🔅 Sorghum
Important points related to cultivation of Sorghum.
- India, Nigeria, China are the largest producers of millets in the world. Millet is the 4th most widely cultivated food crop after Rice, Wheat and Maize.
- Coarser Millets include: Jowar, Bajra, Ragi etc. NABARD 2021
- Millets belongs to C4 group of plants.
Sorghum/Jowar

- Botanical Name:
Sorghum bicolor - Family:
Poaceae - Origin:
East Central Africa - Chromosome: 2n = 20
- Sorghum is poor in lysine but rich in leucine.
- Sorghum is known as
Camel Cropbecause it has the capacity to grow in arid soils and can withstand against prolonged drought. King of Coarse Cereals.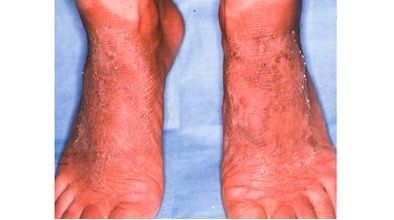
- Due to higher Leucine (amino acid) content, higher dose of sorghum in food causes
Pellagra disease. It is due to deficiency ofNiacin (Vitamin B3). - Symptoms = D4 (Diarrhea, Dermatitis, Dementia, and Death).
Climate
- Sorghum is a
short-dayplant. - Warm season crop. Suitable temperature for optimum crop growth is 27-32ºC.
- Requirement of rainfall throughout growth period is 400-600 mm.
- It can tolerate drought conditions as well as water logging condition.
Soil
- Soils with clay loam or loam texture.
- It does well in pH range of 6.0-8.5 as it tolerates considerable salinity and alkalinity.
- The black cotton soil of central India is very good for its cultivation.
Seed Rate
- Grain:
12-15 kg/ha - Fodder: 30-35 kg/ha
- Seed depth: 3-4 cm
- Test weight: 25 – 30 gm
- Germination:
Hypogeal - Spacing: 45 x 12 cm
- Plant population: 1,50,000 plants
- Sowing: Last June to first week of July.

- Hybrids: CSH 1 to 6, CSH 9, 10, 13, 16, 17, 18
- 1st Hybrid:
CSH-1in 1964 (Coordinated Sorghum Hybrid - 1). - One of the most important male sterile variety:
Combine Kafir 60(CK-60). - Roots are finer and more fibrous than maize.

- Inflorescence is called
Panicle(commonly calledHead).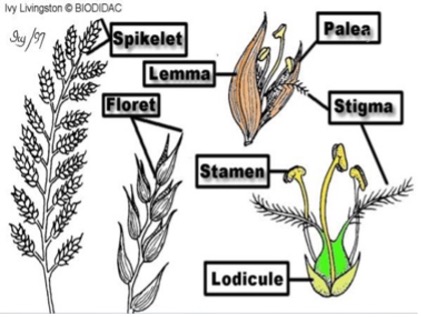
- Usually
no tillering,prop rootsmay develop. - C4 and
often cross-pollinatedplant. - Thinning is important operation at 12-15 cm (within row).
- Sorghum crop for fodder purpose should be used
after 50% floweringbecause sorghum leaves at knee stage possess a high amount ofHCNwhich is poisonous to the animals. HCN (Dhurin alkaloid)present in early stage (40-50 days) in upper leaves of crop. It is synthesized by roots of the sorghum plant.- Under draught condition if animal are grassed of sorghum leaves with 0.5 gm of HCN may be die.
Varieties of Sorghum:
- Best high yield variety of Rabi Jowar: M 35-1
- Drought and salinity tolerant for rain-fed: CSH 1, 6, 9, 11 and 3
- Sweet sorghum: RSSV 46, 53, 59, 84, 96, NSS 216
- Both grain and fodder: CSH 13 and CSV 15
- Low HCN: IS 208, IS 28450 and 288692
- Multi-cut fodder: MFSH 7, 885 F, CO (FS) 29
- Prabhani Shakti: India’s first biofortified Sorghum (jowar), with significantly higher iron and zinc than regular sorghum, was formally launched 2018.
- Developed by ICRISAT it was released for cultivation by Vasantrao Naik Marathwada Krishi Vidyapeeth (VNMKV), Maharashtra.
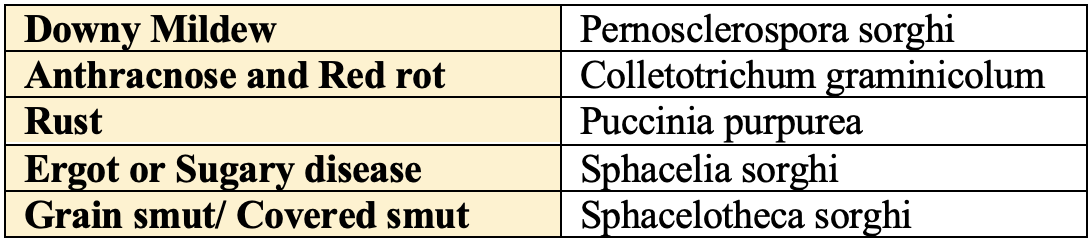
Disease
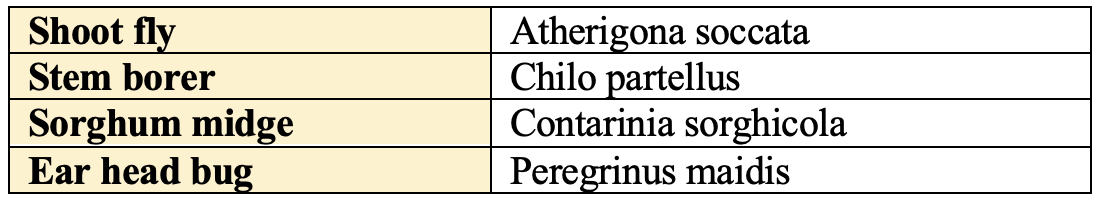
Insect-Pests
Yield
- The right stage for harvest is when grains have become hard having less than 25 % moisture.
- Grain/ Irrigated: 25-30 q/ha.
- Fodder: 300-400 q/ha
- India, Nigeria, China are the largest producers of millets in the world. Millet is the 4th most widely cultivated food crop after Rice, Wheat and Maize.
- Coarser Millets include: Jowar, Bajra, Ragi etc. NABARD 2021
- Millets belongs to C4 group of plants.
Sorghum/Jowar

- Botanical Name:
Sorghum bicolor - Family:
Poaceae - Origin:
East Central Africa - Chromosome: 2n = 20
- Sorghum is poor in lysine but rich in leucine.
- Sorghum is known as
Camel Cropbecause it has the capacity to grow in arid soils and can withstand against prolonged drought. King of Coarse Cereals.
- Due to higher Leucine (amino acid) content, higher dose of sorghum in food causes
Pellagra disease. It is due to deficiency ofNiacin (Vitamin B3). - Symptoms = D4 (Diarrhea, Dermatitis, Dementia, and Death).
Climate
- Sorghum is a …
Become Successful With AgriDots
Learn the essential skills for getting a seat in the Exam with
🦄 You are a pro member!
Only use this page if purchasing a gift or enterprise account
Plan
Rs
- Unlimited access to PRO courses
- Quizzes with hand-picked meme prizes
- Invite to private Discord chat
- Free Sticker emailed
Lifetime
Rs
1,499
once
- All PRO-tier benefits
- Single payment, lifetime access
- 4,200 bonus xp points
- Next Level
T-shirt shipped worldwide

Yo! You just found a 20% discount using 👉 EASTEREGG

High-quality fitted cotton shirt produced by Next Level Apparel