🍰 Sugarcane
Important points related to Sugarcane.
Sugarcane

- World’s 62% sugar is obtained from sugarcane.
- Family: Graminae (Poaceae)
- Origin: Indo-Burma
- Chromosome No: 80

- Area & Production:
Brazil(41%) >India (19%)> China > Gutemala - Productivity: Guatemala > Brazil > China > India
Cubais known asSugarcane bowl of world. (Cuba earned the title as the sugar bowl of the world due to the massive amounts of sugar produced in the country. However, due to many challenges, the quantity of sugar produced in Cuba declined which resulted in Brazil getting the title).- India’s leading sugarcane producing states are
Uttar Pradesh>Maharashtra> Karnataka. UPaccounts for about 45 per cent of total production and 58 per cent of the total area of sugarcane in India.- Highest number of sugar mills are in
Maharashtra(181) > Uttar Pradesh (120) > Karnataka (66) [Similarly forsugarproduction] - Institute/Organization related to Sugar & Sugarcane:
- Sugarcane Breeding Institute (
SBI),Coimbatore, Tamil Nadu - Indian Institute of Sugarcane Research, (IISR),
Lucknow, Uttar Pradesh - Indian Sugar Institute (ISI),
Kanpur
- Sugarcane Breeding Institute (
- AICRP on sugarcane was stated in 1970-71.
- Average yield of India in 2018-19:
73.82 tonnes/ha. - India’s sugarcane area in 2018-19: 51.59 lakh ha.
- India’s sugarcane production in 2018-19: 38.08 million MT.
👉🏻 Sugarcane is also known as:
- Intermediate day length &
perennialandtropicalplant - Most important cash crop
- Heavy feeder crop
Highestwater consuming crop
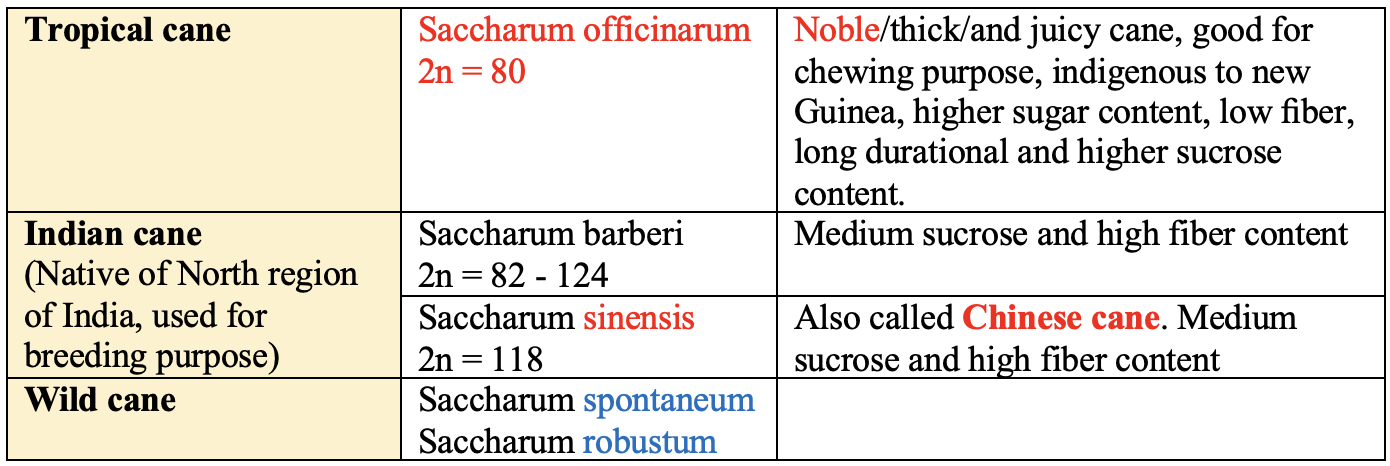
Classification
Climate
- It requires an average annual rainfall of
2500-3000 mm. - Optimum temperature for crop growth is between
28-32°C. - Besides temperature and rainfall, light (day length) plays a very important role in proper growth and development i.e., tillering of cane.
- Sugarcane is a
tropical plant. - Short day length decreases number of tillers plant per plant.
- Sugarcane is a
sun loving plant. Under long day length conditions, plant produces more dry matter.
Soil
- Sugarcane can be grown on all types of soil ranging from sandy loam to clay loam.
- Well drained loamy soil is best suitable for sugarcane.
- Saline, alkaline and acidic soil are not suitable for this crop.
- Optimum soil pH required is 6.5-7.5.
- Zero Tillage is mostly practiced in
Sugarcane. - Inflorescence of sugarcane is called
Arrow(Open panicle).

