🦌 ISFR
Status of Indian Forest as per Latest Indian State of Forest Report 2021
Introduction
- The National Forest Policy of India 1988 envisages a goal of achieving 33 percent of the geographical area of the country under forest & tree cover.
- ISFR serves as a monitoring mechanism towards achievement of this goal.
- The ISFR is used in planning and formulation of policies in forest management as well as forestry and agroforestry sectors.
- The Ministry of Environment Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC) has released
17thIndia State of Forest Report (ISFR) 2021. - The Minister for Environment, Forest and Climate Change is Shri Bhupender Yadav.

Forest Survey of India (FSI)has been assessing the forest and tree resources of our country on abiennialbasis since 1987.- FSI is an organization under the Ministry of Environment Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC).
Forest Cover
- Forest cover is defined as an area
more than 1 hain extent and having tree canopy density of 10% or above including bamboos, orchards, coconut, palm etc within recorded forest, private, community or institutional lands (means irrespective of land use, ownership and legal status).
Recorded Forest refers to all the geographic areas recorded as ‘Forests’ in government records. It mainly consists of Reserved Forests (RF) and Protected Forests (PF), which have been notified under the provisions of Indian Forests Act, 1927 or State acts.
Besides RFs and PFs, the recorded forest area may also include all such areas, which have been recorded as forests in the revenue records or have been constituted so under any state act or local laws.
What is Canopy cover?
- It is commonly expressed as a percentage of total ground area covered by the vertical projection of tree crowns.
- Ex: At 50 percent canopy cover, half of the total ground area is covered by the vertical projection of tree crowns. Unless otherwise specified, canopy cover refers to non-overlapping canopy cover.
Classification of Forest Cover
👉🏻 Forest cover classified on the basis of canopy cover.


