🍲 Pigeonpea
Important points related to cultivation of Pigeonpea.
Pigeonpea

- Botanical Name:
Cajanus cajan - Cajanus cajan flavus (Early maturing)
- Cajanus cajan
bicolor (Latematuring) - Family: Leguminaceae / Papilonaceae
- Chromosome No: 2n = 22
- Origin: Africa
- Pigeonpea is also called as
Arhar,TurandRed gram. - Cajanus is derived from a Malay word ‘katschang’ or ‘katjang’ meaning pod or bean.
- Arhar crop works as
mini fertilizer crop. - After chickpea, arhar is the second most important pulse crop.
- The prominent pigeonpea growing states are
Maharashtra(highest), MP, UP, Bihar, Haryana, Rajasthan, Punjab, Gujarat, AP and Tamil Nadu.
Climate
- Pigeon pea grows well under
warm tropical and subtropicalclimate. - During vegetative growth, crop prefers a fairly moist and warm climate.
- During flowering and ripening stage, it requires bright sunny weather for proper fruit setting.
- It is highly susceptible to frost at the time of flowering.
- Pigeonpea can be grown with a temperature ranging from 26° to 30°C in the rainy season (June to October) and 17° to 22°C in the post-rainy (November to March) season.
- The length of growing season extends from 120 to 180 days.
- It has the capacity to tolerate moisture stress to a greater extent because of its deep/tap rooted system.
AlachlorandPendimethaline(as pre-emergence) andBasalin(as postemergence) are used to control weeds in pigeonpea field.- Protein content is
22 per cent. - Hardy crop,
most drought tolerant crop among major pulse. ⭐️ - It is an
often-cross pollinatedcrop. An average cross pollination is 20 per cent. A plant produces many flowers of which only 10 per cent set pods. - C3, Short day plant.
- Seed germination is
hypogeal type. - Thermal energy is required to break the seed coat.

Soil
- It does best on light texture, fertile and well drained loamy soils.
- It requires a soil pH range of 5-8.
- The saline-alkaline (> 8 pH) and waterlogged soils are unfit for its cultivation.
Sowing
Sowing Time
- Medium-early Pegionpea: 1st fortnight of April (for double cropping)
- Late Pegionpea: 1st week of July
- Pre-rabi Pegionpea: Sept or October
- Punjab and Haryana: 1st week of June
- UP and Rajasthan: 2nd fortnight of June Seed Rate
- Early Pegionpea:
15-18 kg/ha - Late Pegionpea: 10-15 kg/ha
- For bunds planting: 2 kg/ha
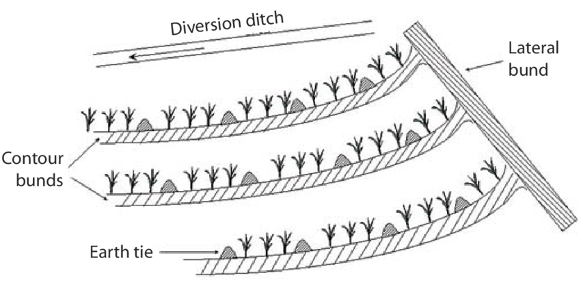
- Spacing: Common: 60 x 30 cm.
- Plant population for kharif is 55,000 plants/ha.
- Critical stage of Irrigation: Pre-flowering, Pod development
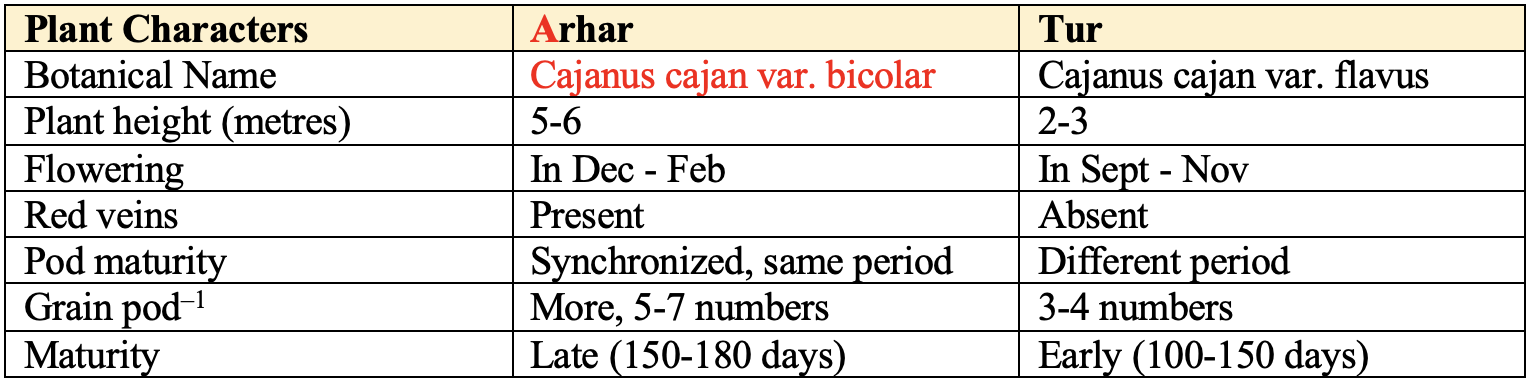
Comparison between Arhar and Tur
- Crop rotation: Pigeonpea is grown in summer as a Kharif crop in North India, and Kharif and Rabi in South India. The important crop rotations are:
- Paddy – Paddy – Pigeonpea
- Groundnut + Pigeonpea – Sorghum/Bajra/Maize
- Groundnut – Rabi Pigeonpea
- Urd bean – Rabi Pigeonpea
- Soybean – Rabi Pigeonpea
- Pigeonpea + Urd bean – Wheat
- Mung bean – Pigeonpea
- Pigeonpea – Cotton
Fertilizer
- N - 20-25 kg N/ha (Starter application)
- P - 50-65 kg P/ha
- K - 20-35 kg K/ha
- Zn - 2-4 ppm zinc (foliar applications of 0.5 per cent Zinc Sulphate)
- Ca - 0.25 per cent lime
Varieties of Pigeonpea released in India

