🧑🏻🌾 Silviculture
Definition, Tree Characteristics, Tending, Silviculture Systems, Forest Succession
- It is derived from
Latinword, Silva which means Wood Land. - Silviculture is that branch of forestry which deals with establishment, development, care and reproduction of stands of timber.
- Silviculture is the art and science of cultivating forest crops.
- Silviculture is the theory and practices of raising forests crops. (Champion & Seth 1968).
- Just like agronomy in agriculture, in forestry there is silviculture.
- Study of silviculture help us to get:
- Production of more volume & high quality of woods per unit area
- Reducing the rotation period of species (Produce Forest crops in less time)
- Afforestation & Reforestation, Site Protection
- Introduction of exotics i.e. Poplar, Eucalyptus etc.
- Creation of Man-Made forest in place of Natural forest
- Dendrology
- It is the science and study of wooded plants (trees, shrubs, and lianas), specifically, their
taxonomic classifications. - Identification of trees according to species and their systematic classification is called as dendrology.
- The most important characteristics to use in tree identification are bark, fruit, leaves or twigs.
- It is the science and study of wooded plants (trees, shrubs, and lianas), specifically, their
- Phenology
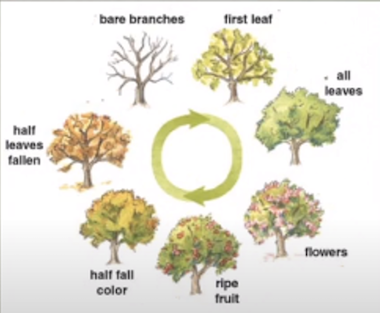
- The science that deals with the time of appearance of characteristic periodic events is known as Phenology.
- Seasonal changes in the plant i.e. flowering, fruiting, leaves shedding etc.
- The unit of silviculture is
stand. - Stand is defined as an aggregation of trees occupying a specific area sufficiently uniform in composition, age, arrangement and condition to be distinguishable from the forest on adjoining areas.
- All forest management operations are applied on stand. Therefore, foresters recognize stand as the basic management unit in a forest.
- We can say forest is a collection of stands.

Tree Characteristics
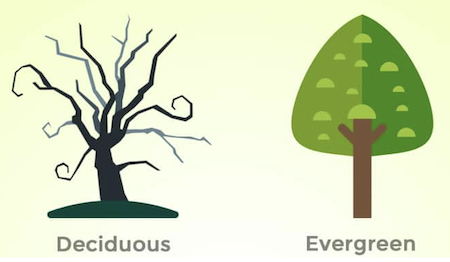
Evergreen species
- Evergreen species are the perennial plant that is never entirely without green foliage.
- In these species, the old leaves persist until the new leaves are appeared.
Deciduous species
- Deciduous means falling off at maturity or tending to fall off.
- Deciduous species are the perennial plants, which have distinct leafless period for some part of the year.
- In temperate climate, trees which shade leaves during Autumn or Winter are called Deciduous. NABARD 2021
Stem
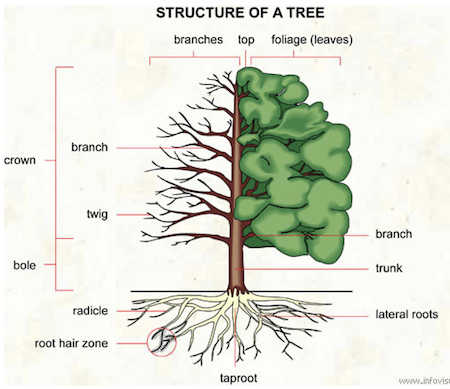
- Stem is the principal axis of plant from which buds and shoots are developed.
Bolerefers the lower part of stem up to a point where main branches are given off.- Stem = Bole = Trunk (are used as Synonyms)
Crown
Crownis the upper branchy part of the tree above the bole.