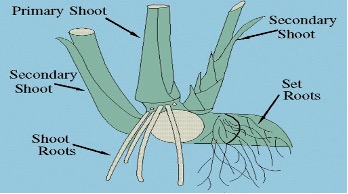
- Sugarcane has two types of root system:
- Sett roots: Temporary and provide moisture and nutrients for growing primary roots.
- Shoot roots: Permanent and produced from lower rings of the lower nodes of the shoots.
Planting
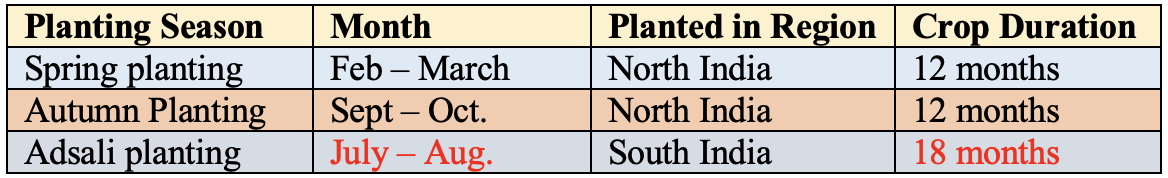
- Planting Season
- Planting material: Upper 1/3 to half part of cane is used for planting because it contains higher nitrogenous and glucose which helps in better germination.
- Planted setts should have 3 buds with 10 to 12 months age.
- Planting Spacing:
- N. India: 60-90 cm
- Planting Spacing: S. India & Adsali: 90-120 cm
- Seed/Sett rate:
- Planted setts should have 3 buds with 10-to-12-month age.
- 3 budded –
35,000-40,000 setts/ha - 2 budded – 80,000 setts/ha
- 1 budded – 1, 20,000 setts/ha
- Ratoon crop: 30-40 % area in India is under ratoon system.
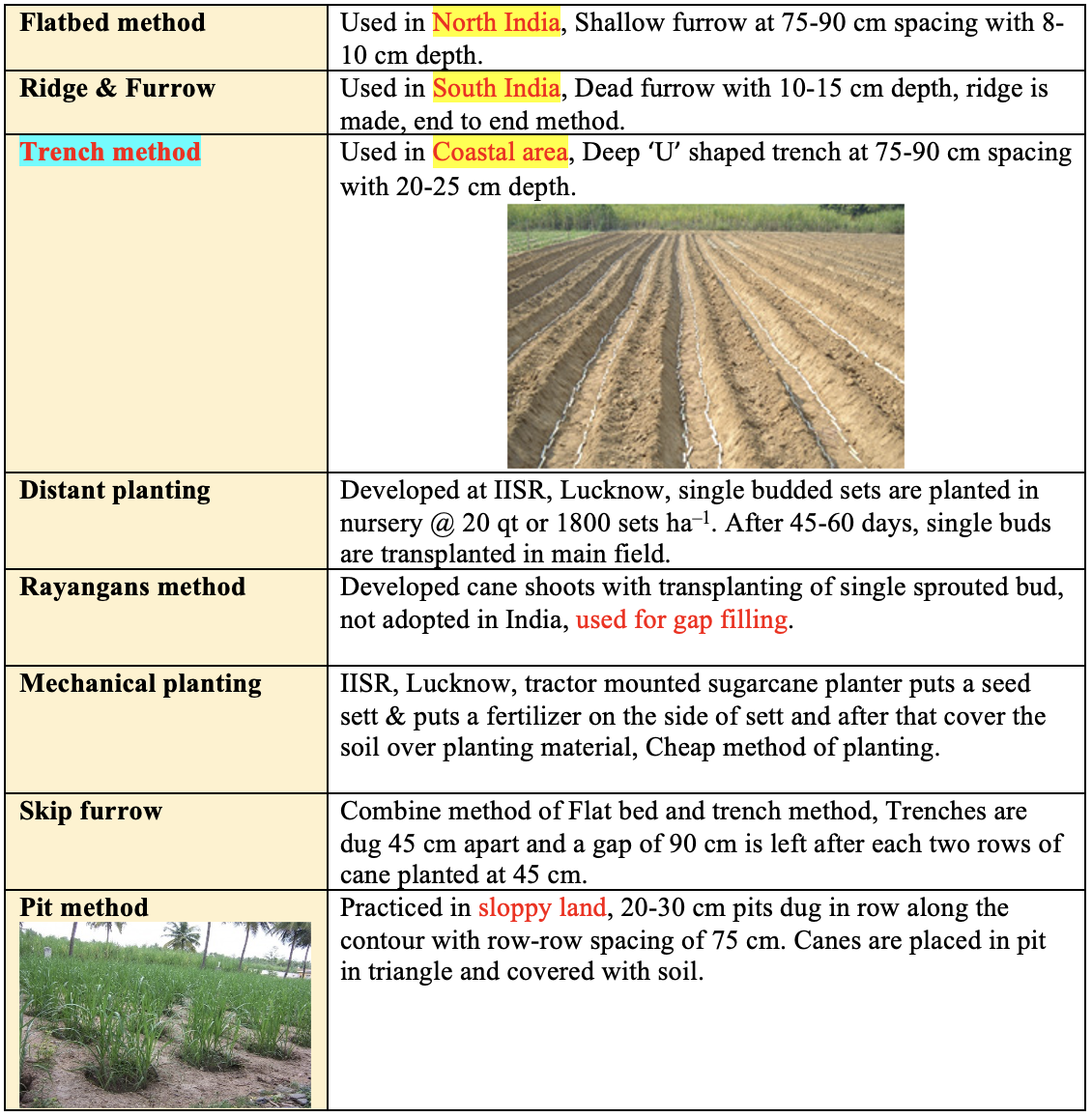
Planting Methods
Sett Treatments
👉🏻 To get better germination and reduce seed borne diseases.
- Cold water treatment: Whole cane is dipped in cold water for 12-48 hours.
- Hot water treatment: Setts soaked in hot water at
52°Cfor 30-40 minutes (10 minutes for upper side of sett). - Chemical treatment: Organo-mercurial i.e.
AgallalandAreton@ 200 gm/50 lt. of water. - Other: Sett treatment with 0.1-0.5 per cent solution of KMnO4, MgSO4 for 12-24 hours
