🚬 Tobaco
Important points related to Tobaco.
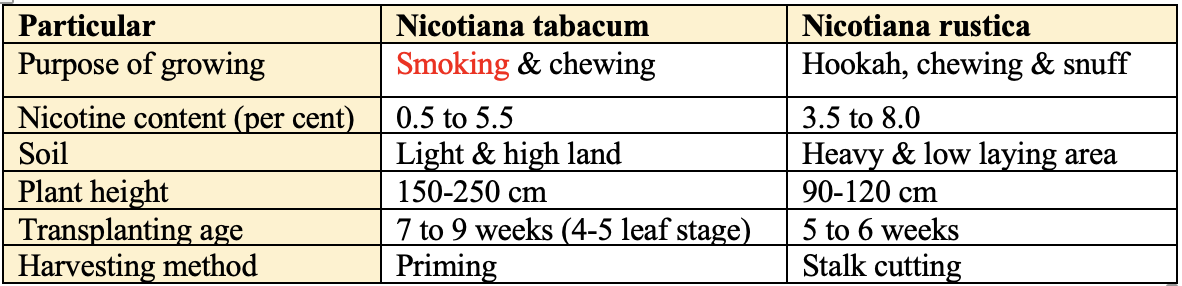
Tobacco

- Cultivation of tobacco in India is introduced by -
Portuguese - Family: Solanaceae
- Chromosome No: 2n =
48 - Origin: Central America
- Area:
China> India - Production:
China (40%)> India (12%) - Productivity: Pakistan
- Indian tobacco

- Flue cured virginia (FCV):
Cigarae tobacco, cover 30 per cent area &20 per centproduction of total. - Non-Virginia: Cover 70 per cent area &
80 per centproduction of total tobacco.
Climate
- Tobacco is a
tropical crop. - Sensitive Waterlogging.
- Average temp of 26°C.
- Tobacco seeds require about 21°C temperature for germination.
- Rainfall / irrigation during active vegetative growth is essential.
Soil
- Tobacco is adapted to moderately acidic soils with a pH ranging from
5.5 to 6.5. - Sodic soils are unfit for tobacco production because the plants absorb a lot of chloride ions which results a poor burning quality of leaves.
- Among 12 alkaloids present in tobacco,
nicotineis the most important one contributing about97%. - Seed rate:
2.5 to 3.0 kg/ha. - The seeds of tobacco are - positively photoblastic (germination is influenced by light) and proteolytic.
- The optimum time for sowing is the second fortnight of August.
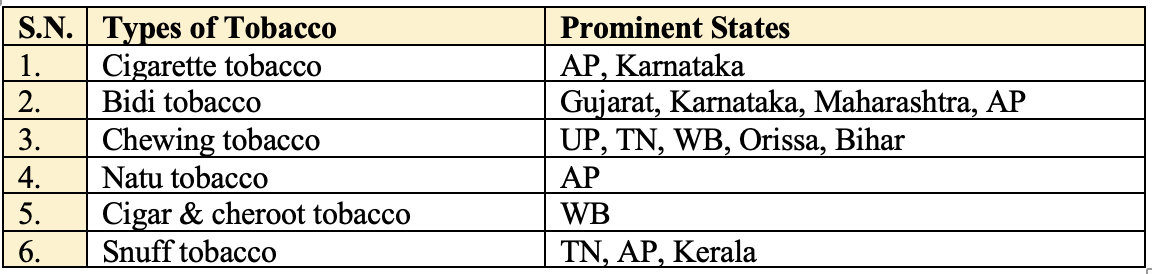
- Types of tobacco required heavy nutrition supply including N: Chewing, Bidi, Hookah.
- Types of tobacco required low N:
Flue-cured,Cigarette,Cigar - Mutant variety: Jayashri, Bhavya
- Hybrid –
GTH-1 - Most critical stages for irrigation is
Topping
Important Operation
- The sequence of different operations in tobacco crop is:
Topping👉🏻Desuckering👉🏻Priming👉🏻CuringUPPSC 2021
Topping
- Removal of flower heads either alone or with few upper/top leaves from the plant to improve the size and quality of leaves.
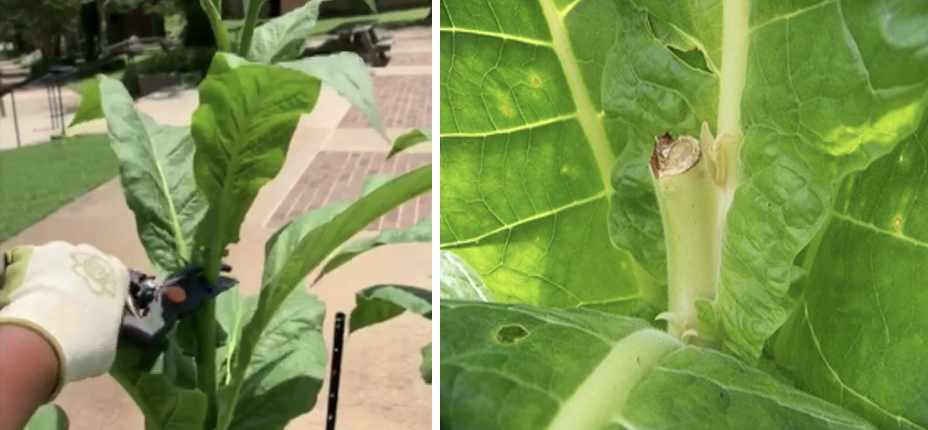

