🌅 Inflation
Learn about Inflation
Defination
- When too much money chases too few goods,
reduced value of moneyis known as inflation. - Inflation may be defined as a consistent or a persistent and appreciable rise in the general level of prices of goods and services in an economy over a long period of time.
Types of Inflation

Deflation
- Deflation is a condition of falling prices on account of insufficient effective demand.
- It results in over production, involuntary unemployment and a fall in economic activity.
- Deflation results from an insufficiency of effective demand and causes general depression resulting in large scale unemployment.
Stagflation 🦌

- It is a situation where the economy experiences stagnation or unemployment along with a high rate of inflation.
- Stagflation = Stagnation + Inflation
- It is also known as the inflationary recession.
Reflation
- It is a condition in which inflation is deliberately promoted to undertake the problem of recession or depression.
Disinflation
- Disinflation may be defined as the process of controlling inflation without causing unemployment.
Open Inflation
- Open inflation is the type of inflation in which prices are permitted to rise without any government control and checks.
Suppressed inflation
- It is a type of inflation in which prices are kept under control by the government using several checks such as rationing etc.
Creeping Inflation 🐛
- It is a condition of economy in which prices are slightly increasing (
less than 3 %which prices are per annum). - It is also known as mild inflation.
Walking Inflation 🚶
- Walking inflation is the type of inflation when the prices are moderate rising (intermediate) at the rate of
3 to 7 %per annum. - It is also known as the Trotting Inflation.
- This stage is working as a warning signal for the government to be aware to check inflation otherwise it may go up which might be more difficult to control.
Running Inflation 🏃🏻
- When there is a sustained rise in prices at the rate of
10% per annum, has fallen under the category of running inflation. - Government has to take certain necessary measures to control inflation at this stage.
Hyperinflation ❤️🔥
- This is the type of inflation in which prices may rise at the range of
16 % per annum. - It is most dangerous and destructive type of inflation which is not to be permitted by any economy.
- This condition occurs when the price line goes out of control in which government and monetary authorities find it beyond their control limit.
Measurement of Inflation in India
Wholesale Price Index (WPI)
- It is the most widely used inflation indicator in India.
- Published by the Office of Economic Adviser,
Ministry of Commerce and Industry. - All transactions at the first point of bulk sale in the domestic market are included.
- Major criticism for this index is that the general public does not buy products at wholesale price.
- The base year of All-India WPI has been revised from 2004-05 to 2011-12 (=100) in 2017.
- Include Three groups: Primary articles, Fuel and Power, Manufactured Goods
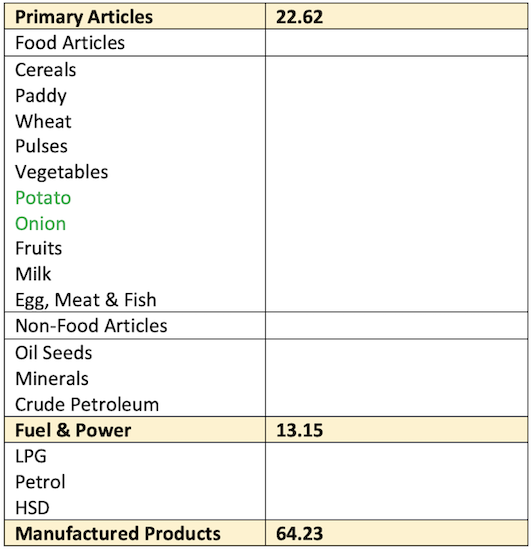
Consumer Price Index (CPI)
- It measures price changes from the perspective of a retail buyer.
- It measures changes over time in the level of retail prices of selected goods and services on which consumers of a defined group spend their incomes. Four types of CPI are as follows:
- CPI for Industrial Workers (IW)
- CPI for Agricultural Labourer (AL)
- CPI for Rural Labourer (RL)
- CPI (Rural/Urban/Combined)
- Of these, the first three are compiled by the Labour Bureau in the Ministry of Labour and Employment. Fourth is compiled by the Central Statistical Organisation (CSO) in the
Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation(MoSPI). - Base Year for CPI is 2012 (= 100).
CPI vs. WPI
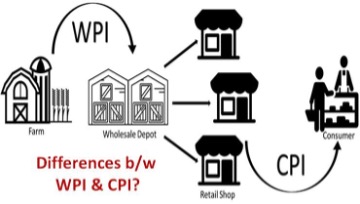
- WPI, tracks inflation at the producer level and CPI captures changes in prices levels at the consumer level.
- Both baskets measure inflationary trends (the movement of price signals) within the broader economy, the two indices differ in which weightages are assigned to food, fuel and manufactured items.
- WPI does not capture changes in the prices of services, which CPI does.
- In April 2014, the RBI had adopted the
CPIas its key measure of inflation.
Defination
- When too much money chases too few goods,
reduced value of moneyis known as inflation. - Inflation may be defined as a consistent or a persistent and appreciable rise in the general level of prices of goods and services in an economy over a long period of time.
Types of Inflation

Deflation
- Deflation is a condition of falling prices on account of insufficient effective demand.
- It results in over production, involuntary unemployment and a fall in economic activity.
- Deflation results from an insufficiency of effective demand and causes general depression resulting in large scale unemployment.
Stagflation 🦌

- It is a situation where the economy experiences stagnation or unemployment along with a high rate of inflation.
- Stagflation = Stagnation + Inflation
- It is also known as …
Become Successful With AgriDots
Learn the essential skills for getting a seat in the Exam with
🦄 You are a pro member!
Only use this page if purchasing a gift or enterprise account
Plan
Rs
- Unlimited access to PRO courses
- Quizzes with hand-picked meme prizes
- Invite to private Discord chat
- Free Sticker emailed
Lifetime
Rs
1,499
once
- All PRO-tier benefits
- Single payment, lifetime access
- 4,200 bonus xp points
- Next Level
T-shirt shipped worldwide

Yo! You just found a 20% discount using 👉 EASTEREGG

High-quality fitted cotton shirt produced by Next Level Apparel