- Mud & Dung mixture is also used in treatment of setts for 12-48 hours.
- Soaking in cold saturated Lime solution + 450 gm MgSO4 for 8-12 hours results an increase in 10 per cent germination and 12 per cent sugar yield.
Nutrient Management (Kg/ha)
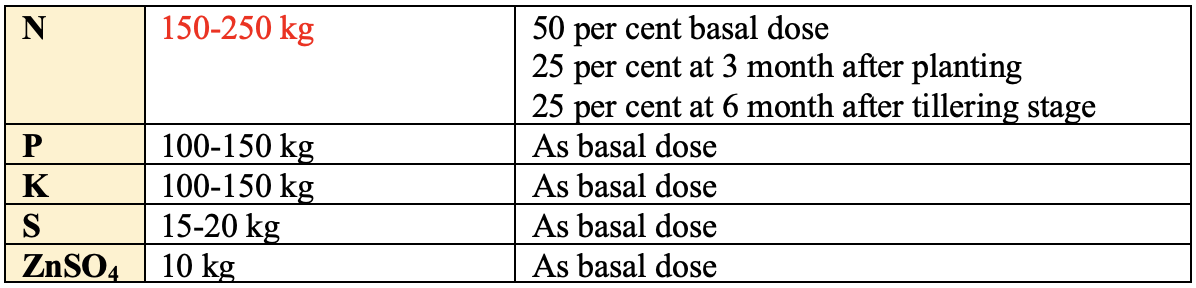
- Higher dose of nitrogen enhances vegetative growth, resulting in reduced
sucrosecontent. - Application of nitrogen fixing (
Azospirillumand Gluconacetobacter) and phosphate solubilizing (Phosphobacteria) bio-fertilizers were found to reduce the requirement of chemical fertilizers to the extent of 25%.
Water Management
- The water requirement is
2500-3000 mm. - Water management starts at
50 per centavailable soil moisture condition. - 60-70 tonnes water is required to produce 1 tonne cane.
- Sugarcane needs
10-12 irrigations. - 1st irrigation is applied at 20 days after planting (DAP).
- Subsequent irrigation is applied at an interval of 25-30 days in winter and 10-15 days in summer season.
Phases of Sugarcane
- Germination Phase: 0 to 60 Days After Planting (DAP)
- Formative Phase: 60 - 130 DAP
- Grand Phase: 130 - 250 DAP
- Maturity Phase: 250 - 365 DAP
- Most imp. critical stage for irrigation is Formative stage (Tillering) and second is Grand phase.
Inter-culture Operations
- Detrashing: To remove the leaves, only 8-10 leaves helpful for photosynthesis out of total 35-40 leaves.

