🥜 Groundnut
Important points related to Groundnut.
Oil Percentage of Oilseed Crops
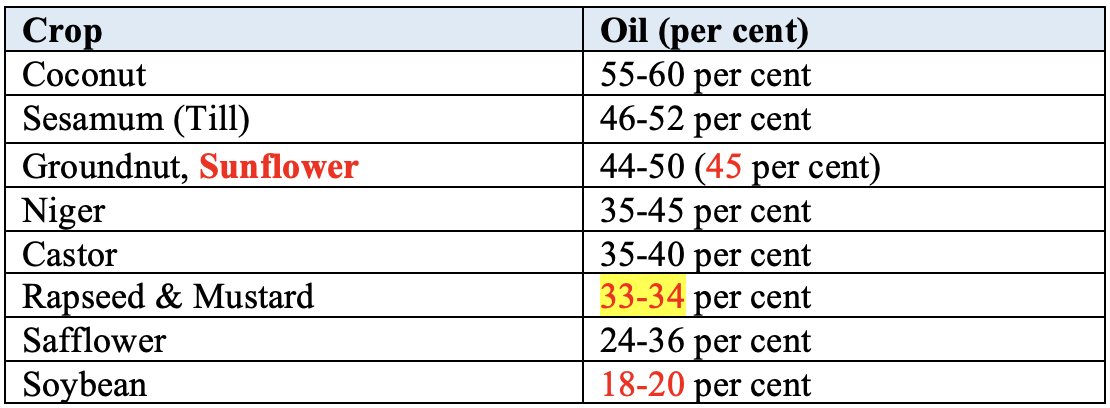
- World (Production):
Soybean> Cotton Seed Oil > Rapeseed Oil > Groundnut > Sunflower - India (Production):
Soybean> Groundnut > Rape Seed and Mustard - Generally,
SulphurandPhosphorusare required in higher amount in Oilseed crops than other crops. IBPS 2018
Groundnut

- Botanical name:
Arachis hypogea - Arachis hypogea
fastigate(Bunch/Erect /Spanish type) - Arachis hypogea
procumbens(Spreading/Verginia runner type) - Family: Papilionaceae
- Origin: Brazil
- Area: India > China > Nigeria
- Production: China (36%) >
India (17%)> Nigeria - Productivity: USA
- Groundnut is also called as Peanut, Monkeynut, Earthnut and Mungfalli. Poor Man’s Almonds.
- Chromosome No: 2n = 40
King of Oilseed(Queen -> Sesame)- Arachis hypogea word is derived from two Greek words:
- Arachis means Legume
- Hypogea means Below the ground or soil
Climate
- Groundnut is wide spectrum adoptable crop which grown in all 3 seasons.
- It requires
tropicalclimate. - It requires an average annual rainfall of
500-1000 mm. - Best suited temperature for crop growth is between
25-35 °C. - Flowering and seed setting affected by cloudy weather.
- It resists drought and tolerate flooding for one week once it establishes.
- Groundnut is a
self-pollinated,C3andshort-dayplant.
Soil
- Groundnut thrives best in well-drained sandy and sandy loam soils, as light soil help in easy penetration. (Black Soil)
- Clay soil is strictly avoided to grow groundnut because of presence of high moisture.
- Soil with pH between
6.0-6.5.
