📖 Forestry
Definition, Classification and Branches
- Forestry is defined as the theory and practice of all that constitutes the creation, conservation and scientific management of forests and the utilization of their resources.
- It includes all thinking and all actions pertaining to creation and management of forests, including harvesting, marketing and utilization of all forest products and services. It includes not only management of existing forests but also the creation of new forests.
Forestry Classification
Based on the intensity of management
Intensive forestry
- For achieving maximum production per unit area (usually timber, in volume & quality) through efficient application of modern silvicultural and management practices.
- Utilized site potential up to the maximum possible extent.
Extensive Forestry
- Practice of forestry for raising multipurpose tree species (MPTS) i.e. for the production of fuelwood, fodder, timber, wildlife conservation, etc.
- It cannot utilize site potential efficiently.
- Also known as ‘Multiple-use forestry’.
Protection Forestry
- Protection or amelioration of natural resources, i.e., Soil, water, noise & Air pollution, etc. Soil and water conservation Reduce the hazardous effect of drought, floods, tsunami, cyclones, etc.
Production Forestry
- The production forestry can be further classified into:
Commercial Forestry
- Commercial forestry aims to get maximum production of timber, fuel wood and other forest products as a business enterprise.
Industrial Forestry
- Hint: For Industry
- Industrial forestry aims at producing raw material required for industry.
- In Production forestry, there is a greater concern for the production and economic returns.
Branches of Forestry
- Forestry has different branches but silviculture is the core branch of forestry.
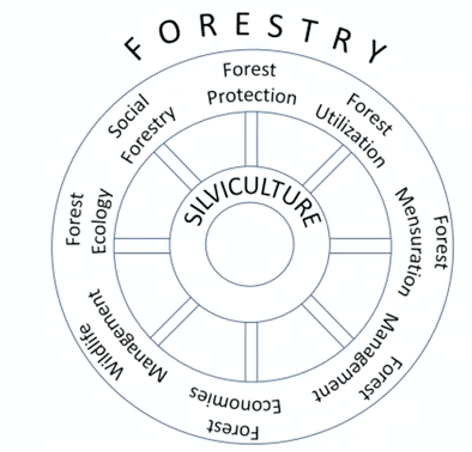
Silviculture
- The word Silva means woody patches.
- Silvics: Silvics is the study of
life historyandgeneral characteristicsof forest trees or crops with particular reference to environmental factors. - If refers to certain aspects of theory and practices of raising forests crops, methods of raising tree crops, their growth and after caring up to the time of final harvesting.
Forest Mensuration
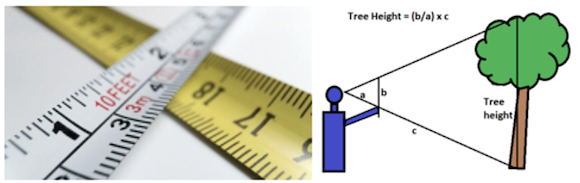
- The word mensuration is derived from a Latin word mensura, which means measure.
- Forest mensuration/
Dendrometryis the branch of forestry that deals with the determination of dimension (e.g., diameter, height, volume, etc.), form, age and increment of single tree, stands or whole forests either standing or after felling.
Social Forestry

- Social forestry may be defined as the science and art of growing trees in and outside traditional forest areas and managing like existing forest with intimate involvement of the people and more or less integrated with other operation resulting in balanced and complementary land used with view to provide wide range of goods and services to the individual as well as to the society.
Forest Management
- Forest management is the practical application of the scientific, technical and economic principles of forest estate for the achievement of certain objectives.
- Maximum sustained yield is the backbone of forest management.
Forest Utilization

- Branch of forestry which deals with harvesting, marketing conservation and applying the forest produce to a variety of uses.
- E.g. Timber, fuel, charcoal, pulp wood, plywood.
Forest Ecology

- “Ecology is defined as the study of the relations of living organisms, or groups of organisms to their environment, or the science of the interrelations between living organisms and their environments.”
- This study is conducted in forest ecosystem then it is called forest ecology.
Wildlife Management

- All living organisms (plants, animals, microorganisms) in their natural habitats which are neither cultivated/domesticated nor tamed are known as wildlife. And their management in the natural environment is known as wildlife management.
- Eg. Tiger census for tracking their population.
Forest Protection
- Forest protection is the branch of forestry that deals with the activities directed towards the prevention and control of damage to entire forest ecosystem by human beings, domestic animals, insects, diseases, plants and adverse climatic conditions.
- Just like Plant Protection in agriculture, in forestry we have forest protection, which includes forest entomolgy and forest pathology.
- Forestry is defined as the theory and practice of all that constitutes the creation, conservation and scientific management of forests and the utilization of their resources.
- It includes all thinking and all actions pertaining to creation and management of forests, including harvesting, marketing and utilization of all forest products and services. It includes not only management of existing forests but also the creation of new forests.
Forestry Classification
Based on the intensity of management
Intensive forestry
- For achieving maximum production per unit area (usually timber, in volume & quality) through efficient application of modern silvicultural and management practices.
- Utilized site potential up to the maximum possible extent.
Extensive Forestry
- Practice of forestry for …