🚜 Tractor
Types of Tractors, Components, Power Tillers
- Tractor is a self-propelled power unit having wheels or tracks for operating agricultural implements and machines including trailers.
- Tractor engine is used as a prime mover for active tools and stationary farm machinery through Power Take-Off shaft (PTO) or belt pulley.
Indiais the world’s largest manufacture of tractors with 50% of world’s output in 2016. It is also the world’s largest tractor market.Mahindra & Mahindrais the largest manufacturer of tractors in the world in volume and Indian market lead in the tractor industry with share of ~44% as on FY18.- Most popular tractor found in India 31 – 40 HP segment, which account near about 60% of total sales in our country.
- Highest tractor production in India: Mahindra > TAFE > Escort
History of tractor development
- The present tractor is the result of gradual development of machine in different stages.
- 1890: The word tractor appeared first on record in a patent issued on a tractor or traction engine invented by George H. Harris of Chicago
- 1906: Successful gasoline tractor was introduced by Charles W. Hart and Charles H. Parr of Charles City, Iowa
- 1908: First Winnipeg tractor trails were held
- 1911: First tractor demonstration was held at Omaha (Nebraska)
- 1915-1919: Power take off was introduced.
- 1920-1924: All purpose was developed
- 1936- 1937: Diesel engine was used in tractor and pneumatic tires were introduced
- 1950-1960: Manufacturing of diesel tractors on extensive basis throughout the world was taken up.
- Tractor in India:
1960-1961: Tractor manufacturing was started in India by first manufacturerEicher Good Earth. (Faridabad, Haryana)- 1961: TAFE tractor manufactured started.
- 1965: Gujarat tractor Ltd.
1965: Mahindra & Mahindra- 1971: Escorts Tractor Ltd. Started producing Ford Tractors
- 1973: Manufacture of HMT Tractor was started
- 1974: Manufacture of Pitti and Kirlosker Tractor was started 1975 - Harsha Tractors was established
- 1981: Auto tractors were started
- 1982: Universal Tractors was established
- 1983-2003: GTCL tractors, M.M Tractors, Sonalika, VST, L&T, Bajaj Tractors were produced
Types of tractor
- Basis of classification:
- The tractors can be classified based on the following:
- Type of Construction
- Type of Drive
- The purpose for which the usage is done
Classification based on the type of construction
Riding type tractor
- The driver can easily sit and drive the machine.
- Ex: General purpose four wheel tractor.
Walking type tractor
- The operator walks along side.
- Ex: Power tiller
Classification based on the type of drives
Track type tractors