Stages of Tree Growth
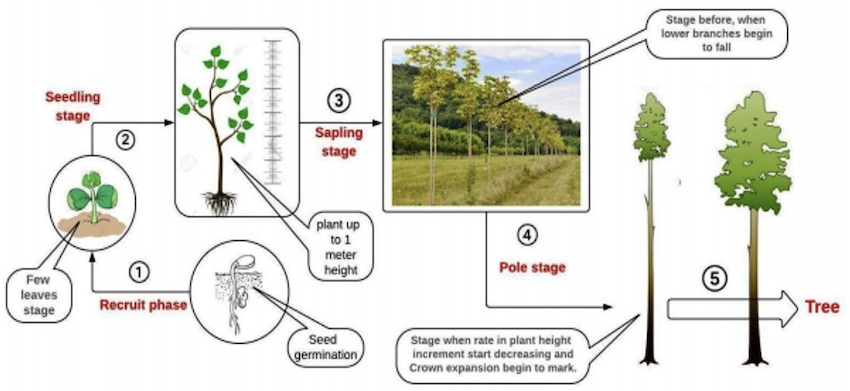
- Recruit/Juvenile phase: From seed germination to the stage when the young plant has few leaves.
- Seedling is a plant grown from seed till it reaches about one meter height and has a few leaves.
- Sapling: From the 1 m height of young plants to the stage when the lower branches of plant begin to fall.
Pole: From the beginning of fall of the lower branches to the time when the rate of increase in plant height begins to fall and the crown expansion becomes marked.- Tree is a plant, which has a well-defined single pole and is more than 6 m in height.
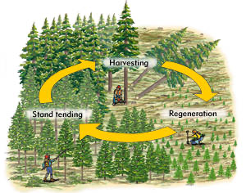
Forest Regeneration
- The act of replacing the old crop with younger ones, either naturally or artificially is called as regeneration or reproduction.
- Types:
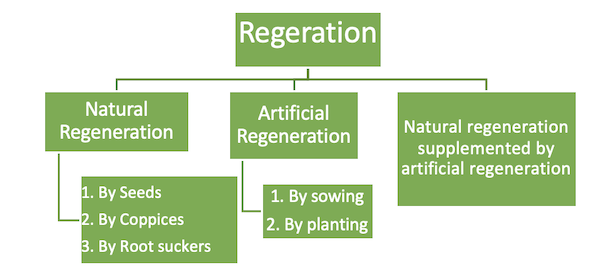
- Natural regeneration: by nature.
- Artificial regeneration: when humans were involved in its propagation
- Natural regeneration supplemented by artificial regeneration
A) Natural Regeneration
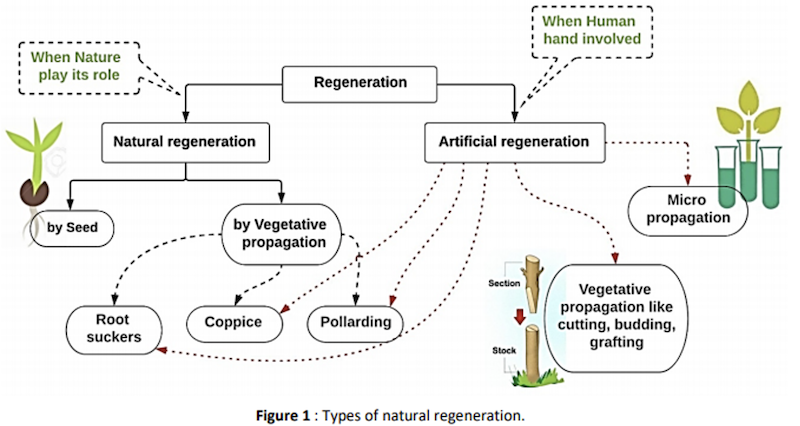
- When this seedling crop grows into a forest it is called a High Forest.
- The regeneration obtained from coppice is called coppice crop which when develops into a forest is called Coppice Forest.
👉🏻 For Natural regeneration by Coppicing
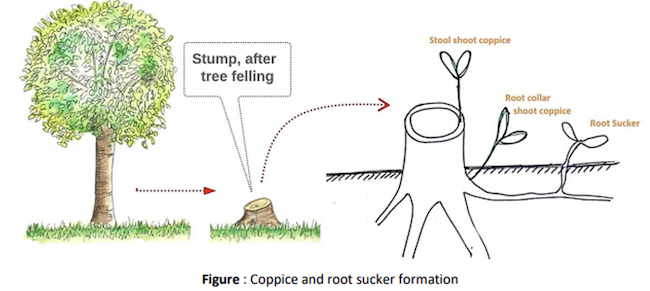
- When certain plants or seedling are cut from near ground level, they produce a flush of fresh shoots. This is known as coppicing.
- Coppicing is done at
30 – 45 cmheight.
👉🏻 For Natural regeneration by Pollarding
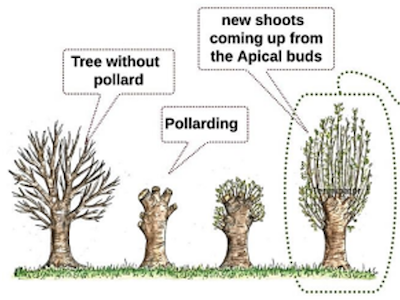
- Pollarding is the method of pruning/cutting of the stem at a suitable height to obtain a flush of shoots.
- Generally, Pollarding is carried out at
1 to 1.25 mheight so the browsing animals cannot reach and trees on which we apply this practice. - Advantage: Reach of the cattle out.
B) Artificial Regeneration
- The renewal of a forest crop by sowing, planting or other artificial means is called artificial regeneration (synonyms = plantation).
- It includes both (i)
afforestationandreforestation. - Afforestation is the establishment of a forest by artificial means on a non-forest area (the area from which forest vegetation has been absent).
- Reforestation is a re-stocking of a felled or cleared forest by artificial means on an area which previously bore forest vegetation, and which may have been felled or otherwise cleared in the recent past.
- Deforestation or forest clearance is the removal of a forest or stand of trees from land that is then converted to non-forest use.
Seed orchards

