🚋 Tillage Implements
Primary and Secondary Tillage Implements
Primary Tillage Implements
- The initial major soil working operations designed to plough the soil deeply to reduce soil strength, cover plant materials and rearrange aggregates is called primary tillage.
- Tractor draws implements include mould-board ploughs, disc ploughs, heavy duty disk harrows, subsoiler, chisel ploughs etc.
Ploughs
- Plough was invented during 2900 BC.
- The main implement which is used for primary tillage is Plough used for ploughing operations.
- Ploughing is the primary tillage operation which is performed to cut, break and invert the soil partially or completely.
- Iron plough was invented by James Small.
- Normal ploughing under primary tillage operation is usually done up to 15 cm depth.
- Vertical suction/clearance: Adjustment for depth control in M.B. plough.
- Horizontal suction/Side clearance: This suction helps M.B. plough to cut the proper width of furrow slice.
- Through clearance: It is perpendicular distance between point of share and lower position of the beam of the plough.
- Pull: total force required to pull an implements.
- Draft: Horizontal component of the pull, parallel to line of motion.
- Side draft: Horizontal component of the pull, perpendicular to line of motion.
- Unit draft: Draft per unit area.
- Effective field capacity: It is the actual area covered by implements, based on its total time consumed and its width (ha/hr).
- Theoretical field capacity: It is the theoretical area covered by implements, based on its total time consumed and its width (ha/hr).
- Field Efficiency = (Effective field capacity/Theoretical field capacity) x 100
- Soil pulverization is quality of work in terms of soil aggregates and clod size. This is measured by
Penetrometer. - Cohesion: Force of attraction between
similarparticles.(e.g. soil and soil) - Adhesion: Force of attraction between
dissimilarparticles (e.g. soil and metal) - Gathering: Whenever a plough works round a strip of ploughed land, it is said to be gathering.
- Casting: Whenever a plough works round a strip of un-ploughed land, it is said to be casting.

- Certain important terms related with ploughing of land:
- Furrow: A trench formed by an implement in the soil during the field operation.
- Furrow slice: The mass of soil cut, lifted and thrown to one side.
- Furrow wall: An undisturbed soil surface by the side of a furrow.
- Crown: The top portion of the turned furrow slice.
- Back furrow: A raised ridge left at the centre of the strip of land when ploughing is started from centre to side.
- Dead furrow: An open trench left in between two adjacent strips of land after finishing the ploughing.
Types of plough
👉🏻 The different type of ploughs are as follows:
- Indigenous plough
- Mould board plough
- Disc plough
- Chisel plough
- Sub soiler
- Rotary plough
List of Primary Tillage Implements
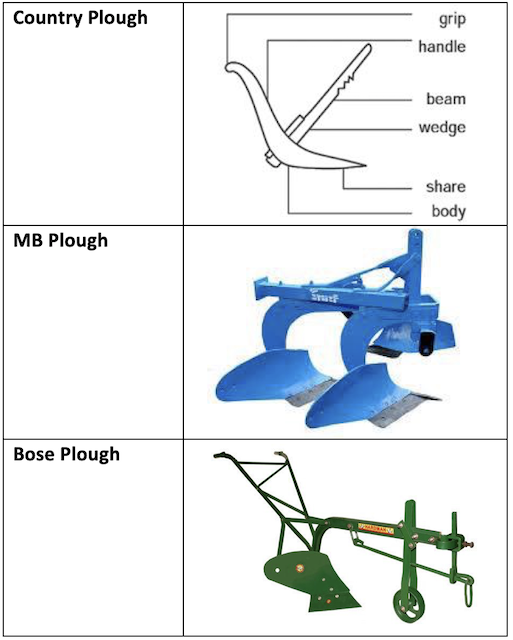
Country Plough (Indigenous Plough)
- Main parts of a plough:
- Body
- Share
- Shoe
- Beam
- Handle
- Body: It is the main frame to which the shoe, beam and handle are attached.
- Share: It is a narrow steel bar attached to the upper surface of the shoe longitudinally along the centre line and the handle are generally attached to the body of the plough.
- Types:
- Slip share
- Slip nose
- Shin
- Bar point
- Material of Share: The shares are made of chilled cast iron or steel. The steel mainly contains about 0.70 to 0.80% carbon and about 0.50 to 0.80% manganese besides other minor elements.
- Shoe: The share is attached to the shoe which penetrates into the soil and breaks it open. The shoe also helps in stabilizing and balancing the plough while in operation.
- The plough is provided with a wooden beam and a handle.
- Important points:
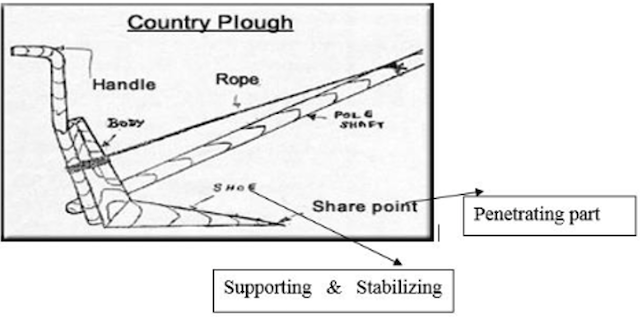
- It is an animal drawn plough.
- It penetrates into the soil and breaks it open. It forms V shaped furrows with
15-20 cmtop width and 12-15 cm depth. - It can be used for ploughing in dry land, garden land and wetlands.
- The size of the plough is represented by the width of the body and the field capacity is around
0.4 ha per day of 8 hours. - Working efficiency of desi plough is 0.32 hp/day.
Sub Soiler
- All plough and Sub-soiler (open up hard span below 40 cm depth) are the primary tillage implements.
- Infiltration of soil is with hard pan can be increased by subsoiling.
- Sub soiler works up to the depth of
45 - 75 cm.
Mould Board Plough
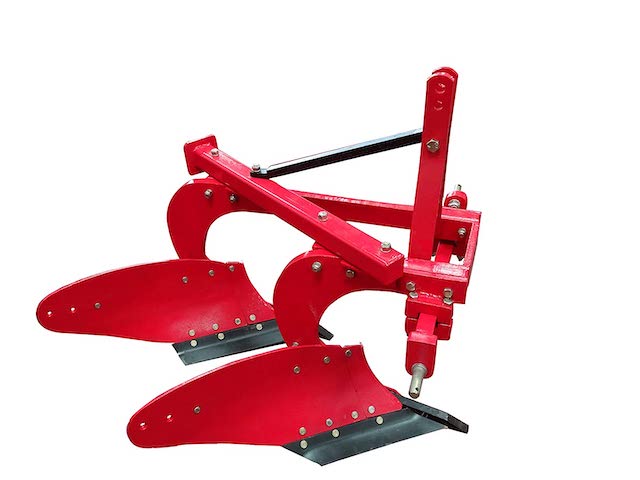

