⛏ Factors of Production
Learn about Factors of Production
Factors of Production
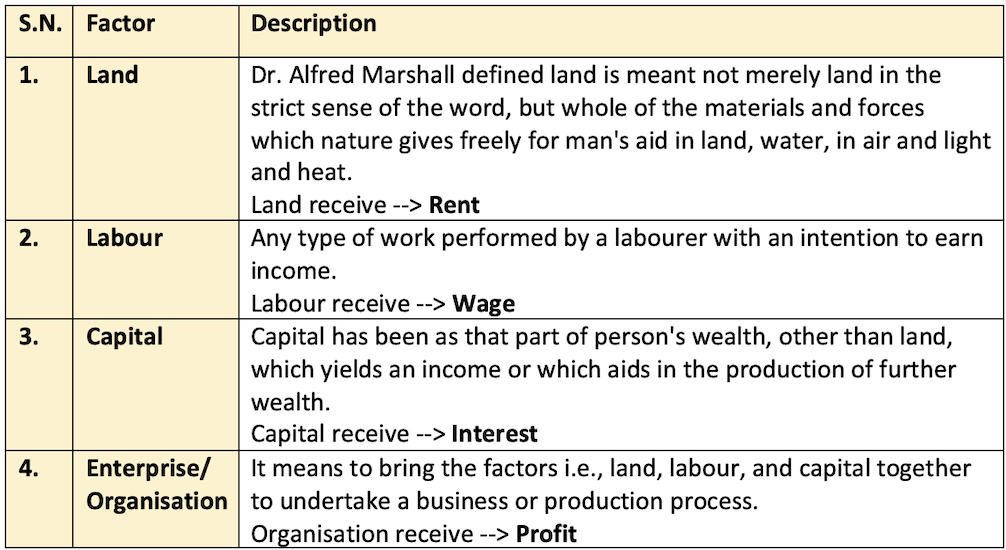
- Apportionment of returns among different factors of production is called
distribution. - It is also called
factor pricing.
Rent
The remuneration paid for the use of land. Rent is almost zero for publicly owned resources because one cannot use it for one’s own purpose. These are meant for public welfare.
Economic Rent
- Economic rent is the rent received exclusively from the use of land only.
- In farming the rent paid by a tenant to the landlord is not economic rent. Because it is included in contract rent.
Contract Rent
- This implies the money paid by the tenant to the land lord for cultivating the land in a given year.
- Normally a certain rent is charged by a farmer not only for land but also for making availability of certain infrastructure on land like buildings, machinery, wells, fencing, etc.
- This means that he would like to realize some return on the investment made on the farm. Then it is not exclusively rent for land only.
- Thus economic rent is a part of contract rent.
Quasi Rent
- The basis for evolving this rent is the short run fixity of manmade assets of production like machines, buildings, etc. When in the short run, the demand for these assets increases, consequently their income also increases. This results in a
surplus incomedue to increased demand. This surplus income of assets is called quasi rent. Thus rise in quasi rent is a temporary phenomenon. - In fact, the supply of these assets being elastic it is increased in the long run to match with the demand causing the surplus earnings to disappear.
- The concept of quasi rent does not apply to land because
supply of land is inelastic. - Concept of Quasi rent was given by
Alfred Marshall.
Scarcity Rent
- This is the rent which arises due to scarcity of land in relation to demand. Scarcity rent is due to inelastic supply of land.
- This is surplus rent over the market rent for land due to increased demand for land.
Wages
- A wage may be defined as a sum of money paid under contract by an employer to a worker for services rendered (Benham).
- Wages are paid for casual labourers, while salaries are paid for permanent staff and consultation fee for doctors, lawyers etc.
Methods of Wage Payment
- Cash Wages and Kind Wages
- Time Wages: Wage per unit time (hourly, daily, weekly, fortnightly and monthly basis).
- Piece Wages: Production unit is divided into sub process.
- Task Wages: Work assigned like transplanting, weeding, harvesting. According to agreed wages also called contract wages.
Types of Wages
Nominal Wage or Money Wage
- It is the wage paid in terms of money at current market prices.
Real Wages
- It indicates the purchasing power of money wage. Real wage of the worker is obtained by dividing nominal wage (W) of the workers at different time periods by
general price index(P). - R = W/P
Interest
- According to Marshall “the payment made by a borrower for the use of loan for, say a year, is expressed as the ratio which that payment bears to the loan” is called interest.
- Interest is the price paid for the use of loanable funds (Meyers).
Profit
- Profit is the reward for entrepreneurial function of decision-making and uncertainty bearing.
- Profit can be either positive or negative, since it is a residual income.
Factors of Production

- Apportionment of returns among different factors of production is called
distribution. - It is also called
factor pricing.
Rent
The remuneration paid for the use of land. Rent is almost zero for publicly owned resources because one cannot use it for one’s own purpose. These are meant for public welfare.
Economic Rent
- Economic rent is the rent received exclusively from the use of land only.
- In farming the rent paid by a tenant to the landlord is not economic rent. Because it is included in contract rent.
Contract Rent
- This implies the money paid by the tenant to the land lord for cultivating the land in a given year.
- Normally a certain rent is charged by a farmer not only for land but also for making availability of certain infrastructure on land like buildings, …
Become Successful With AgriDots
Learn the essential skills for getting a seat in the Exam with
🦄 You are a pro member!
Only use this page if purchasing a gift or enterprise account
Plan
Rs
- Unlimited access to PRO courses
- Quizzes with hand-picked meme prizes
- Invite to private Discord chat
- Free Sticker emailed
Lifetime
Rs
1,499
once
- All PRO-tier benefits
- Single payment, lifetime access
- 4,200 bonus xp points
- Next Level
T-shirt shipped worldwide

Yo! You just found a 20% discount using 👉 EASTEREGG

High-quality fitted cotton shirt produced by Next Level Apparel