- Are plantations which may rise exclusively with the aim of producing seed.
- Seed Production areas or seed stands: These are area set aside exclusively for the purpose:
- To produce seed of high quality from genetically superior trees available in the stand.
- To concentrate seed collecting operation in a small sphere or area. The seed stands are established by removal of the inferior trees, seed orchards are plantation of genetically superior trees isolated to reduce pollination from genetically inferior once.
- Seeds orchards may be of two types:
- Clonal: Raised by grafting clones of superior trees on 2-3-year-old seedlings.
- Seedling raised from seeds of superior trees.
Forest Nursery

- Nursery refers to an area from which seedlings are raised for eventual planting out.
Pricking out

- ‘Pricking out’ your seedlings is a term that means transplanting them.
- Once seeds develop shoots and two or more leaves, they require transplanting into a larger container.
- This is known as pricking out or to transplant small seedlings individually in to nursery beds or boxes.
Hardening of Seedlings
- Hardening of seedling is essential before planting out in field.
- First, the shade to seedling is gradually removed.
- Thereafter, watering schedule is altered in such a way that quantum of water is reduced sequentially. This hardens the young seedlings and improves its adaptability under drought conditions in the field.
Tending Operation
- In a forest, competition among plants can be increased with increasing age. In order to obtain a maximum yield, the competition among the plants can be optimally managed by reducing the number of stems per unit area with the progress of age. All these can be covered under the tending operations.
- Tending is defined as any operation carried out for the benefit of a forest crop at any stage of its life between the seedling and the mature stages.
- From the establishment of the regeneration and subsequent growth to the harvesting, several operations are carried out at different stages of growth in order to provide a healthy environment for their growth. These operations are called tending operations.
- These operations are –
- Weeding,
- Cleaning,
- Thinning
- Improvement felling
- Climber cutting
- Pruning
- Girdling of unwanted growths.
- This does not include regeneration, felling, soil working, drainage, irrigation and controlled burning.
- Tending helps in producing higher quality timber and thus by maximizes income.
Lopping