- Propping: For support to plant, tying the canes by using the lower bottom leaves.

- Flower control: Spraying of
Ethrelat 500 ppm. Blind/light hoeingis done at 1 week after planting.- Blind hoeing not only breaks the hard pan of the soil surface, but it is also increases the germination of the sprouts by increasing respiration rate.
- Earthing up is done at 4 months after planting to protect from lodging, facilitate irrigation and economical water use efficiency.

- Conversion of glucose into sucrose and fructose takes place in extreme cold temperature (generally during Nov-Feb).
- Potassium (K) is responsible for translocation of sugar in sugarcane.
Weed Management
- Most critical weed competition period in sugarcane is up to 4 months after planting.
- Most used herbicides are
Simazine,AtrazineandAlachlor.
Varieties
- Wonder cane: COC-617 and CO-419
- National level commercial: CO Pant-85004, 86032, 87263.
- Red rot resistant: CO-7704, 7717, 8023, 8610, 8210, 86011, 93011 etc.
Most important crop rotation:
a) North India: S’cane with Cotton, Gram, Brassica spp, Sorghum, Maize, Peas etc. b) South India: S’cane – Cotton – Gram
Disease
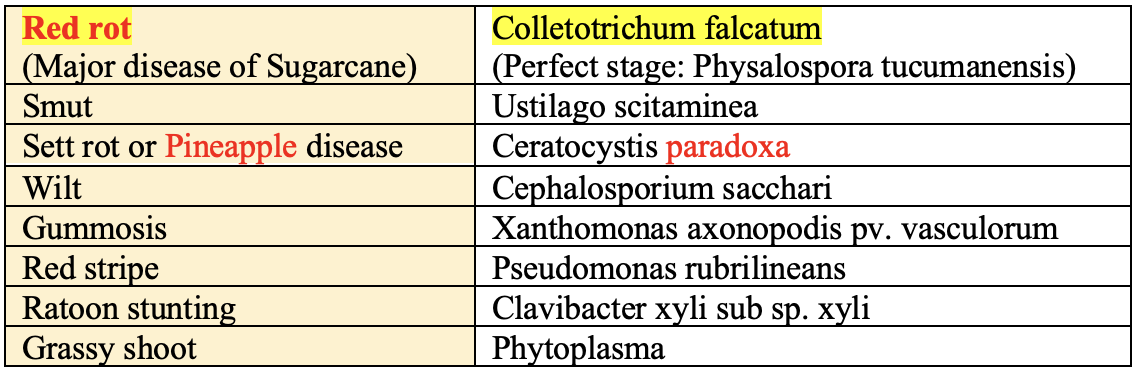
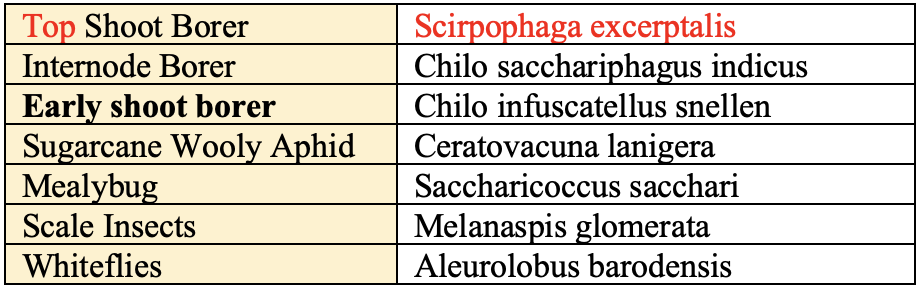
Insect-Pest
Harvesting
- Symptoms for Judging S’cane maturity:
- Arrowing and plant’s growth is stopped.
- Cane become brittle, produces metallic sound and breaks easily at nodes (most important symptoms)
- Buds swell out at nodes.
- Brix (Brix hydrometer/Refractometer) reading is between
18-20%. - Glucose content is < 0.5 per cent when tested by Fehling solution.

Crop Loggingis a method of plant analysis for assessing nutrient requirement of crops, given byH.F. Clements. It was 1st used in sugarcane atHawai.- N. India (in 10-12 months): 60-100 tonnes/ha