- Also called Chain Type or Crawlers Type.
- In these types of Tractors, instead of wheels, one track is fitted on either side. This track gets drive from the sprocket run by real axle shaft.
- To steer the Tractor, there is no steering gear fitted.
- Here, the machine is steered by applying brakes to one side of the track while the other track is in motion.
- The Track Type Tractors are further classified into Half Track and Full Track types of tractors.
Half Track Type
- In these types of Tractors, a small track chain is fitted at the rear end only while tyres are fitted at the front axle.
- these tractors used for
- Reclaiming barren lands and are not much used for agricultural tasks.
- These machines are fitted with tracks in such a way that the contact area with ground is larger and facilitates in increased traction power.
- These machines are very useful in dams and in areas where earth moving tasks are required.
Wheel Type Tractors
- These are most commonly used agricultural tractors. They can run fast and wheel tyres absorb a certain amount of field shocks also.
- These can further divided as:
- Two wheel tractors: These tractors are used for small farms, hilly area and gardening purposes and are called power tillers.
- Three-wheel tractors: These tractors were very popular 15 years back but now its place has been taken by four wheel tractors. These tractors had single or dual wheel fitted at the front end in the centre and were considered good for negotiable shorter turns.
- Four-wheel tractors: These are most commonly used tractors in the country. These are also known as all-purpose tractors. On the basis of available power, these have been classified as:
- Small tractors:
15 to 25 hp - Medium tractors:
25 to 45 hp - Large tractors:
> 45 hp
- Small tractors:
- Inflation pressure of rear wheel of tractor: 0.8 – 1.5 kg/cm2
- Inflation pressure of front wheel of tractor: 1.5 – 2.5 kg/cm2
- A pneumatic tires life: 6000 working hour for drawbar work.
Classification based on the purpose for which they are used:
- Utility Tractors:
- It is a general-purpose machine and is designed for ploughing and driving any other equipment through its drive and is considered good for such farms where farmer cannot afford more machines to perform specific jobs.
- It is not being manufactured at present in the country.
- Row Crop Tractor:
- This is an all-round machine and is designated in such a way that it meets all the agricultural demands like ploughing, harrowing, levelling, pulling seed drills, weed control, running different machines like water pumps, threshers using belt pulley.
- Row-crop tractor is tailored specifically to the growing of crops grown in rows, and most especially to cultivating these crops.
- These tractors are universal machines, capable of both primary tillage and cultivation of a crop.
- Orchard Type:
- These special type Farm machines are only used in Orchards.
- These tractors have big height so that while sitting on the tractor the driver can easily pluck the fruits or the trees can easily be trimmed.
- There is no part of this machine outside the surface and this allows easy passage in between the trees.
- Industrial Tractor:
- These types of machines are also known as Tuggers.
- They are useful in pulling loads and are fined with crane boom for easy rifting of loads.
- Garden Tractor:
- These machines fall in the power range of 1 to 10 HP (Horse Power) and have very small construction size.
- They are mostly used for grass cutting or for making flower beds in the garden.
- The wheels fitted to such machines are having the size of a scooter and have a thicker depth.
- Rotary Tillers
- They fall under the category of Walking Type tractors and are used in small fields or on hills where fields are smaller in size and are at different height levels.
- Here, ordinary equipment cannot work efficiently.
- Blades are fitted to the tillers for the purpose of preparing seed beds efficiently by pulverizing the content of soil.
- Earth Moving Tractors
- These farm machines are heavy in weight and quite strong.
- They are available in both track and tyre type varieties.
- Their primary usage is for doing earth moving work on dams, quarries and different types of constructional works.
Tractor components:
👉🏻 A tractor is made of the following main units:
- I.C. engine:
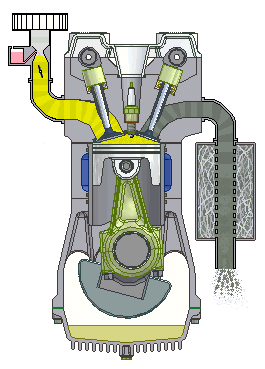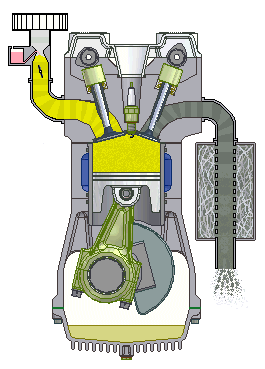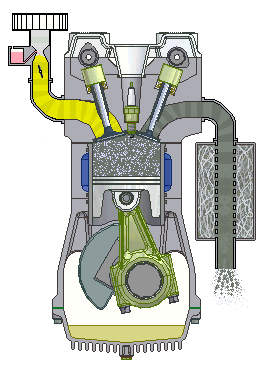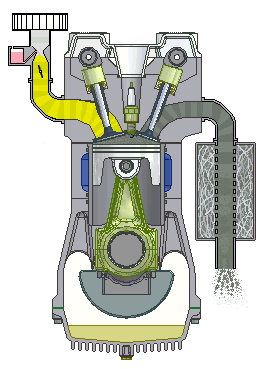
- Most common
dieselengine. - I.C. of suitable horse power is used as a prime mover in a tractor.
- Engines ranging from 8 to 200 hp are used in agricultural tractors.
- In India, four wheel tractors for agricultural operations are fitted with
25 to 80 hp. - Walking type tractors are fitted with
8 to 12 hpengines.
- Most common
- Clutch: connects and disconnects the tractor engine from the transmission gear and drive wheels. Friction clutch-four wheel tractor dog clutch-power tiller.

- Transmission gear: selective sliding type and constant mesh type.

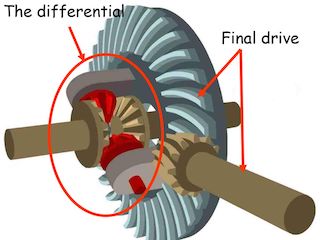
- Differential unit: differential unit is a special arrangement of gear to permit one of the rear wheels of the tractor to rotate slower or faster than the other.
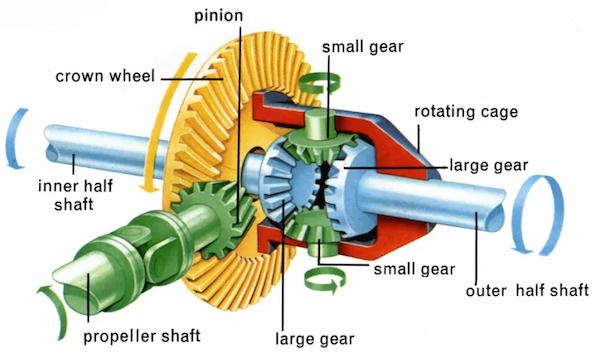
- Final drive: final drive is a gear reduction unit in the power trains between the differential and the drive wheels.
- Slogging/lugging ability: In diesel engine, torque is considerably high at lower than rated speed, this behavior is called slogging or lugging ability.
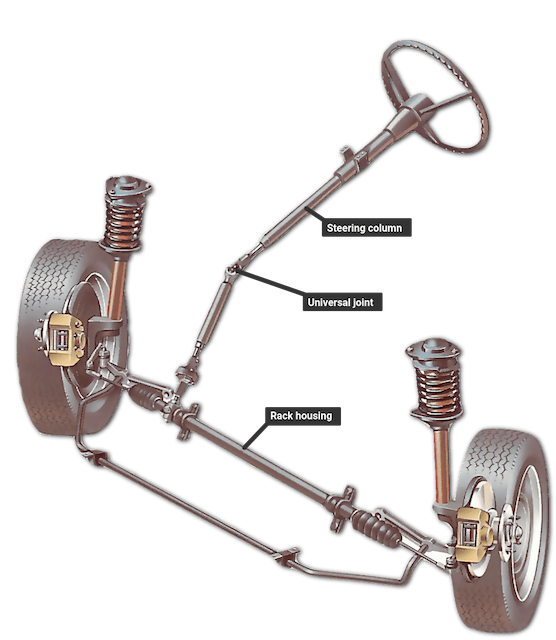
- Steering mechanism
- Hydraulic control