Tree cover
- Tree cover is defined as all tree patches of size
less than 1 haoccurring outside the recorded forest area. This covers trees in all formations including scattered trees. - There are many small patches of trees, called tree cover, in small scale plantations, compact blocks, woodlots, or trees along linear features, such as roads, canals, bunds etc. and scattered trees which are not being captured by satellite sensors used for forest cover mapping due to technological limitations. These patches of trees, though small, play a significant role in socio-economic and ecological status of the country. The contribution of such trees are captured in the form of tree cover with the help of high resolution remote sensing data and supplemented by the field inventory data of TOF. Thus, information on tree cover along with the forest cover of the country gives a complete picture of tree resources of the country.
Key Finding of ISFR 2021
- The current assessment shows an increase of 1,540 sq km of forest cover, 721 sq km of tree cover and
2,261 sq kmof forest and tree cover put together at the national level as compared to the previous assessment i.e., ISFR 2019. - In this forest cover is
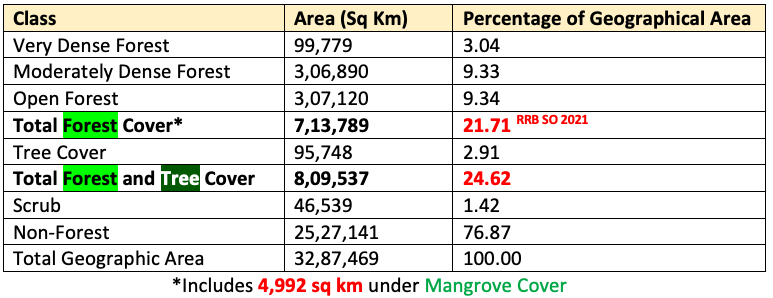
7,13,789 sq kmwhich is21.71 %and tree cover is95,748 sq kmwhich is2.91 %. - The total forest and tree cover is
8,09,537 sq km(80.9 million hectare) which is24.62 per centof the geographical area of the country. (2019: 24.56%). - 17 states/UT’s have above 33 percent of the geographical area under forest cover.
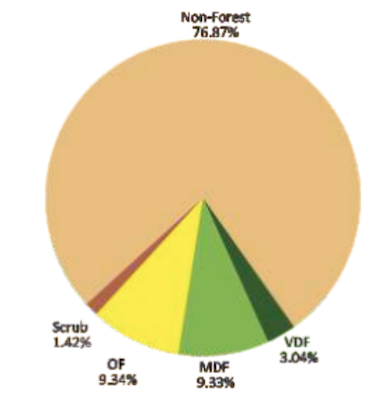
- Out of these states and UT’s, five states/UTs namely Lakshadweep, Mizoram, Andaman & Nicobar Islands, Arunachal Pradesh and Meghalaya have more than 75 percent forest cover while 12 states/UTs namely Manipur, Nagaland, Tripura, Goa, Kerala, Sikkim, Uttarakhand, Chhattisgarh, Dadra & Nagar Haveli and Daman & Diu, Assam, Odisha, have forest cover between 33 percent to 75 percent.
STATES WITH MAXIMUM FOREST COVER (AREA WISE)
Madhya Pradesh(77,493 sq. km)- Arunachal Pradesh (66,431 sq. km)
- Chhattisgarh (55,717 sq. km)
STATES/UT WITH MAXIMUM FOREST COVER (PERCENTAGE WISE)
- Lakshadweep (90.33%) 💡 (UT)
Mizoram(84.53%) 💡 (State)- Andaman & Nicobar Is. (81.75%)
CATEGORY WISE TOP STATES
- State with Highest Very Dense Forests:
Arunachal Pradeshfollowed by Maharashtra - State with Highest Moderately Dense Forests:
Madhya Pradesh - State with Highest Open Forests:
Madhya Pradesh Maharashtrais having largest extent of Trees Outside Forest (TOF) in the country, followed by Odisha and Karnataka.- In terms of percentage of geographical area, the State of
Keralahas highest percentage of TOF, followed by Goa and Nagaland. - Dependence of fuelwood on forests is highest in the State of Maharashtra, whereas, for fodder, small timber and bamboo, dependence is highest in Madhya Pradesh.
TOP STATES WITH MAXIMUM INCREASE IN FOREST COVER
- Andhra Pradesh (647 sq. km)
- Telangana (632 sq. km)
- Odisha (537 sq. km)
STATES WITH DECREASE IN FOREST COVER
- Five states in the Northeast – Arunachal Pradesh > Manipur > Nagaland > Mizoram > Meghalaya and have all shown loss in forest cover.
- It is important to mention here that these states are in the
North Eastern regionof the country where the total forest cover is very high. Total forest cover is 1,70,541 sq km, which is 65.05% of its geographical area. - The assessment of Forest Cover in hill districts of the country is done separately to monitor the progress of the country towards achieving the goal of maintaining two third of the area in hills under Forest Cover, as has been envisaged in the National Forest Policy 1988. Due to the fragility of hill areas and vulnerability to land degradation, the Forest Cover plays an important role in prevention of soil erosion, land degradation and also maintaining ecological balance and environmental stability.
- Hill or district or taluka is one where altitude is above 500m from the mean sea level.
- Forest cover in the country
hill districtsof the country is 2,83,104 sq km, which is 40.17% of the total geographical area of these districts. - As per the report, there is a decrease of 902 sq km of Forest Cover in the hill districts of the country.
- The total forest cover in the
tribal districtsis 4,22,351 sq km, which is 37.54% of the geographical area of these districts. - There is an overall decrease in Forest Cover in the tribal districts by 55 sq km, however, the Forest Cover inside the Recorded Forest Areas/Green wash areas in the tribal districts shows a decrease of 655 sq km.
- There are 218 tribal districts in 27 States/UTs as identified by the Government of India under the Integrated Tribal Development Programme.
- There is an overall decrease of 1,020 sq. km of Forest Cover in the Northeastern States.
👉🏻 The main reasons for the decrease are:
- Shifting cultivation
- Anthropogenic pressures
- Rotational felling
- Diversion of forest lands for developmental activities
- Submergence of forest cover
- Agriculture expansion
- Natural disasters
Mangrooves

