🍲 Chickpea
Important points related to cultivation of Chickpea.
⭐️ World Pulses Day is a designated United Nations global event to recognize the importance of pulses (chickpeas, dry beans, lentils, dry peas and lupins among others) as a global food. It has been proclaimed on February 10 of each year since 2019 by the General Assembly of the United Nations on December 20, 2018.
Chickpea/Gram

- Botanical Name: Cicer spp.
- Cicer aeritinum: Desi/Brown Chickpea/Kala Chana
- Cicer kabulium: Kabuli/White Chickpea

- Family: Papilionaceae (Leguminaceae)
- Chromosome: 2n = 14/16
- Chickpea is also known as Gram or Bengal gram.
- Gram is originated in
South-West Asia(Afghanistan). Indiais the largest producer of Gram in the world sharing 65% area & 70 % of total global production.Chickpeaconsists of more than 1/3 of the area and 40 per cent of the total production of pulses in India. (highest among pulses)- Gram is major pulse crop in India followed by Pigeon pea.
- Chickpea is called as
King of Pulses(Queen -> Pea) and contains 22-23 per cent protein content.

- The sour taste of leaves and pods is due to the presence of Malic Acid
90-96%and Oxalic Acid 4-10%. - Its leaves are recommended for intestine disorder patient, due to presence of Malic and Oxalic acid.
- Gram fruit is known as
Pod. - Germination type:
Hypogeal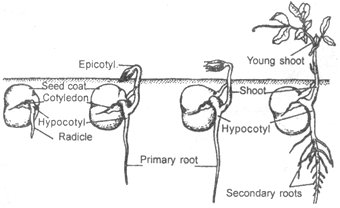
Types of Chickpea
- Desi: It has small, darker seeds and a rough coat, cultivated mostly in the Indian subcontinent, Ethiopia, Mexico, and Iran. The desi type is used to make Chana Dal, which is a split chickpea with the skin removed.
- Kabuli: It has lighter/white coloured, larger seeds and a smoother coat, mainly grown in Southern Europe, Northern Africa, Afghanistan, Pakistan and Chile, also introduced during the 18th century in India.
- Desi chickpeas have markedly higher fiber content than Kabulis and hence a very low glycemic index which may make them suitable for people with blood sugar problems.
Climate
- Gram is a winter season crop.