- Hitch system

- Brakes

- Power take-off unit (PTO):
- It is a device that transfers an engine’s mechanical power to another piece of equipment. AFO 2018
- 70-80% power is extracted by PTO.

Selection of Tractor:
👉🏻 Selection of tractors depend up on following factors
- Land holding:
- Under a mono cropping/single cropping pattern, it is normally recommended to consider
1 hp for every 2 hectares of land. - In other words,
one tractor 20-25 hpis suitable for40-hectare farm. IBPS AFO 2018
- Under a mono cropping/single cropping pattern, it is normally recommended to consider
- Cropping pattern:
- Generally,
1.5 hectare/hphas been recommended whereadequate irrigation facilityare available andmore than one cropis taken. So, a30-35 hp tractoris suitable for40 hectares of land. AIC 2017
- Generally,
- Soil condition: A tractor with less wheel base, higher ground clearance and low overall weight may work successfully in lighter soils but will not be able to give sufficient depth in black cotton soils.
- Climatic condition: For very hot zone and desert area,
air cooled enginesare preferred over water cooled engines. Similarly, for higher altitudeair cooled enginesare preferred because water cooled engines are liable to be frozen at high altitudes - Repair facilities: It should be ensured that the tractor to be purchased has a dealer at nearby place with all the technical skills for repair and maintenance of the machine.
- Running cost: Tractors with less specific fuel consumption should be preferred over others so that the running cost may be less.
- Initial cost and resale value: While keeping the resale value in mind, the initial cost should not be very high, otherwise higher amount of interest have to be paid
Power Tiller

- What is a Power Tiller?
- It is a walking type tractor. The operator walks behind the power tiller, holding the two handles of the power tiller in his own hands.
- Power tiller maybe called a single axle walking type tractor, though a riding seat is provided in certain designs.
- It is a prime mover in which the direction of travel and its control for field operation is performed by the operator walking behind it.
- It is also known as Hand tractor or walking type tractor. The concept of power tiller came in the world in the year
1920. - Japan is the first country to use power tiller on large scale. In Japan, the first successful model of power tiller was designed in the year 1947.
- In India power tiller was introduced in the year 1963.
- Manufacturing of several makes of power tillers like Iseki, Sato, Krishi, Kubota, Yanmar and Mitsubishi were started in India after 1962.
- All the power tillers are fitted with an I.C. engine. At present, most of the power tillers are fitted with diesel engine.
- Only
Isekimade have used kerosene engine. - The other makers like Kubota, Mitsubishi, Krishi, Yanmar and Satoh have used diesel engines in India.
- Usually 2 to 4 ply pneumatic tyres are used in power tillers. The pressure of the tyre ranges from 1.1 to 1.4 kg/cm2.
- Tractor is a self-propelled power unit having wheels or tracks for operating agricultural implements and machines including trailers.
- Tractor engine is used as a prime mover for active tools and stationary farm machinery through Power Take-Off shaft (PTO) or belt pulley.
Indiais the world’s largest manufacture of tractors with 50% of world’s output in 2016. It is also the world’s largest tractor market.Mahindra & Mahindrais the largest manufacturer of tractors in the world in volume and Indian market lead in the tractor industry with share of ~44% as on FY18.- Most popular tractor found in India 31 – 40 HP segment, which account near about 60% of total sales in our country.
- Highest tractor production in India: Mahindra > TAFE > Escort
History of tractor development
- The …
Become Successful With AgriDots
Learn the essential skills for getting a seat in the Exam with
🦄 You are a pro member!
Only use this page if purchasing a gift or enterprise account
Plan
Rs
- Unlimited access to PRO courses
- Quizzes with hand-picked meme prizes
- Invite to private Discord chat
- Free Sticker emailed
Lifetime
Rs
1,499
once
- All PRO-tier benefits
- Single payment, lifetime access
- 4,200 bonus xp points
- Next Level
T-shirt shipped worldwide

Yo! You just found a 20% discount using 👉 EASTEREGG

High-quality fitted cotton shirt produced by Next Level Apparel