- Mould board is an implement which is used for ploughing. AFO-2021
- Mould Board ploughs are available for animals, power tiller and tractor operation.
- While working, a mould board plough does four jobs namely:
- Cutting the furrow slice
- Lifting the furrow slice
- Inverting the furrow slice and
- Pulverizing the furrow slices
- Capacity
1.5-2.0ha/day.
Disc Plough

- It is a plough which cuts, turns and in some cases breaks furrow slices by means of separately mounted large steel discs.
- A disc plough is designed with a view to reduce friction by making a rolling plough bottom instead of sliding plough bottom.
- Disc plough is used for primary tillage and it is specially used where M.B. Plough is not useful such as hard and dry soil.
- In some model disc plough is designed to operate as 2, 3 or 4 bottoms, by adding or removing sub beams the sub beam assemblies according to requirement.
- Disc: It is a circular, Vertical Disc plough revolving steel plate used for cutting and inverting the soil.
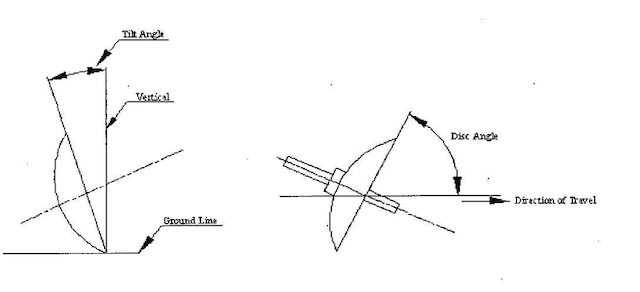
- Disc angle:
- It is the angle at which the plane of the cutting edge of the disc is inclined to the direction of travel.
- Usually the disc angle of good plough varies between
42 to 45°.
Width of cutof plough is increases by increasing disc angle.- Tilt angle:
- It is the angle at which the plane of the cutting edge of the disc is inclined to a vertical line.
- The tilt angle varies from
15° to 25°for a good plough.
- Scraper: It is device to remove the soil that tend to stick to the working surface of disc.
Secondary Tillage Implements
- Tillage operations performed after primary tillage to create proper soil tilth for seeding and planting are called secondary tillage.
- These operations are lighter and finer operations performed on the soil after primary tillage operations.
- Harrows, cultivators, sweeps, cloud crushers, levelers, bund formers, puddlers, roller and hoes are come under secondary tillage implements.
Harrow
- A harrow is an implement that cuts the soil to a shallow depth for smoothening and pulverizing the soil as well as to cut the weeds and to mix materials with soil.
- It is an implement used to break the clods after ploughing, to collect trash from the ploughed land and to level the seed bed.
- Harrow is used for harrowing, which is a secondary tillage operation, which pulverizes, smoothens and packs the soil in seed bed preparation and to control weeds.
- Types of harrows used in India
- Disc harrow
- Spring tooth harrow
- Spike tooth harrow
- Blade harrow (Bakhar)
- Triangular harrow
- Zig-zag harrow
- Bodela
- Guntaka
- Bindha
- Rotary tiller
- Other harrows
Disc Harrow