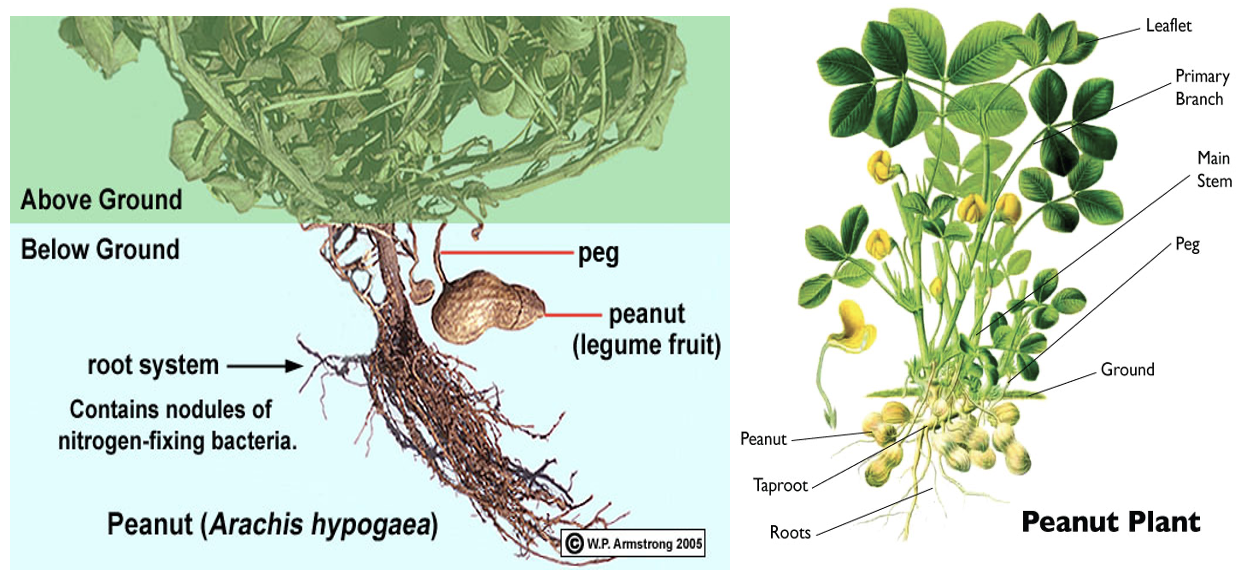
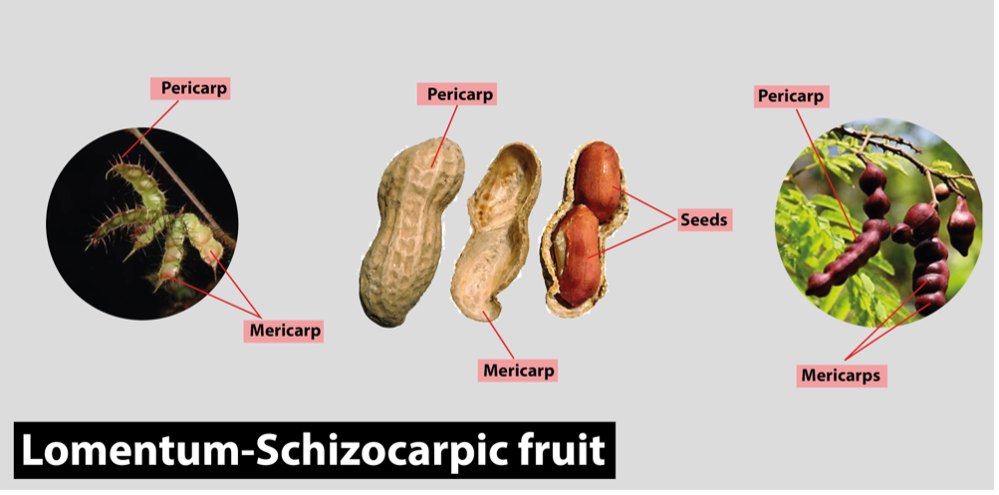
- Groundnut is a
modified fruit. - Fruit of groundnut is
Nutand fruit type isLomentum.
Gynophoreof groundnut is known asPeg(intercalary meristem from fertilized flower). Peg formed from fruits.- Geotropism: At the base of ovary, a meristematic region grows and becomes a stalk like structure (gynophore) that bends downwards and forces the ovary into the soil. The peg (gynophore) carrying the ovary pushes itself into the soil. After entering the soil, ovary begins to develop and takes up to horizontal position and pods begins to enlarge.
- Flowering starts
24 to 40 daysafter sowing. - Pegs become viable in 5-7 days after flowering and takes 2-10 days to insert into the soil.
Testais a thin skin that covers the seed or nut.- Inflorescence:
Raceme
- Ratio of:
Flower : Pegs : Podsis7 : 4 : 1. - Groundnuts contain
45 % oilin kernel and26 % proteinin kernel. - Groundnut cake contains
7-8 per cent nitrogen. - Shelling percentage of groundnut is
70 per cent. - Groundnut accounts more than 30 per cent acreage and 40 per cent of total oilseed production of India.
