👕 Cotton
Important points related to Cotton.
Cotton

- Cotton is also known as
White gold of America/King of Appraisal fiber. - It is back bone of textile industry with 45% of world’s fibre need is met form cotton.

- Botanical Name: Gossipium spp.
- Family: Malvaceae
- Origin:
India🇮🇳 - World (Production):
India🇮🇳 > China 🇨🇳> USA 🇺🇸 - India (Production):
Gujarat> MH > Telengana - World Cotton Day is celebrated on 7th October.
Species of Cotton
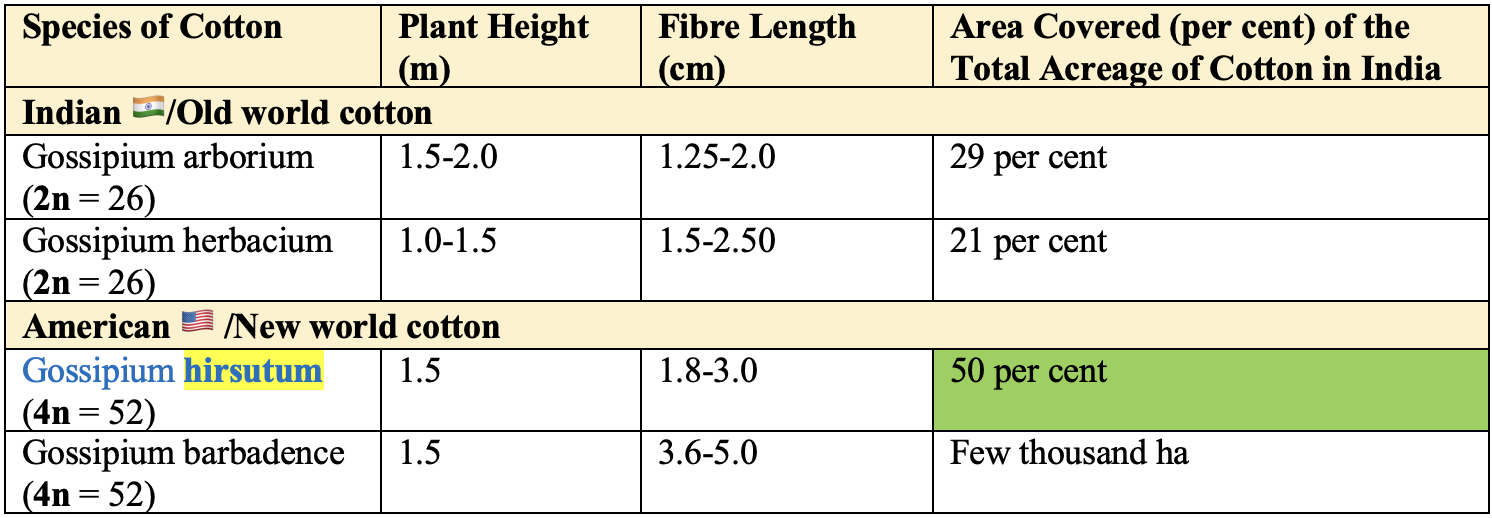
- G. barbadence is also known as
Sea Island Cotton.
Comparative Study of Indian and American Cotton