- It is a harrow, which performs the harrowing operation by means of a set of rotating discs, each set being mounted on a common shaft.
- Disc harrow is found very suitable for hard ground with full of stalks and grasses.
- It cuts the lumps of soil, clods and roots.
- Types of disc harrows:
- Depending upon the source of power, disc harrows are of two types:
- Tractor drawn (depending upon the disc arrangements, disc harrows are divided into two classes — Single action and Double disc.
- Animal drawn

- Single action disc harrow: Harrow with two gangs placed end to end which throws the soil in opposite directions.
- Double action disc harrow:
- A disc harrow containing two or more gangs, in which a set of one or two gangs follow behind the set of the other one or two, arranged in such a way that the front and back gangs throw the soil in opposite directions.
- Thus the entire field is worked twice in each strip.
- It maybe of two types: Tandem and off-set.
- Tandem Disc Harrow
- Off-set Disc harrow
- Parts of Disc Harrow:
- Disc: Concave disc 35-70 cm diameter
- Gang: It is an assembly of concave discs mounted on a common shaft with spools in between.
- Spool or Spacer: The flanged tube, mounted on the gang axle between every two discs to retain them at fixed position laterally on the shaft is called Spool or Spacer.
- The other parts are Gang bolt, Gang angle, Gang control lever, Spools or Spacer, Bearings, Transport wheels, Scraper and Weight Box.
- Tractor drawn harrow has a capacity of
2.5 ha/day.
Power harrow – tractor drawn

- A power harrow tills the soil maintaining the same profile of the field.
- It pulverizes the upper and lower layer of soil without turning them upside down and thus it forms a good seed bed as well as good soil mulch.
- It consists of two horizontal cross bars fitted with rigid pegs which reciprocate taking power from the PTO of a tractor.
- The pegs are spaced 200 mm wide and are staggered with respect to each cross bar.
- The two bars move in opposite directions and hence the implement is dynamically balanced.
- The oscillating pegs break the clods and pulverizes the soil to a fine tilth.
- The width of the operation is 2000 mm and the field capacity is around 1.5 ha/day.
Rotary Tiller (Rotavator)

- The rotary tiller or rotary cultivator is widely considered as the most important implement as it provides fine degree of soil pulverization.
- It is directly mounted to the tractor and operated.
- The rotor is operated at
180 – 200 rpm. - Capacity is
0.5 ha/hr. - Types of blades used in rotary tillers
- ‘L’ type blade: Works well in trashy conditions. More effective in cutting weeds and but do not pulverize the soil much.
- Twisted blade: Suitable for deep tillage in relatively clean grounds, but clogging and wrapping of trashes on the tynes and shafts needs frequent cleaning.
- Straight blade: Employed on mulchers designed mainly for secondary tillage.
- The benefits of the rotary tiller are:
- effective pulverization of soil ensures good plant growth
- cutting and mixing of stubbles and roots and mixing with soil and
- leveling of the field
Other Important Implements
- Basin lister: Prevent runoff and form basins.

- Sweep cultivator: Harvesting groundnut and used in stubble mulching.

- Potato digger: Used to harvest potatoes

- Groundnut digger: Used to harvest groundnut.

- Maize Sheller: Used to separate maize grains from cobs.

- Seed dressing drum: Used to treat the seed with chemicals.

- Hand gin: Used to separate lint from seed cotton.

- No-till planter: Used for sowing. AFO 2017

Primary Tillage Implements
- The initial major soil working operations designed to plough the soil deeply to reduce soil strength, cover plant materials and rearrange aggregates is called primary tillage.
- Tractor draws implements include mould-board ploughs, disc ploughs, heavy duty disk harrows, subsoiler, chisel ploughs etc.
Ploughs
- Plough was invented during 2900 BC.
- The main implement which is used for primary tillage is Plough used for ploughing operations.
- Ploughing is the primary tillage operation which is performed to cut, break and invert the soil partially or completely.
- Iron plough was invented by James Small.
- Normal ploughing under primary tillage operation is usually done up to 15 cm depth.
- Vertical suction/clearance: Adjustment for depth control in M.B. plough.
- Horizontal …
Become Successful With AgriDots
Learn the essential skills for getting a seat in the Exam with
🦄 You are a pro member!
Only use this page if purchasing a gift or enterprise account
Plan
Rs
- Unlimited access to PRO courses
- Quizzes with hand-picked meme prizes
- Invite to private Discord chat
- Free Sticker emailed
Lifetime
Rs
1,499
once
- All PRO-tier benefits
- Single payment, lifetime access
- 4,200 bonus xp points
- Next Level
T-shirt shipped worldwide

Yo! You just found a 20% discount using 👉 EASTEREGG

High-quality fitted cotton shirt produced by Next Level Apparel