Varieties of Pigeonpea with to different characters
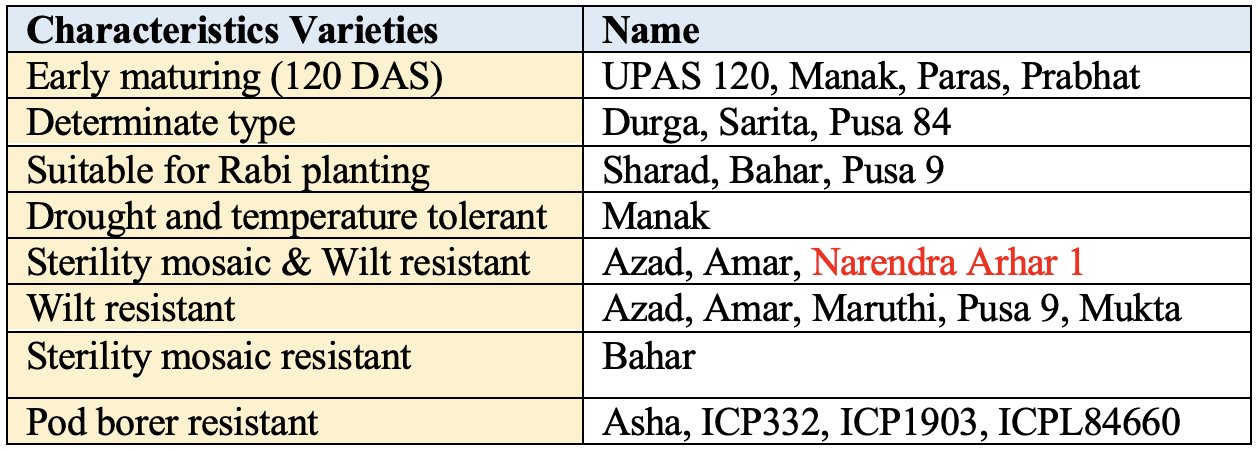
- Earliest variety of Pigeonpea is
UPAS-120. World’s first hybridvariety of Pigeonpea isICPH-8, developed by ICRISAT, Hyderabad in 1991 by using genetic male sterility (GMS). This variety matures in 130 to 132 days with an average productivity of 20 qt/ha.
Disease