Varieties of Cotton
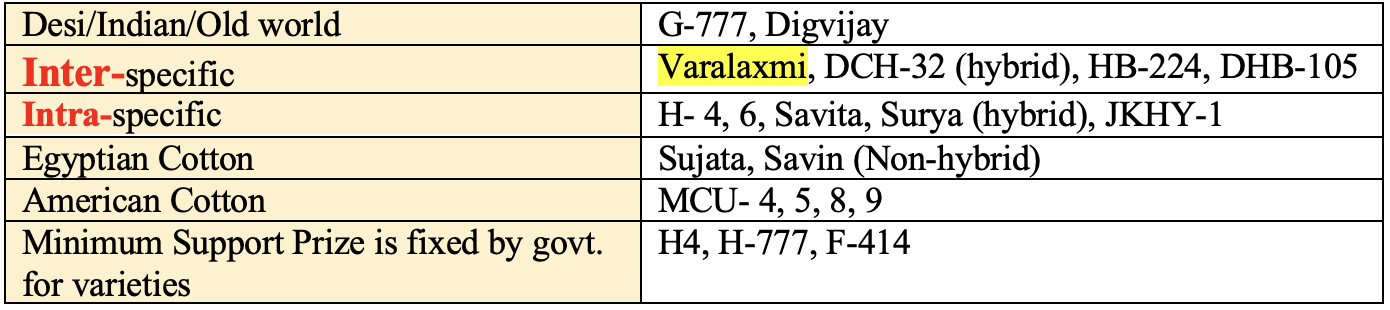
👉🏻 Two yearsafter the release of H4 the world’s first interspecific hybrid between G. hirsutum and
G. barbadense was released from the cotton Research Station, Bangalore under the name
Varalaxmi.
Interspecific: G. hirsutum X G. barbadense
Varalakshmi: Laxmi X SB-289E
👉🏻 Initially, Varalaxmi was released for cultivation in Karnataka state, but later on spread to other states such as TN, AP and Maharashtra under irrigated areas.
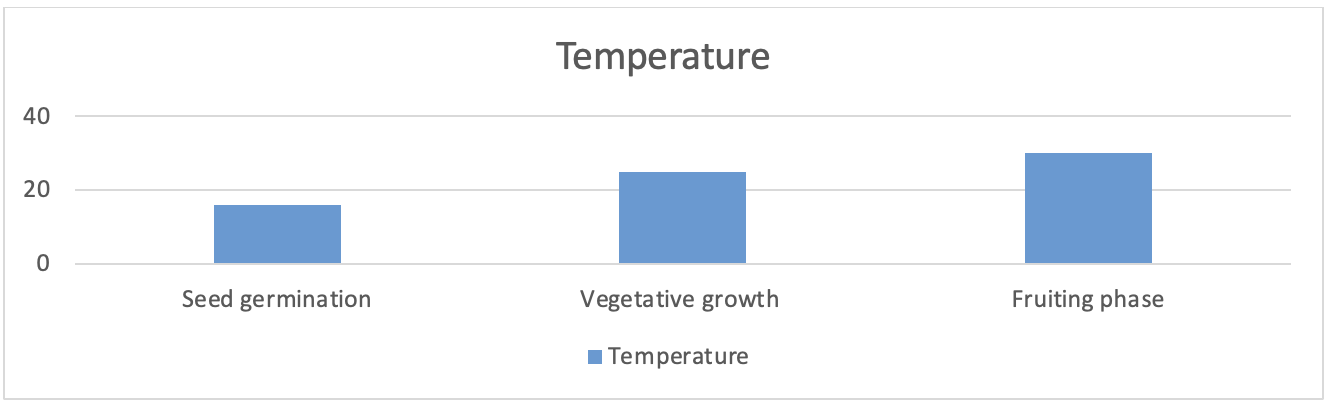
Climate
- Cotton is a warm season crop.
- It requires an average annual temperature and rainfall of over 18°C and
500-700 mm, respectively. - A daily mean temperature of
16 °Cfor seed germination,21-27 °Cfor proper vegetative growth and27-32 °Cfor fruiting phase.
- Critical stage of Irrigation: Flowering, Boll formation.
- Abundant sunshine during boll maturation and harvesting is essential to obtain a good quality crop produce.
- Heavy showers of rain or heavy irrigation during fruiting period causes shedding of flowers and young bolls.
Day Neutral plant.
Soil
Black cotton soilis best for cotton cultivation.
- Cotton can be successfully grown on all soil except sandy, saline, and waterlogged soil.
- Cotton needs a fertile soil with good moisture holding capacity.
- Tap root system (depth > 1.6 m)
- Branches:
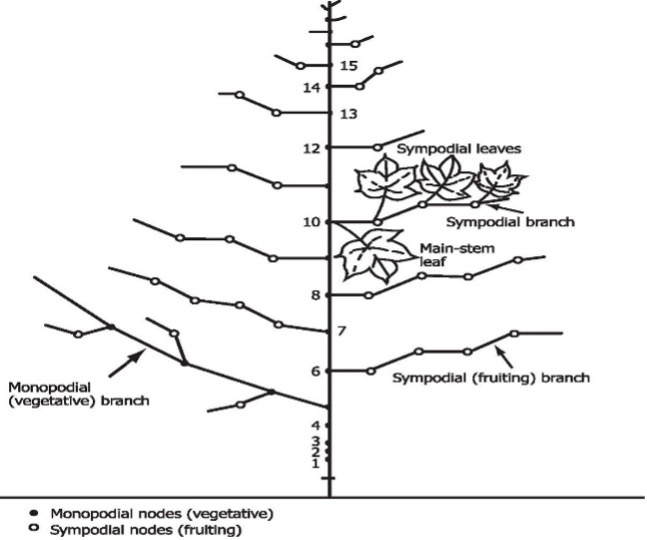
- Sympodial: Reproductive branches
- Monopodial: Vegetative branches
- Normally squaring occurs 35-70 DAS. Peak flowering – 70 – 100 DAS.
Seed Rate
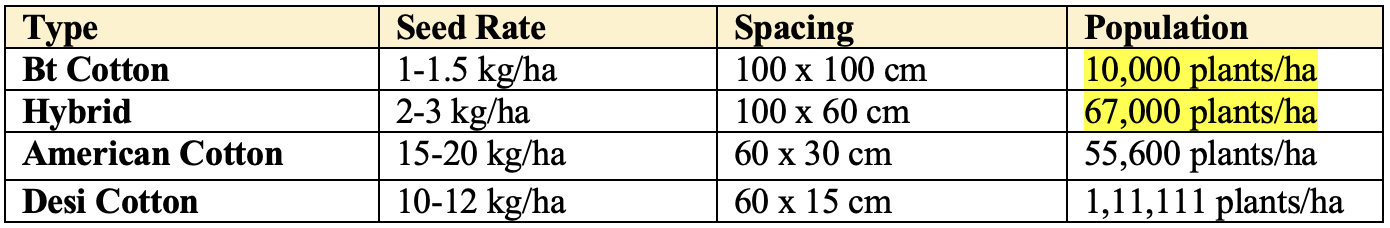
- Spacing for
Ultra Narrow Row(developed byUSA):19 x 19 cm(2,77,000 plants/ha).

