some marketing agencies (say, sellers) combine to form a union with a view to reducing their effective number and the extent of competition in the …
Become Successful With AgriDots
Learn the essential skills for getting a seat in the Exam with
🦄 You are a pro member!
Only use this page if purchasing a gift or enterprise account
Plan
Rs
- Unlimited access to PRO courses
- Quizzes with hand-picked meme prizes
- Invite to private Discord chat
- Free Sticker emailed
Lifetime
Rs
1,499
once
- All PRO-tier benefits
- Single payment, lifetime access
- 4,200 bonus xp points
- Next Level
T-shirt shipped worldwide

Yo! You just found a 20% discount using 👉 EASTEREGG

High-quality fitted cotton shirt produced by Next Level Apparel