- It pertains to the cutting of branches or even young stems. This leads to the development of new shoots.
- It is carried out on Diospyros for bidi industry, also in number of broad-leaved species for fuel and fodder and as Quercus incana (Indiana oak), Morus etc., for rearing silkworm.
Pruning

- Means the cutting of branches from the bole in order to maintain the quality of timber.
- Tree lopping is basically the trimming of branches of trees in order to reduce the tree size. On the other hand, pruning is associated with tree health. It can help in providing immunity to the trees against certain diseases and can ensure a long and healthy life.
Silvicultural System
- Silviculture is the art and science of cultivating forest crops.
- It deals, in a general way, with the natural laws of growth and development of trees and forests, the effect of environment on them, techniques of regenerating them naturally or artificially and the methods of tending them.
- Since the techniques of regenerating forest crops vary with types and sub-types of forests, and physical conditions in which they exist, it becomes necessary to identify different methods or techniques for different sub-types in different localities. These methods or techniques are called Silvicultural Systems.
- Silvicultural system is defined as the set of silviculture procedure worked out in accordance with accepted set of silvicultural principles by which crop constituting forest are tended, harvested and replaced by new crops of distinctive form.
- It acts as a tool for achieving the objectives of forest management.
OR - It is a planned silvicultural treatment which is applied to a forest crop, throughout its life, so that it assumes a distinctive form. It begins with regeneration fellings, tending the crop to its final felling.
👉🏻 Scope and objectives of silvicultural system
- The pattern of felling to be adopted for harvesting
- The method of regeneration to be adopted
- The tending of the new crop
- The form or character of the crop to be produced
👉🏻 Need for classification of silvicultural systems
- Silvicultural system systematizes the knowledge on regeneration and felling under various forest conditions.
- It gives precaution against wrong use.
- It directs planed treatment of crops to get maximum yield in a sustained manner.
👉🏻 Need for standardization of naming of silvicultural systems
- To give proper name all over the world uniformly.
- To avoid confusion if large number of systems are available in different region.
- To give proper worldwide understanding about different systems to foresters.
- To avoid usage of any other terms for particular treatment.
Classification of silvicultural system
- In India, silvicultural system is classified based on mode of regeneration.
High forest systems
- High forest systems are those silvicultural system in which the regeneration is of seedling origin, either natural or artificial.
- So, rotation is generally long.
- These are further classified on the basis of pattern of felling which in turn, affects the concentration or diffusion of regeneration and character of new crop.
- E.g.:
Clear Felling system
- Clear felling is the removal of all trees from an area chosen for harvesting.
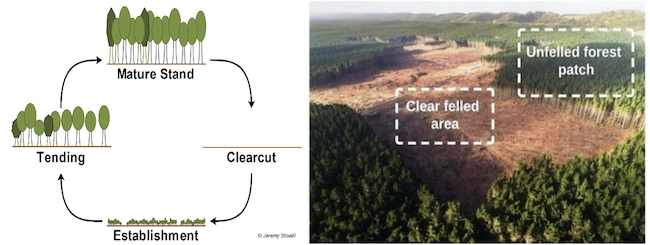
Concept of felling
- Felling comprises of removal of trees either singly or in small groups scattered all over the forest.
- The total area of the forest is ‘A’ and rotation for this forest is ‘r’ years. Then the area to be clear felled for each year is A/r and is usually referred to as the annual coupe.
- Coupe: A felling area, usually one of an annual series unless otherwise stated. Preferable numbered with Roman numbers as, I, II, III etc.
- The term is usually applied to the area where fellings or thinning etc. are carried out and are called ‘felling coupe’ or ‘thinning coupe’.]
- The number of annual coupes (annual felling areas), equal to the number of years in the rotation.
Annual Coupe- Annual Allowable Cut (AAC), it is the volume of timber that may be harvested from a particular area of forest in any one year.- From the industrial forestry perspective, the AAC should be set at a level that provides the maximum harvest volume while ensuring that the prospects for future harvests do not deteriorate.
Coppice forest systems
- Coppice system refers to the silvicultural system in which the new crop originates mainly from
coppiceand where the rotation of crop is shorter. - The different coppice systems are described in detail below:
👉🏻 Types: On the Basis of Pattern of Felling
- The Simple Coppice System
- Coppices of two rotation system
- The Shelterwood Coppice System
- The Coppice Selection System
- The Coppice-with-Standards System***
- The Coppice-with-Reserves System***
- The Pollard System
Simple coppice system