- Germination:
Epigeal - Seed depth: 3 cm (Dibbling)
Choulfi methodis used for square planting of cotton in Maharashtra and in Malva area of Madhya Pradesh.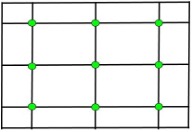
Sowing Time
- North India: 1st fortnight of May
- Central India: Last week of June to 1st week of July
- In Tamil-Nadu: Sept - Oct.
Manure & Fertilizer

- Topping: Removal of terminal growing point once from each plant at a height of 1.2 m (80-90 DAS) to protect further terminal growth and to encourage sympodial branching and boll development by diverting the energy flow.
- Cotton fibers develop from the outermost cells of the seed-coat.
- Cotton seed: Only Seeds
- Seed Cotton: Seeds with lint

- Ginning: Separation of fiber from the seed cotton is known as Ginning.
- Ginning percentage = (Wt. of lint)/(Wt. of Seed Cotton ) x 100
- For G. hirsutum: 28-32 per cent (American cotton)
- For G. arborium and G. herbacium: 36-42 per cent
- Lint Index = (Weight of 100 cotton seed)/100 X Ginning %
- H2SO4 is used for delinting of cotton seed.

Arealometeris used to measurelength of Cotton fiberand tojudge maturity.- The oil content in desi cotton is 14.6-25.6 per cent, while American cotton has 14-18 per cent.
170 kg cotton=1 bale.
- The oil content in the cotton seed ranges from 15-25 % depending on the varieties.
- Cotton seed cake is a good organic manure and contains about 6.5% N, 3% P2O5, 2% K2O.
Bt-Cotton
- GM cotton is only crop permitted by
Genetic Engineering Appraisal Committee (GEAC)under Ministry of Environment and Forestry first permitted in March2002. Bt-cotton (Bacillus thuringensis)is resistant against the pestHelicoverpa (Spotted bollworm), developed by U.S. based seed companyMonsantoand registered under the nameBollgaurd.