- Chickpea is a self-pollinated, C3 and
long-dayplant. - Suitable temperature for optimum crop growth is
20-25 °C. - Requirement of water throughout growth period is
350-450 mm. - Severe cold and frost at the time of flowering causes detrimental effect to gram seed development.
- Chickpea is usually considered a Dry-land/Rainfed crop.
- It favours moderate rainfall with mild cold weather.
- Chickpea requires a
looseand wellaeratedroughseedbed. Light alluvialsoil is best for cultivation of gram.- Chickpea may be cultivated as a sole crop, or mixed with barley, lathyrus (grasspea), linseed, mustard, peas, corn, coffee, safflower, potato, sweet potato, sorghum, or wheat.
- In India, chickpea is also grown as a catch crop in sugarcane fields and often as a second crop after rice.
- When chickpea is grown as mixed crop, it checks blight disease.
Seed & Sowing
- Early sown:
75-80 kg/ha - Late sown:
80-100 kg/ha - Late planting of chickpea is done to protect the seedlings
from wilt disease. In such type of delayed planting, seed rate is increased by 25 per cent to obtain a good yield. - Sowing time:
2nd fortnight of October(15th to 20th October) is optimum time. - Spacing: 30 x 10 cm
- Plant population: 3,33,333 plants
- The seed should be placed
8-10 cmdeep because the shallow sown crop is more liable to be damaged by wilt.
Fertilizer
NPK requirement (Kg/ha)
- Normally – 20 : 60 : 30
- Rainfed – 15 : 20 : 15
- Phosphorous should be applied at below or side of the seed to increase the gram yield.
- The critical stages for irrigation:
- Pre-flowering/Late vegetative phase
- Pod development
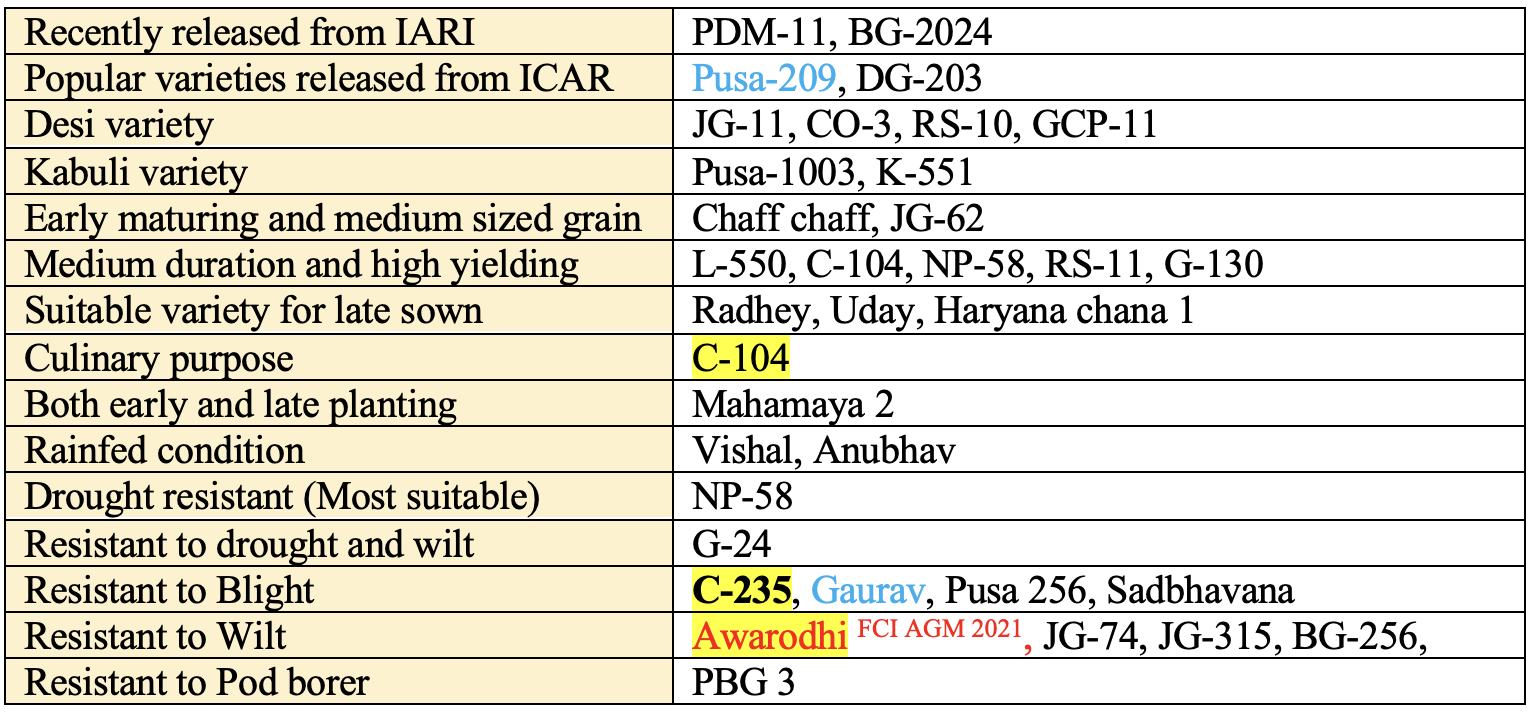
Important Varieties
Root System
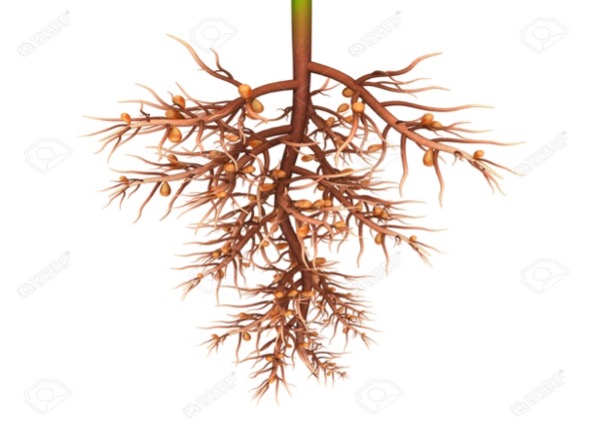
- The roots usually include a central strong tap root, with numerous lateral branches that spread out in all directions in the upper layer of soils.
- There are numerous
noduleson roots. - The
rhizobium bacteriapresent in these nodules fix up atmospheric nitrogen.
Nipping/Topping