- Leading groundnut producing states are
Gujarat> Tamil Nadu > Andhra Pradesh. - The effects are:
- Gynophores are swelled & shrinkage and quality affected.
- Pod growth is affected due to soil compaction.
- At the time of sowing, 0.1 per cent Ethrel + 3 gm Thirum is used for seed treatment and to break seed dormancy.
- Generally, Groundnut grown during Rabi season gives higher yield as compared to Kharif season crops due to fewer incidences of insect and pests and diseases.
Sowing Time
- Kharif: 3rd week of June to 1st week of July
- Rabi: November
- Summer: Last week of Dec to end of January
Seed Rate
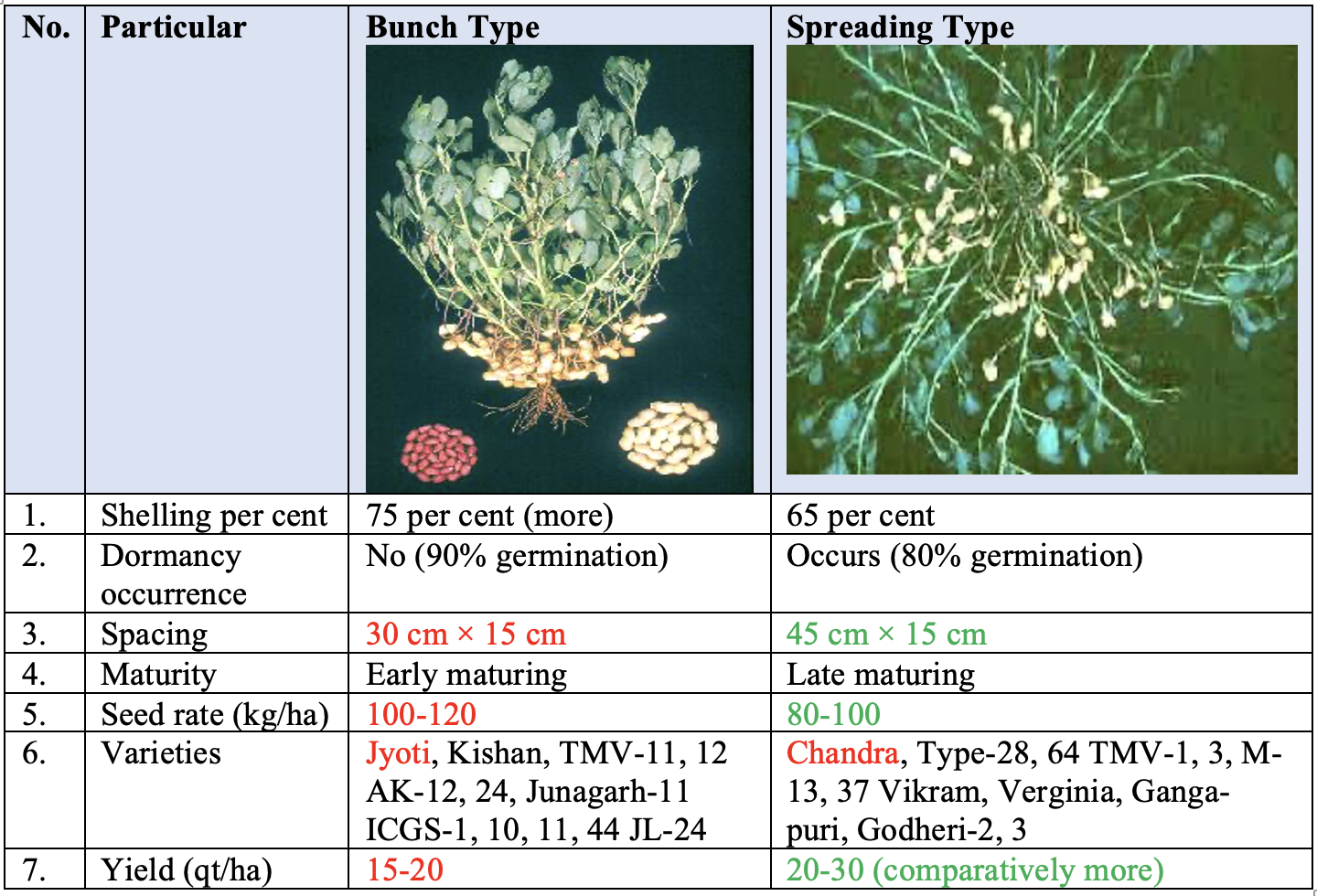
- Bunch type varieties:
100-120 kg/ha - Spreading type varieties: 80-100 kg/ha
- Germination type:
Hypogeal
Irrigation
- Kharif: no need
- Rabi: 5-6 irrigation
- Summer: 10-12 irrigation
Critical stages of crop growth:
- Establishment (10-20 DAS)
- Vegetative phase (25-35 DAS)
- Flowering and peg initiation stage (35-50 DAS)
- Pod formation stage (50-75 DAS)
- Pod/Seed development stage (75-90 DAS)
Critical stages for irrigation:
- Flowering stage
- Pegging stage
- Pod formation stage
- Check basin irrigation is most suitable irrigation method for groundnut.
