🌽 Maize
Package of practices for cultivation of Maize and other important concepts and facts.

Basics
- Botanical name:
Zea mays - Family: Poaceae
- Origin: Central America & Mexico
- Chromosomes: 2n = 20
- Area: China
- Production:
USA> China - Productivity: USA
- In India, maize is the
thirdmost important food crop after rice and wheat. - Highest production is in
Karnataka(2018-19) - Maize is known as the
Queen of Cereals/Backbone of America, because has the highest genetic yield potential. - Maize Productivity in India is 26 q/ha as against 120 q/ha in USA and 55 q/ha in China.
QPM is an improved variety of maize which contains higher amount of “tryptophan” and “lysine” with lower amount of leucine and isoleucine in the endosperm than those contained in normal maize.
- Maize is a
cross pollinatedcrop. - Maize contains 65 to 70 % starch,
8-10% protein (Zein)and 4-5% oil.
Climate
- Maize is warm weather crop, grow form sea level to 3000 meter altitude.
Kharifseason is the main growing season inNorth India.RabiMaize is extensively grown inBihar.- Most suitable temperature for germination and growth is 21-23ºC and 30-35ºC, respectively.
- Maize crop requires 600-800 mm rainfall for proper growth.
- Maize is a
Day Neutralplant.
Soil
- Maize is best adapted to well drained sandy loam to silty loam soil.
- Very sensitive to water logging (does not float of water more than 4-5 hours).
- It can be grown successfully in soils whose pH ranges from 5.5 to 7.5.
- Ridge and farrow method – ridge should be
6 mlong.
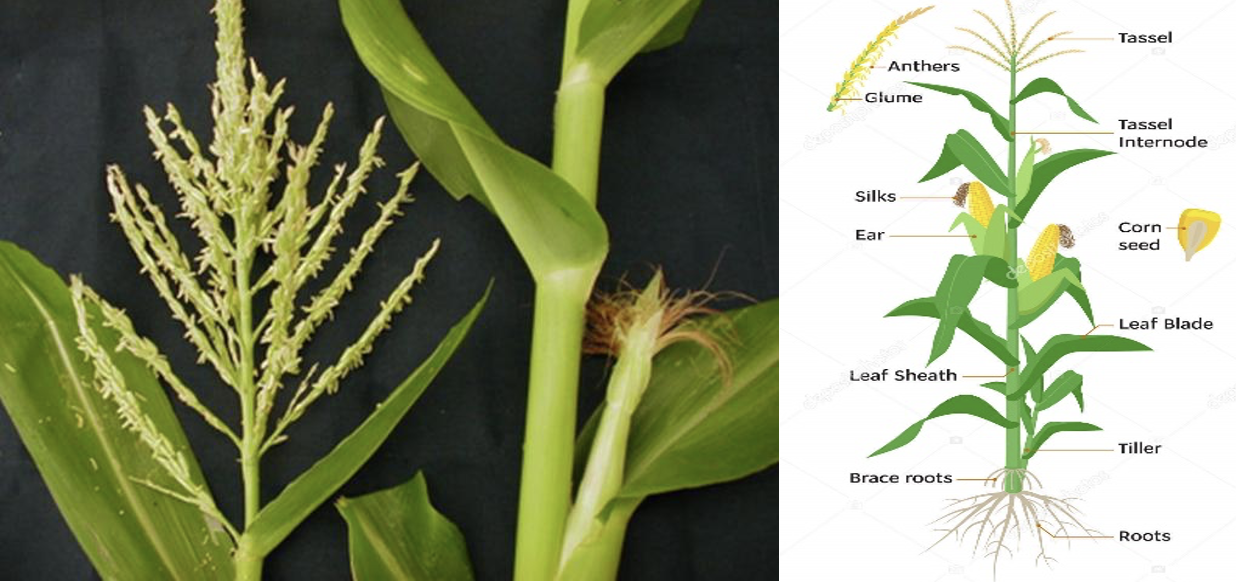
Botany
- Male Inflorescence:
Tassel: The terminalmaleflower cluster are called tassel. - Female Inflorescence:
Silk: The style is a very long silky filament, bears the female hairy cluster of which is known as silk. - Proto
andry:Maleinflorescence appears first.