- Nipping is the process of plucking the apical buds after
45-60 DAS, in order to stop apical growth and encourage more branching and fruit development. - Nipping terminal bud at 45 and 60 days after sowing significantly reduced the plant height and increased the number of primary and secondary branches and pods per plant.
- It can be done by a flock of sheep.
- Chemical for nipping
TIBA@ 75 PPM (Tri-Iodo-Benzoic Acid).
Disease
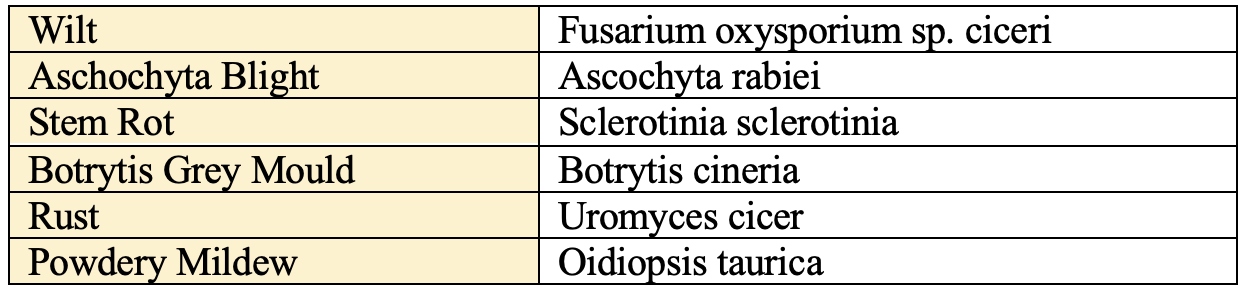
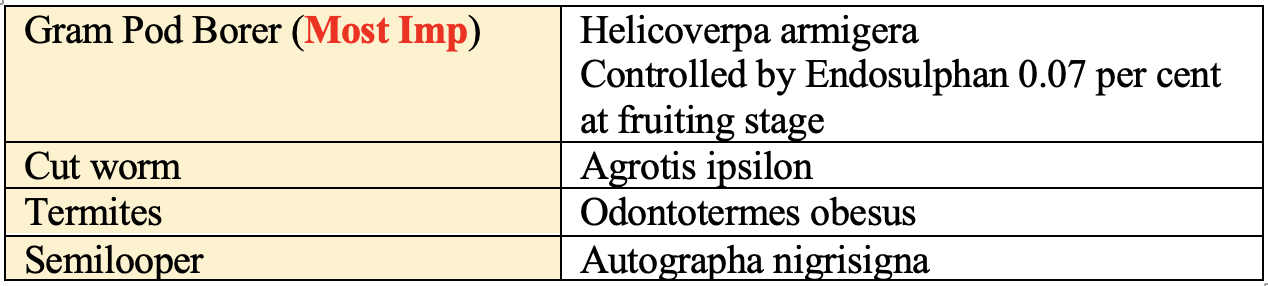
Insect-Pest
Yield
- Rainfed condition – 5 to 6 qt/ha
- Irrigated condition – 12 to 15 qt/ha
- Shelling percentage is
49per cent.
⭐️ World Pulses Day is a designated United Nations global event to recognize the importance of pulses (chickpeas, dry beans, lentils, dry peas and lupins among others) as a global food. It has been proclaimed on February 10 of each year since 2019 by the General Assembly of the United Nations on December 20, 2018.
Chickpea/Gram

- Botanical Name: Cicer spp.
- Cicer aeritinum: Desi/Brown Chickpea/Kala Chana
- Cicer kabulium: Kabuli/White Chickpea

- Family: Papilionaceae (Leguminaceae)
- Chromosome: 2n = 14/16
- Chickpea is also known as Gram or Bengal gram.
- Gram is originated in
South-West Asia(Afghanistan). Indiais the largest producer of Gram in the world sharing 65% area & 70 % of total global production.Chickpeaconsists of more than 1/3 of the area and 40 per cent of the total …
Become Successful With AgriDots
Learn the essential skills for getting a seat in the Exam with
🦄 You are a pro member!
Only use this page if purchasing a gift or enterprise account
Plan
- Unlimited access to PRO courses
- Quizzes with hand-picked meme prizes
- Invite to private Discord chat
- Free Sticker emailed
Lifetime
- All PRO-tier benefits
- Single payment, lifetime access
- 4,200 bonus xp points
- Next Level
T-shirt shipped worldwide

Yo! You just found a 20% discount using 👉 EASTEREGG

High-quality fitted cotton shirt produced by Next Level Apparel