- Mangroves are a diverse group of salt tolerant plant communities found in tropical and subtropical intertidal region of the world receiving rainfall between 1,000 to 3,000 mm and temperature ranging from 26°C – 35°C.
- Mangroves are commonly found throughout the world between latitudes 24° N and 38.5° S within tropical and subtropical sheltered coastal areas subjected to tidal influences.
- Mangroves are the most productive and biologically important forest having complex ecosystems.
- Due to the rich biodiversity and ecological and environmental significance of Mangrove ecosystems, the conservation of Mangroves is a focus area in India.
- Mangrove cover in India accounting for nearly 3% of the world’s mangrove vegetation. Sundarbans in West Bengal (42.45%) accounts for almost half of the total area under mangrove in India. Mangrove in India is 0.15% of total country’s total geographical area.
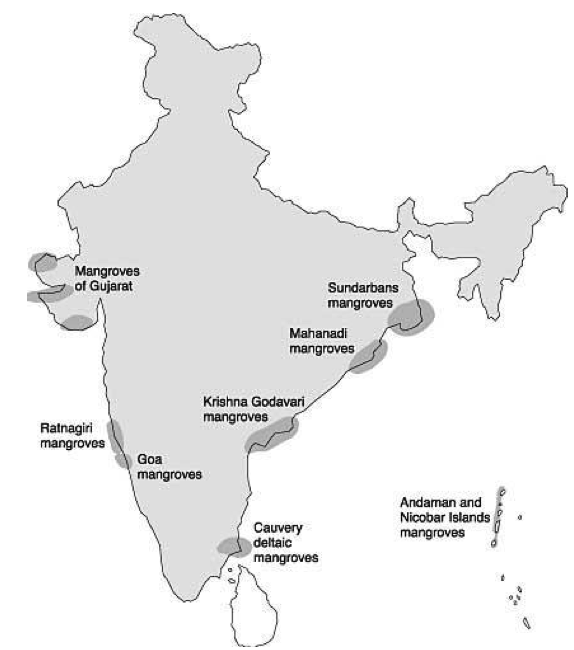
- According to ISFR 2021, total mangrove cover stands at
4,992 sq kmand has increased by17 sq kms. - Top three gainers in terms of mangrove cover are:
- Odisha (8 sq km)
- Maharashtra (4 sq km)
- Karnataka (3 sq km)
BAMBOO COVER

- Total bamboo bearing area of the country is estimated as 1,49,443 sq km.
- There is decrease of 10,594 sq km in bamboo bearing areas as compared to 2019.
- Area of Bamboo:
M.P.> Arunachal Pradesh > MH
CARBON SINK
- Striving towards achieving NDC goal India is striving towards achieving its NDC goal of creating additional carbon sink of
2.5 to 3.0 billion tonnesof CO2 equivalent through additional forest and tree cover by 2030. - As per present assessment total carbon stock in forest is estimated to be
7,204 million tonnes. There is an increase of 79.4 million tonnes in the carbon stock of country as compared to the last assessment. - State-wise Maximum carbon stock:
Arunachal Pradesh> Madhya Pradesh > Chhattisgarh > Maharashtra - Forest carbon stock is the amount of carbon that has been sequestered from the atmosphere and is now stored within the forest ecosystem, mainly within living biomass and soil, and to a lesser extent also in dead wood and litter.
Role in SDGs
Introduction
- The National Forest Policy of India 1988 envisages a goal of achieving 33 percent of the geographical area of the country under forest & tree cover.
- ISFR serves as a monitoring mechanism towards achievement of this goal.
- The ISFR is used in planning and formulation of policies in forest management as well as forestry and agroforestry sectors.
- The Ministry of Environment Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC) has released
17thIndia State of Forest Report (ISFR) 2021. - The Minister for Environment, Forest and Climate Change is Shri Bhupender Yadav.

Forest Survey of India (FSI)has been assessing the forest and tree resources of our country on abiennialbasis since 1987.- FSI is an organization under the Ministry of Environment Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC).
Forest …
Become Successful With AgriDots
Learn the essential skills for getting a seat in the Exam with
🦄 You are a pro member!
Only use this page if purchasing a gift or enterprise account
Plan
- Unlimited access to PRO courses
- Quizzes with hand-picked meme prizes
- Invite to private Discord chat
- Free Sticker emailed
Lifetime
- All PRO-tier benefits
- Single payment, lifetime access
- 4,200 bonus xp points
- Next Level
T-shirt shipped worldwide

Yo! You just found a 20% discount using 👉 EASTEREGG

High-quality fitted cotton shirt produced by Next Level Apparel