Maize species: (Sturtevant, 1899)
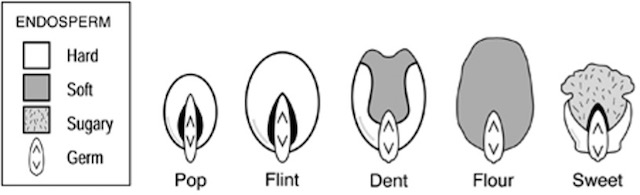
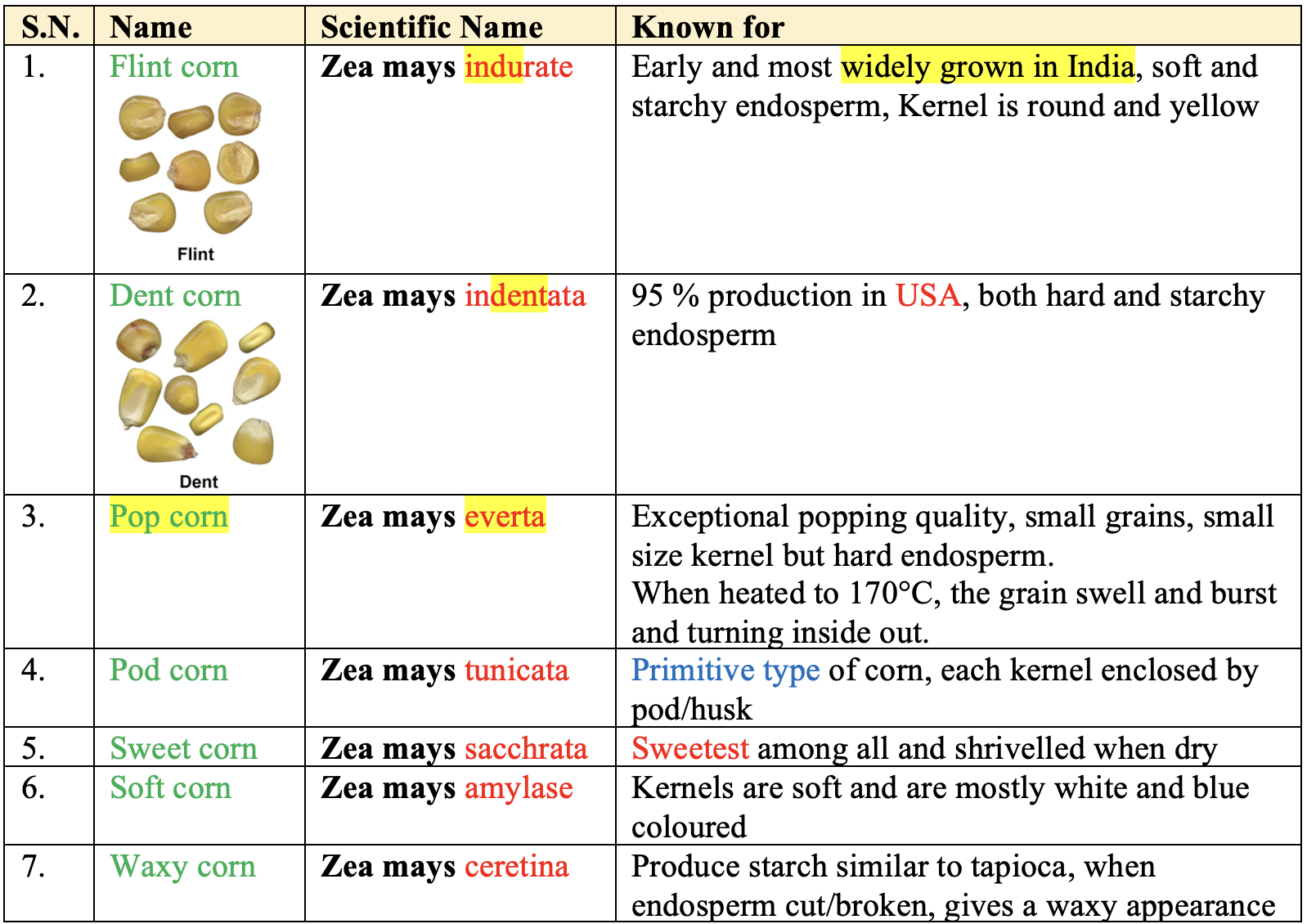
Varieties of Different Maize Type
- Fodder Maize: African tall, J1006
- Sweet Corn: Composite Madhuri, Composite Priya
- Pop Corn: Amber pop, V L Amber Pop, Pearl pop corn
- Baby Corn: Prakash, Parvati, VL 42,
- Quality Protein Corn
- Quality Protein Maize (QPM) varieties released by using
Opaque-2genes. - Varieties: Shaktiman 1 & 2, HQPM 1, Sakti 1, Proteina, Ratan etc.
- Flood prone area: Diara
- Drought resistant: Prakash, Megha
- Hybrid varieties:
- Yellow seeded: Ganga-1, 3, 5, 101, Ranjit, Himalaya, VL-54
- White seeded: Ganga safed-2, High starch, Ganga-4
Seed Rate
- Composite: - 15 to 20 kg/ha
- Hybrid:
20 to 25 kg/ha - Baby Corn: 25 kg/ha
- Fodder Maize: 40 to 50 kg/ha
- Spacing: 60 X 20-25 cm.
- Plant Population: 60-65 thousand.
- Germination:
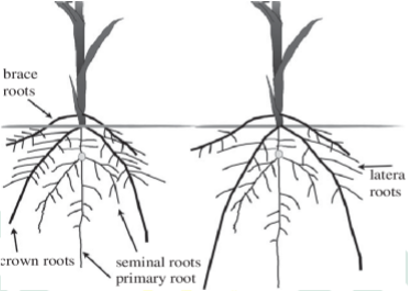
Hypogeal - The root system of maize is Fibrous and deep. It is usually well developed.
- It consists of:
- Seminal roots
- Crown roots
- Brace or Prop roots
Nutrient Management
- Hybrid: 120 : 50 : 40 kg/ha
- Composite: 100 : 40 : 30 kg/ha
- Critical stages for irrigation –
Tasseling and Silking
Yield
- Hybrid: 50 – 60 qt/ha of grain.
- Composites: 40-50 q/ha
- Fodder: 300-400 q/ha
- Average yield (India): 27.5 q/ha.
Sweet Corn

