👜 Jute
Important points related to Jute.
Jute
- B.N: Corchorus spp.
- Family:
Tiliaceae - Origin: India
- Chromosome No.: 2n = 14
- Jute is a
parenchymatus fibre. - Jute crop
does not have hybrid seeds. - Less no. of knots in k/w superior quality.
Climate
- Jute thrives best under a warm and humid climate with temperature range from 24 to 37 °C.
- Optimum temperature being around
34 °C.
Soil
- Jute can be grown on all kinds of soils from clay to sandy loam but loamy alluvial soil suits ii most suitable.
- Laterite and gravely soils are not suitable for Jute crop.
- Normal soil pH 6-7.5.
Sowing time
- Capsularis: March-April
- Olitorious: April –May
- Generally, April sowing gives the best results in both types of Jute.
Seed rate
- Capsularis/White Jute:
6-8 kg/ha. - Olitorious/Tossa:
4-5 kg/ha. - Production: Green plant weight yield is 45 to 50 tonnes per hectare
- Fibre yield is 2.0 to 2.5 tonnes (20-25 q) per hectare.
Jute Species
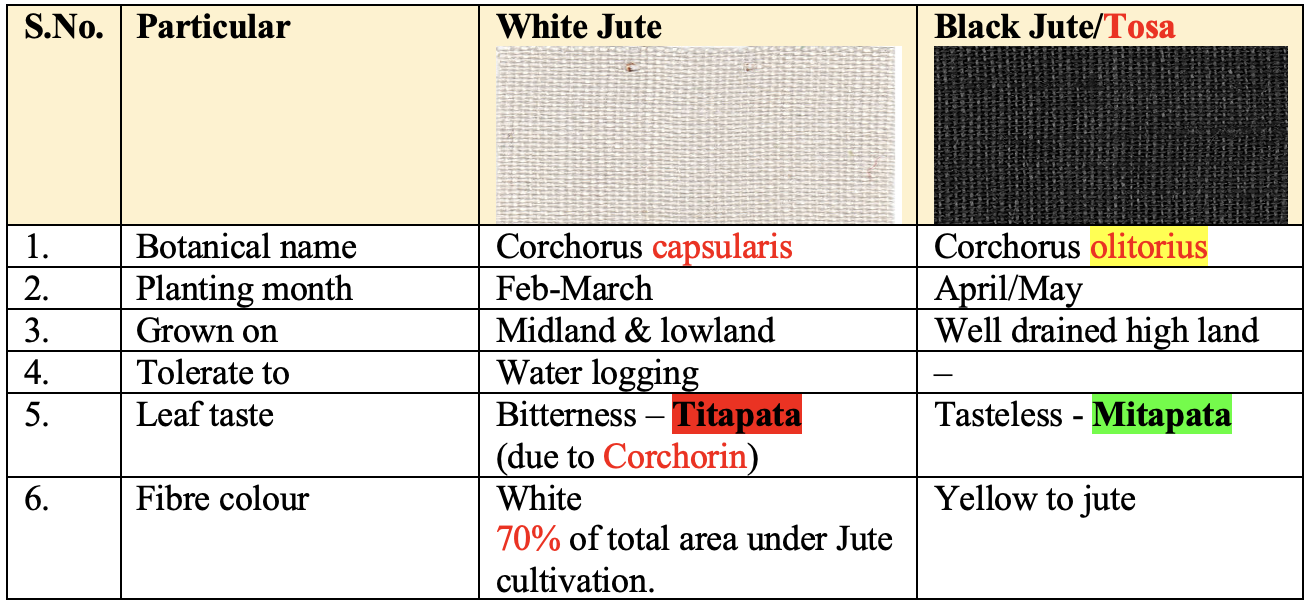
Varieties
- JRC-321 (Sonali), JRC-212 (Sabuj sona), JRC 7447 (Shyamli), D154, Hybrid C (Padma), KC1 (Joydev) etc
Harvesting
- Ideal stage for harvesting - Small pod stage/initiation of pod formation (135-140 DAS).
- Jute is harvested any time between 120 days to 150 days when the flowers have been shed, early harvesting gives good healthy fibers.
- The plant at 8 to 12 feet high, are cut with stickles at or close the ground level.
- The harvested plants are left in field for 3 days for the leaves to shed.
180 kgjute fiber is called 1 bale.
- Steeping/Soaking: After 2-4 days of harvesting the plants are shaken for complete leaf shedding and they are tied in bundles of about 20-22 cm in diameter.
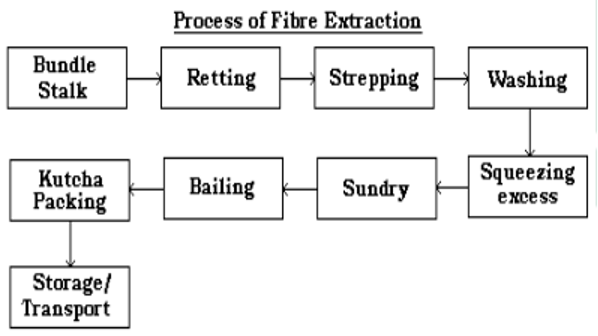
Retting

- Retting is a process in which the tied bundles of jute stalks are taken to the tank by which fibres get loosened and separated from the woody stalk.
- The bundles are steeped in water at least 60 cm to 100 cm depth.
- The retting process is completed in 8 to 30 days, when the barks separate out easily from the stick or wood and the fibers are ready for extraction.
- Optimum temperature for retting is about
34 °C.
Stripping (Fibre Extraction)
- Stripping is the process of removing the fibers from the stalk after the completion of retting.

Ribboning
- This practice is very common in China and Taiwan, but not popular in India.
- It consists of peeled out of
raw barkfrom the green plant, immediately after harvest and bundles of- the ribbons thus obtained are retted.
Sunhemp
- Botanical Name:
Crotolaria juncia - Best and most widely used
green manure crop. - Seed rate: 15-20 kg/ha.
- It is most suitable for alkaline and water logged soil.
Linseed (Flax) – Reflax
🏃🏻 Already covered under oil-seeds section.
Jute
- B.N: Corchorus spp.
- Family:
Tiliaceae - Origin: India
- Chromosome No.: 2n = 14
- Jute is a
parenchymatus fibre. - Jute crop
does not have hybrid seeds. - Less no. of knots in k/w superior quality.

Climate
- Jute thrives best under a warm and humid climate with temperature range from 24 to 37 °C.
- Optimum temperature being around
34 °C.
Soil
- Jute can be grown on all kinds of soils from clay to sandy loam but loamy alluvial soil suits ii most suitable.
- Laterite and gravely soils are not suitable for Jute crop.
- Normal soil pH 6-7.5.
Sowing time
- Capsularis: March-April
- Olitorious: April –May
- Generally, April sowing gives the best results in both types of Jute.
Seed rate
- Capsularis/White Jute:
6-8 kg/ha. - Olitorious/Tossa:
4-5 kg/ha. - Production: Green plant weight yield is 45 to 50 tonnes …
Become Successful With AgriDots
Learn the essential skills for getting a seat in the Exam with
🦄 You are a pro member!
Only use this page if purchasing a gift or enterprise account
Plan
Rs
- Unlimited access to PRO courses
- Quizzes with hand-picked meme prizes
- Invite to private Discord chat
- Free Sticker emailed
Lifetime
Rs
1,499
once
- All PRO-tier benefits
- Single payment, lifetime access
- 4,200 bonus xp points
- Next Level
T-shirt shipped worldwide

Yo! You just found a 20% discount using 👉 EASTEREGG

High-quality fitted cotton shirt produced by Next Level Apparel