- S. India (in 18 months): 80-130 tonnes/ha
- Juice yield: 65-75 per cent
- Average Sugar recovery:
11%from juice - Sugar recovery from sugarbeet is
15-18per cent. - Gasohol is an alternative source of energy, prepared from 80 per cent petrol + 20 per cent alcohol from sugarcane.
Byproducts of Sugarcane

Sugarcane

- World’s 62% sugar is obtained from sugarcane.
- Family: Graminae (Poaceae)
- Origin: Indo-Burma
- Chromosome No: 80

- Area & Production:
Brazil(41%) >India (19%)> China > Gutemala - Productivity: Guatemala > Brazil > China > India
Cubais known asSugarcane bowl of world. (Cuba earned the title as the sugar bowl of the world due to the massive amounts of sugar produced in the country. However, due to many challenges, the quantity of sugar produced in Cuba declined which resulted in Brazil getting the title).- India’s leading sugarcane producing states are
Uttar Pradesh>Maharashtra> Karnataka. UPaccounts for about 45 per cent of total production and 58 per cent of the total area of sugarcane in India.- Highest number of sugar mills are in …
Become Successful With AgriDots
Learn the essential skills for getting a seat in the Exam with
🦄 You are a pro member!
Only use this page if purchasing a gift or enterprise account
Plan
Rs
- Unlimited access to PRO courses
- Quizzes with hand-picked meme prizes
- Invite to private Discord chat
- Free Sticker emailed
Lifetime
Rs
1,499
once
- All PRO-tier benefits
- Single payment, lifetime access
- 4,200 bonus xp points
- Next Level
T-shirt shipped worldwide

Yo! You just found a 20% discount using 👉 EASTEREGG

High-quality fitted cotton shirt produced by Next Level Apparel