- A silvicultural system based on stool coppice, in which the old crop is clear-felled completely and the new crop grows naturally through stool coppice.
The Pollard System

- Example of Coppice system.
- Pollarding refers to the cutting off of tree stem usually above the browsing height to obtain a flush of shoots.
- Pollard system is applicable for obtaining maximum fodder from the tree.
- Salix is pollarded in Kashmir valley to produce shoots for the cricket bat industry.
Forest Succession
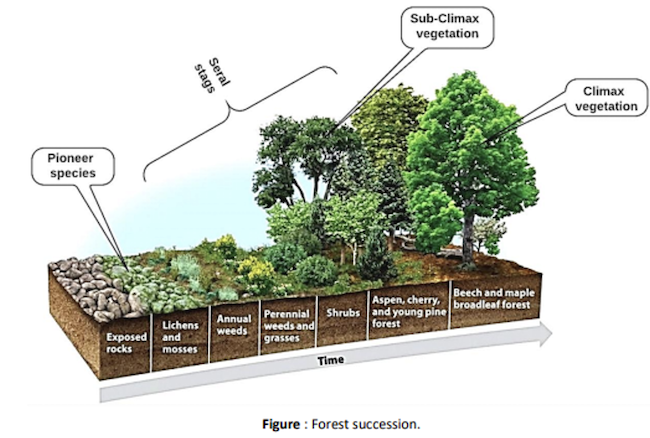
- Succession is the process of replacement of one set of the biotic community by another set of more advance and different nature biotic community.
- The process of development and movement of vegetation from one stage (grassland to tree land) is called succession.

- It is derived from
Latinword, Silva which means Wood Land. - Silviculture is that branch of forestry which deals with establishment, development, care and reproduction of stands of timber.
- Silviculture is the art and science of cultivating forest crops.
- Silviculture is the theory and practices of raising forests crops. (Champion & Seth 1968).
- Just like agronomy in agriculture, in forestry there is silviculture.
- Study of silviculture help us to get:
- Production of more volume & high quality of woods per unit area
- Reducing the rotation period of species (Produce Forest crops in less time)
- Afforestation & Reforestation, Site Protection
- Introduction of exotics i.e. Poplar, Eucalyptus etc.
- Creation of Man-Made forest in place of Natural forest
- Dendrology
- It is the science and …
Become Successful With AgriDots
Learn the essential skills for getting a seat in the Exam with
🦄 You are a pro member!
Only use this page if purchasing a gift or enterprise account
Plan
Rs
- Unlimited access to PRO courses
- Quizzes with hand-picked meme prizes
- Invite to private Discord chat
- Free Sticker emailed
Lifetime
Rs
1,499
once
- All PRO-tier benefits
- Single payment, lifetime access
- 4,200 bonus xp points
- Next Level
T-shirt shipped worldwide

Yo! You just found a 20% discount using 👉 EASTEREGG

High-quality fitted cotton shirt produced by Next Level Apparel