- IW/CPE ratio of groundnut is
0.6. - During pod development stage, field should be well drained, otherwise due to the poor aeration, the formation of toxin (
Aflatoxin) takes place. - Application of 25 : 60 : 60 kg NPK/ha with 25 to 50 kg ZnSO4 and FeSO4 both give higher yield of groundnut.
- Intercultural operations should be avoided during pegging stage.

Star weederis used to control weeds in groundnut fields.NAA @ 40 ppmis used to enhance floral initiation and pod formation.Calcium (Ca)is essential for pod development.
Bunch type and Spreading type
- Earthing-up is done in groundnut crop at
35 to 45 daysafter sowing to facilitate proper development of pegs beneath soil and increases number of seeds per pod. - The most common groundnut based cropping systems are:
- Groundnut + Pigeonpea (4:1)
- Groundnut + Castor
- Groundnut + Sunflower
- Groundnut + Urdbean (4:1)
- Groundnut + Til (3:1)
Yield
- Bunch Type: 15-20 q/ha
- Spreading Type: 20-30q/ha
- Strain used for biological N2 fixation in groundnut is
Rhizobium japonicum. - Groundnut should be stored at
5 per centmoisture content. - Bitterness of kernel is due to
Aflatoxin(toxic substance) developed by two reasons:- When pod moisture content is > 8 per cent
- Fungus namely
Aspergillus nigerandAspergillus flavus. FCI AGM 2021
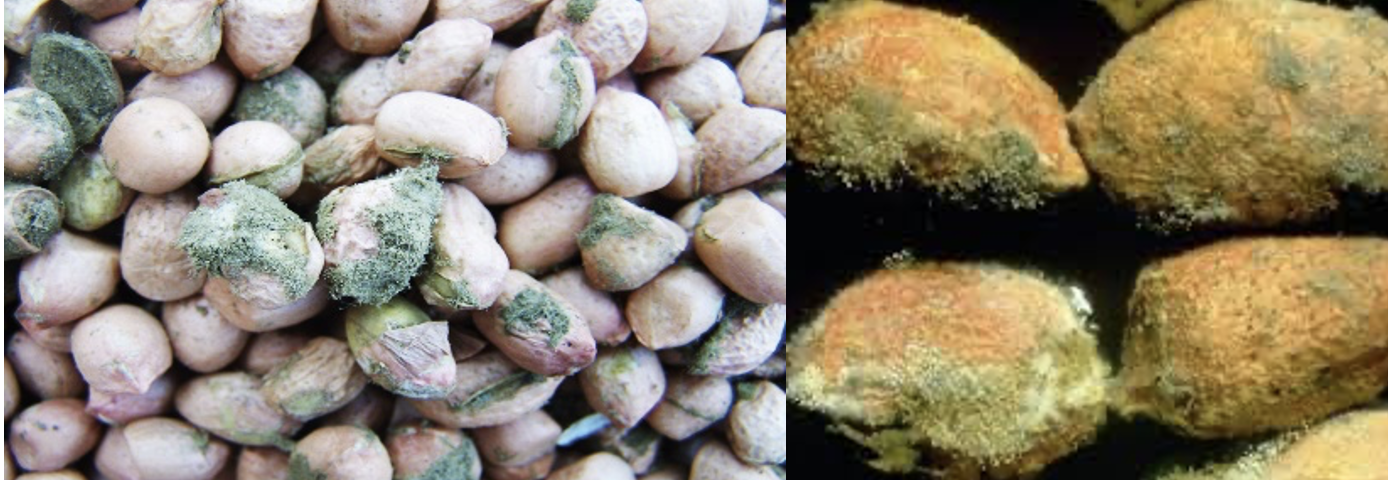

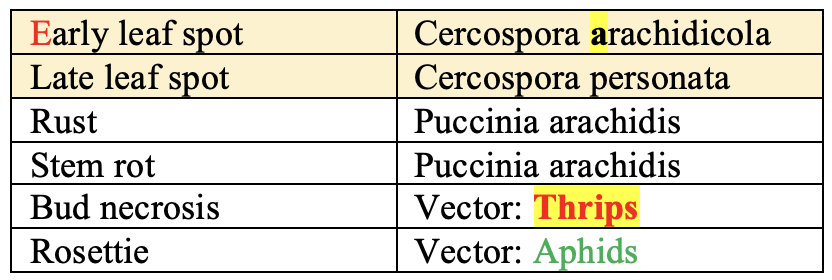
Disease