- Harvesting in Sweat corn is done
2-3 days after silking. UPPSC 2021
Explore More 🔭
🟢 https://youtu.be/i6teBcfKpik 🟢 https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5EsICTVo2dM

Basics
- Botanical name:
Zea mays - Family: Poaceae
- Origin: Central America & Mexico
- Chromosomes: 2n = 20
- Area: China
- Production:
USA> China - Productivity: USA
- In India, maize is the
thirdmost important food crop after rice and wheat. - Highest production is in
Karnataka(2018-19) - Maize is known as the
Queen of Cereals/Backbone of America, because has the highest genetic yield potential. - Maize Productivity in India is 26 q/ha as against 120 q/ha in USA and 55 q/ha in China.
QPM is an improved variety of maize which contains higher amount of “tryptophan” and “lysine” with lower amount of leucine and isoleucine in the endosperm than those contained in normal maize.
- Maize is a
cross pollinatedcrop. - Maize contains 65 to 70 % starch,
8-10% protein (Zein)and …
Become Successful With AgriDots
Learn the essential skills for getting a seat in the Exam with
🦄 You are a pro member!
Only use this page if purchasing a gift or enterprise account
Plan
- Unlimited access to PRO courses
- Quizzes with hand-picked meme prizes
- Invite to private Discord chat
- Free Sticker emailed
Lifetime
- All PRO-tier benefits
- Single payment, lifetime access
- 4,200 bonus xp points
- Next Level
T-shirt shipped worldwide

Yo! You just found a 20% discount using 👉 EASTEREGG

High-quality fitted cotton shirt produced by Next Level Apparel