Desuckering
- After topping auxiliary bud grow, removal of such lateral branches or suckers/ auxiliary buds is called de-suckering.
- The main aim of topping and de-suckering is
to divert energy and nutrient from flower head to leaves. AFO-2021 - Done by:
- NAA in triethenolemin (2 per cent)
- MH (2 per cent)
- IBA (2 per cent)
Priming

Removal of mature lower leaves.- Entire harvest needs 5-6 priming.
- Method of harvesting is popular in Cigarette, Wrapper & Chewing type
Rabbing

- Rabbing the seed bed before sowing with slow burn farm waste materials like paddy husk, tobacco stubbles, waste grass and palmyrah leaves etc.
- This prevents the
damping off disease(Pythium aphanidermatum, P. debaryanum)
Stalk cutting method
- Cutting the entire plant close to the ground. Stalk is then hung upon a stick or lath. It is popular in Hookah, Bidi, Cheroot, Cigar & Chewing.
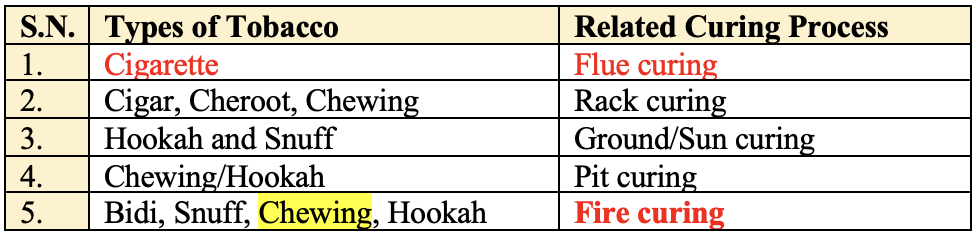
Curing

- A drying process, whereby most of the moisture of leaf is removed to impart required colour, texture and aroma to the final product.
- E.g. Flue curing used for cigarette process.
- The tobacco burning quality is positively related to
Kcontent of leaf. - Nicotine content is produced in
rootsand accumulate inleavesof tobacco.
Floopping in Tobacco

Tobacco

- Cultivation of tobacco in India is introduced by -
Portuguese - Family: Solanaceae
- Chromosome No: 2n =
48 - Origin: Central America
- Area:
China> India - Production:
China (40%)> India (12%) - Productivity: Pakistan

- Indian tobacco

- Flue cured virginia (FCV):
Cigarae tobacco, cover 30 per cent area &20 per centproduction of total. - Non-Virginia: Cover 70 per cent area &
80 per centproduction of total tobacco.

Climate
- Tobacco is a
tropical crop. - Sensitive Waterlogging.
- Average temp of 26°C.
- Tobacco seeds require about 21°C temperature for germination.
- Rainfall / irrigation during active vegetative growth is essential.
Soil
- Tobacco is adapted to moderately acidic soils with a pH ranging from
5.5 to 6.5. - Sodic soils are unfit for tobacco production because …
Become Successful With AgriDots
Learn the essential skills for getting a seat in the Exam with
🦄 You are a pro member!
Only use this page if purchasing a gift or enterprise account
Plan
Rs
- Unlimited access to PRO courses
- Quizzes with hand-picked meme prizes
- Invite to private Discord chat
- Free Sticker emailed
Lifetime
Rs
1,499
once
- All PRO-tier benefits
- Single payment, lifetime access
- 4,200 bonus xp points
- Next Level
T-shirt shipped worldwide

Yo! You just found a 20% discount using 👉 EASTEREGG

High-quality fitted cotton shirt produced by Next Level Apparel