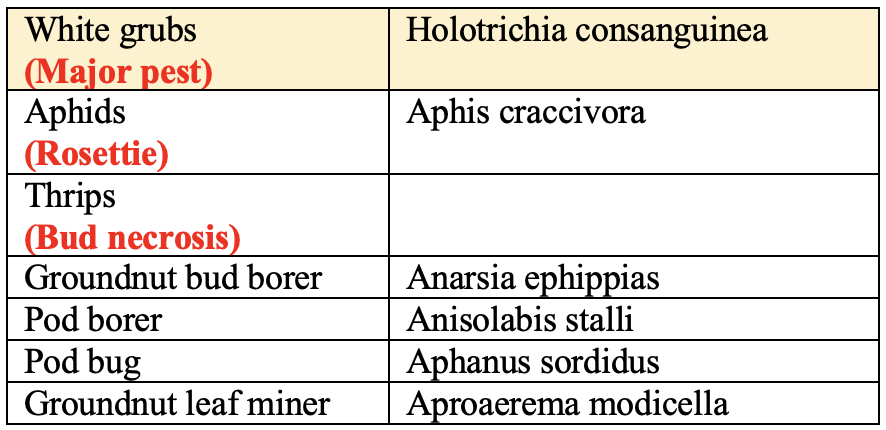
Insect-Pest
Oil Percentage of Oilseed Crops

- World (Production):
Soybean> Cotton Seed Oil > Rapeseed Oil > Groundnut > Sunflower - India (Production):
Soybean> Groundnut > Rape Seed and Mustard - Generally,
SulphurandPhosphorusare required in higher amount in Oilseed crops than other crops. IBPS 2018
Groundnut

- Botanical name:
Arachis hypogea - Arachis hypogea
fastigate(Bunch/Erect /Spanish type) - Arachis hypogea
procumbens(Spreading/Verginia runner type) - Family: Papilionaceae
- Origin: Brazil
- Area: India > China > Nigeria
- Production: China (36%) >
India (17%)> Nigeria - Productivity: USA
- Groundnut is also called as Peanut, Monkeynut, Earthnut and Mungfalli. Poor Man’s Almonds.
- Chromosome No: 2n = 40
King of Oilseed(Queen -> Sesame)- Arachis hypogea word is …
Become Successful With AgriDots
Learn the essential skills for getting a seat in the Exam with
🦄 You are a pro member!
Only use this page if purchasing a gift or enterprise account
Plan
Rs
- Unlimited access to PRO courses
- Quizzes with hand-picked meme prizes
- Invite to private Discord chat
- Free Sticker emailed
Lifetime
Rs
1,499
once
- All PRO-tier benefits
- Single payment, lifetime access
- 4,200 bonus xp points
- Next Level
T-shirt shipped worldwide

Yo! You just found a 20% discount using 👉 EASTEREGG

High-quality fitted cotton shirt produced by Next Level Apparel