- Of the total cotton area at
12.44 million hectaresfor 2017-18, the acreage under Bt was reportedly 11.07 million hectares, which works out to90 per cent.
Major Disease
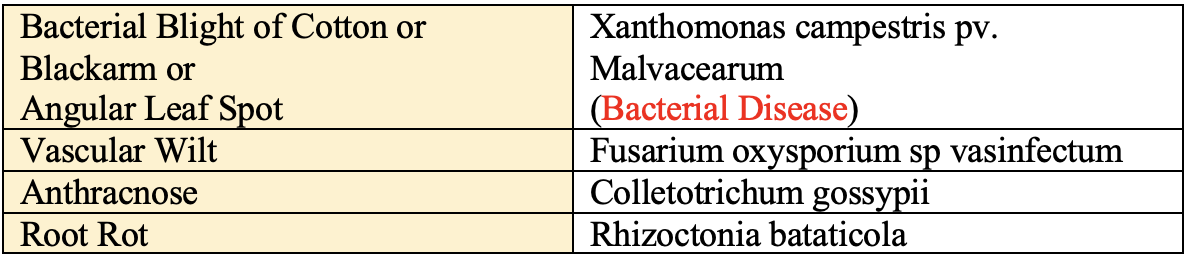
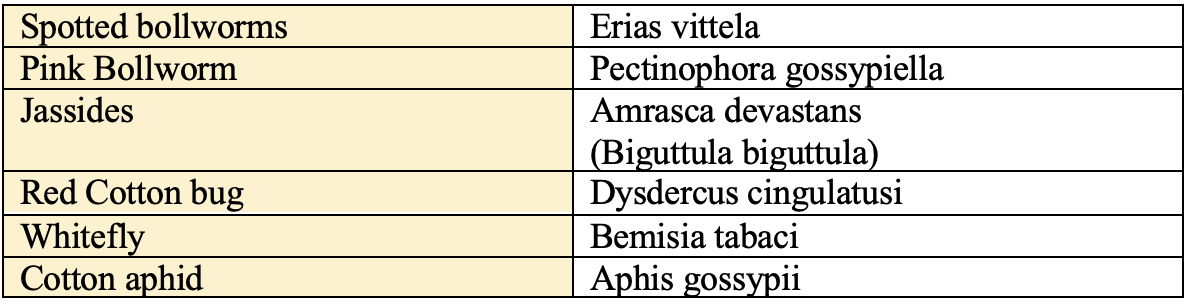
Insect Pest
Yield
- Common: 15-20 q/ha.
- Hybrid: 25-30 q/ha.
Explore More 🔭
🟢 https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=tKLJ6KQAcjI https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=QHgNoSYlhYs
Cotton

- Cotton is also known as
White gold of America/King of Appraisal fiber. - It is back bone of textile industry with 45% of world’s fibre need is met form cotton.

- Botanical Name: Gossipium spp.
- Family: Malvaceae
- Origin:
India🇮🇳 - World (Production):
India🇮🇳 > China 🇨🇳> USA 🇺🇸 - India (Production):
Gujarat> MH > Telengana - World Cotton Day is celebrated on 7th October.
Species of Cotton

- G. barbadence is also known as
Sea Island Cotton.
Comparative Study of Indian and American Cotton

Varieties of Cotton

👉🏻 Two yearsafter the release of H4 the world’s first interspecific hybrid between G. hirsutum and
G. barbadense was released from the cotton Research Station, Bangalore under the name
Varalaxmi.
Interspecific: G. hirsutum X G. barbadense …
Become Successful With AgriDots
Learn the essential skills for getting a seat in the Exam with
🦄 You are a pro member!
Only use this page if purchasing a gift or enterprise account
Plan
- Unlimited access to PRO courses
- Quizzes with hand-picked meme prizes
- Invite to private Discord chat
- Free Sticker emailed
Lifetime
- All PRO-tier benefits
- Single payment, lifetime access
- 4,200 bonus xp points
- Next Level
T-shirt shipped worldwide

Yo! You just found a 20% discount using 👉 EASTEREGG

High-quality fitted cotton shirt produced by Next Level Apparel