🍲 Lentil
Important points related to cultivation of Lentil.
Lentil

- Botanical Name:
Lens esculentumLens culnaris
- Family: Papilionaceae (Leguminoceae)
- Lentil crop is also known as Cover crop and Dryland crop.
- Origin: Egypt, Asia minor
- Classification:
- Bold seeded – Masur,
Macrosperma - Small seeded – Masuri,
Microsperma
- Bold seeded – Masur,
- Lentil crop is well cultivated in light loam and alluvial soil.
- Sowing time: Oct last week to November 2nd week (
Rabi) - Seed Rate:
30-40 kg/ha(in Late condition - 50-60 kg/ha) - Spacing: 30 x 5 cm and sowing depth is 3-5 cm.
- Irrigation: 1-3 irrigations
- Critical stages:
- Flower Initiation stage (40-45 DAS)
- Pod formation stage
- Varieties: JL-3, Pant L-639, 209, 406, IPL-81, DL-62, Lens 4076.
- Nutrient management: 20 : 50 : 20 kg NPK/ha at sowing time in furrow and spraying of ZnSO4 0.5 per cent + Lime 0.25 per cent in standing crop.
- Lentil is intercropped with wheat, barley, linseed, safflower etc.
- Weed management: Fluchloralin @ 1.0 kg ai/ha followed by one hand weeding at 30 DAS.
- Lentil is harvested after 100-120 days after sowing
- Yield: 15-20 qt/ha
Field pea

- Botanical name: Pisum sativum var. arvense
- Family: Papilionaceae (Leguminoceae)
- Chromosome No:
2n = 14 - Origin: Mediterranean region of Southern Europe and to Western Asia.
- Pea crop contains
22 per cent protein, 60 per cent carbohydrate and 1.8 per cent fat.
Classification
- Pisum sativum var.
arvenseField pea/Grain pea – used for dal/pulse purpose - Pisum sativum var.
hortenseGarden pea/Table pea – green pods used as vegetable and canning purpose.
Climate
- Field pea requires a cool growing season, moderate temperatures are essential throughout the growing season.
- For germination about 22 °C temperature is considered favorable.
- The optimum monthly temperature suitable for its growth is 13-18 °C.
- Water requirement for proper growth is
400-600 mm. - Heavy rains during flowering stage are harmful to yield of pea crop.
- Field pea is a
short-day plant.⭐️ - Frost can damage the plant during flowering period.
- High humidity is harmful to pea crop due to incidence of disease.
Soil
- A well-drained soil is essential for successful production of field pea.
- Field pea is highly sensitive to water logging, hence a well-drained loam soil is considered best for pea cultivation.
- They tolerate a moderate soil pH range (6.5-7.5). The optimum pH is 6.5.
Sowing time
Second fortnight of Octoberis the optimum time for sowing of field peas in north Indian states. (Rabi)- Sowing after October results in drastic yield reduction.
Seed rate
- Field pea:
75-80 kg/ha. - Garden pea: 100-120 kg/ha.
- Spacing: 30 x 10 cm
- Seed treatment: Captan/Thirum @2.5gm + Rhizobium leguminosarum 10 gm per kg seed.
- Irrigation: 1-2 irrigations
- Germination type:
Hypogeal - Maturity of pea is measured by
Tendrometer.
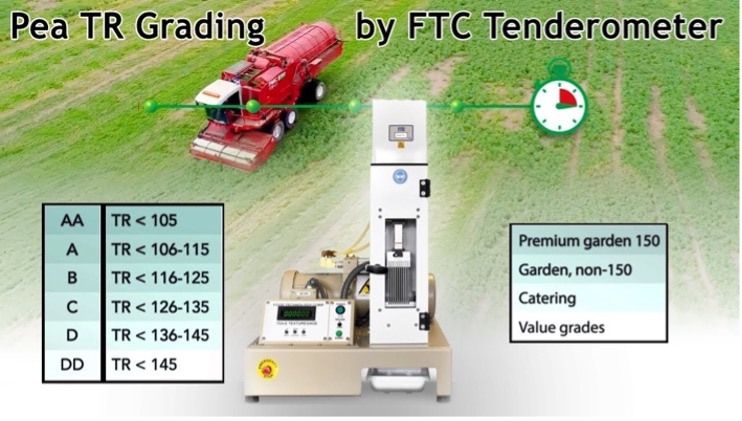
- Critical stages:
- Flower Initiation stage (40-45 DAS)
- Pod filling stage (70-80 DAS)
- Nutrient management: 20 : 50 : 30 : 40 kg NPKS/ha at sowing time.
- Weed management: Two hand weeding at 30 and 45 days after sowing.
Varieties
- Field pea –
Aparna(first dwarf variety), Ambika,Rachana, T-65, 163, Hans, KP-885, Pant C5 - Garden pea –
Arkel(sickle shaped pods),Bonvilley, Sylvia (Whole Pod is edible), Early bajer, Early December, T-19, 59, Pant mater-1, 5, 6, 8 Aajad mater-1, Pant Uphar.
Disease

Yield:
- Field pea/Grain pea: 20-25 qt/ha
- Garden pea/Table pea: 80-100 qt/ha
- Pea is harvested when stems and pods turn straw colour or light brown and seeds are hard and rattle within pod.
- Shelling percentage in pea is
49%.
Lentil

- Botanical Name:
Lens esculentumLens culnaris
- Family: Papilionaceae (Leguminoceae)
- Lentil crop is also known as Cover crop and Dryland crop.
- Origin: Egypt, Asia minor
- Classification:
- Bold seeded – Masur,
Macrosperma - Small seeded – Masuri,
Microsperma
- Bold seeded – Masur,
- Lentil crop is well cultivated in light loam and alluvial soil.
- Sowing time: Oct last week to November 2nd week (
Rabi) - Seed Rate:
30-40 kg/ha(in Late condition - 50-60 kg/ha) - Spacing: 30 x 5 cm and sowing depth is 3-5 cm.
- Irrigation: 1-3 irrigations
- Critical stages:
- Flower Initiation stage (40-45 DAS)
- Pod formation stage
- Varieties: JL-3, Pant L-639, 209, 406, IPL-81, DL-62, Lens 4076.
- Nutrient management: 20 : 50 : 20 kg NPK/ha at sowing time in furrow and spraying of ZnSO4 0.5 per cent + Lime 0.25 per cent in standing …
Become Successful With AgriDots
Learn the essential skills for getting a seat in the Exam with
🦄 You are a pro member!
Only use this page if purchasing a gift or enterprise account
Plan
Rs
- Unlimited access to PRO courses
- Quizzes with hand-picked meme prizes
- Invite to private Discord chat
- Free Sticker emailed
Lifetime
Rs
1,499
once
- All PRO-tier benefits
- Single payment, lifetime access
- 4,200 bonus xp points
- Next Level
T-shirt shipped worldwide

Yo! You just found a 20% discount using 👉 EASTEREGG

High-quality fitted cotton shirt produced by Next Level Apparel