Insect-Pest
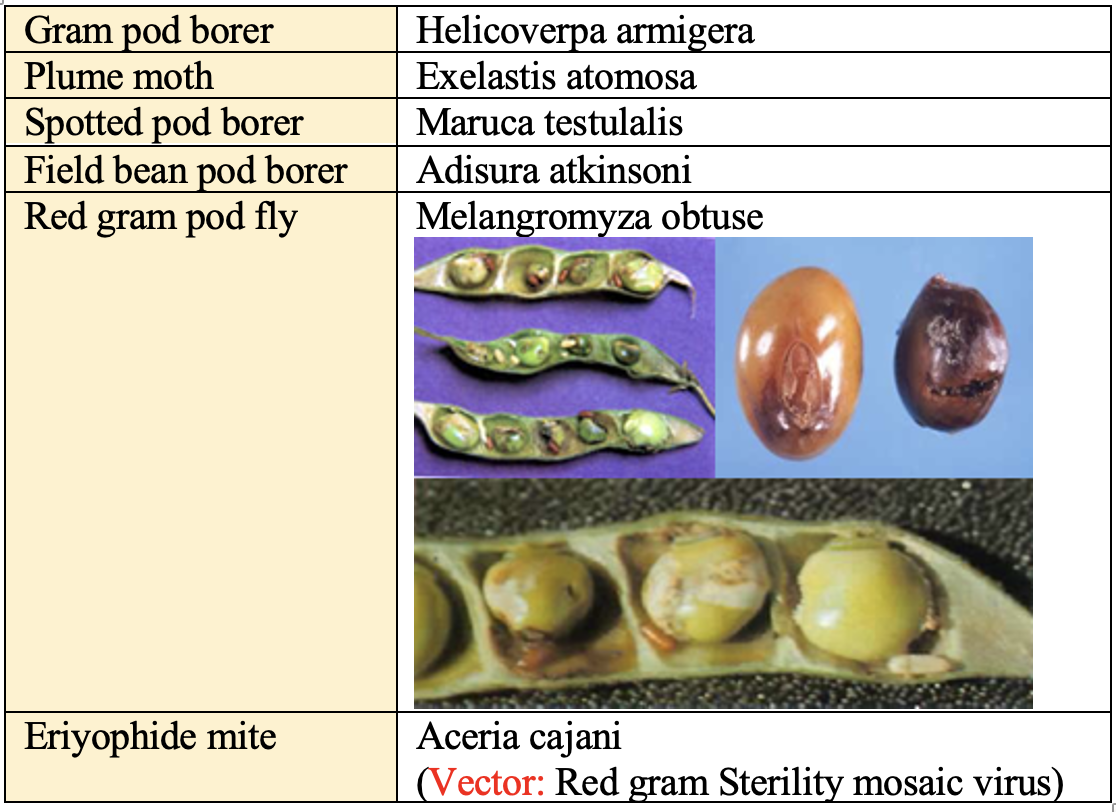
Yield
- Pigeon pea may yield about
20-25 quintalsof grain and 50-60 quintals of sticks per hectare. - In storage time grain moisture should be
10-11%. - Proportion of seed to pod is
50-60per cent. - Harvest index (HI) is
19% (lowest among pulses).
Pigeonpea

- Botanical Name:
Cajanus cajan - Cajanus cajan flavus (Early maturing)
- Cajanus cajan
bicolor (Latematuring) - Family: Leguminaceae / Papilonaceae
- Chromosome No: 2n = 22
- Origin: Africa
- Pigeonpea is also called as
Arhar,TurandRed gram. - Cajanus is derived from a Malay word ‘katschang’ or ‘katjang’ meaning pod or bean.
- Arhar crop works as
mini fertilizer crop. - After chickpea, arhar is the second most important pulse crop.
- The prominent pigeonpea growing states are
Maharashtra(highest), MP, UP, Bihar, Haryana, Rajasthan, Punjab, Gujarat, AP and Tamil Nadu.
Climate
- Pigeon pea grows well under
warm tropical and subtropicalclimate. - During vegetative growth, crop prefers a fairly moist and warm climate.
- During flowering and ripening stage, it requires bright sunny weather for proper …
Become Successful With AgriDots
Learn the essential skills for getting a seat in the Exam with
🦄 You are a pro member!
Only use this page if purchasing a gift or enterprise account
Plan
Rs
- Unlimited access to PRO courses
- Quizzes with hand-picked meme prizes
- Invite to private Discord chat
- Free Sticker emailed
Lifetime
Rs
1,499
once
- All PRO-tier benefits
- Single payment, lifetime access
- 4,200 bonus xp points
- Next Level
T-shirt shipped worldwide

Yo! You just found a 20% discount using 👉 EASTEREGG

High-quality fitted cotton shirt produced by Next Level Apparel