🌾 Wheat
Package of practices for cultivation of wheat and other important concepts and facts.
Basics
- Botanical name: Triticum spp.
- Family:
Poaceae(Gramineae) - Origin: South
WestAsia (Turkey) - Generally, wheat is a
self-pollinated,C3andhexaploid plant. - In India, it is
secondmost important staple food crop after rice. - Wheat is known as
King of Cereals.
World
- Wheat is the largest
staple food crop of world. - India stands
2ndposition in production of wheat after China. - Area:
India> Russia > China - Production:
China(18%) > India (10%) > Russia - Productivity:
Germany> China - India’s share in global wheat production was recorded at 11.78 per cent in the year 2015-16.
- Major exporting countries: USA > Canada > Russia in 2016-17.
- India’s share in global exports was around 0.40 per cent in the year 2015-16.
- Major importing countries: Indonesia > Algeria > Italy
- India’s major export destination:
Nepal> Bangladesh > UAE
India
- Area:
UP - Production:
UP - Productivity:
Punjab - The national average productivity of wheat is
26.5 qt/ha.
Botany
Triticum spp
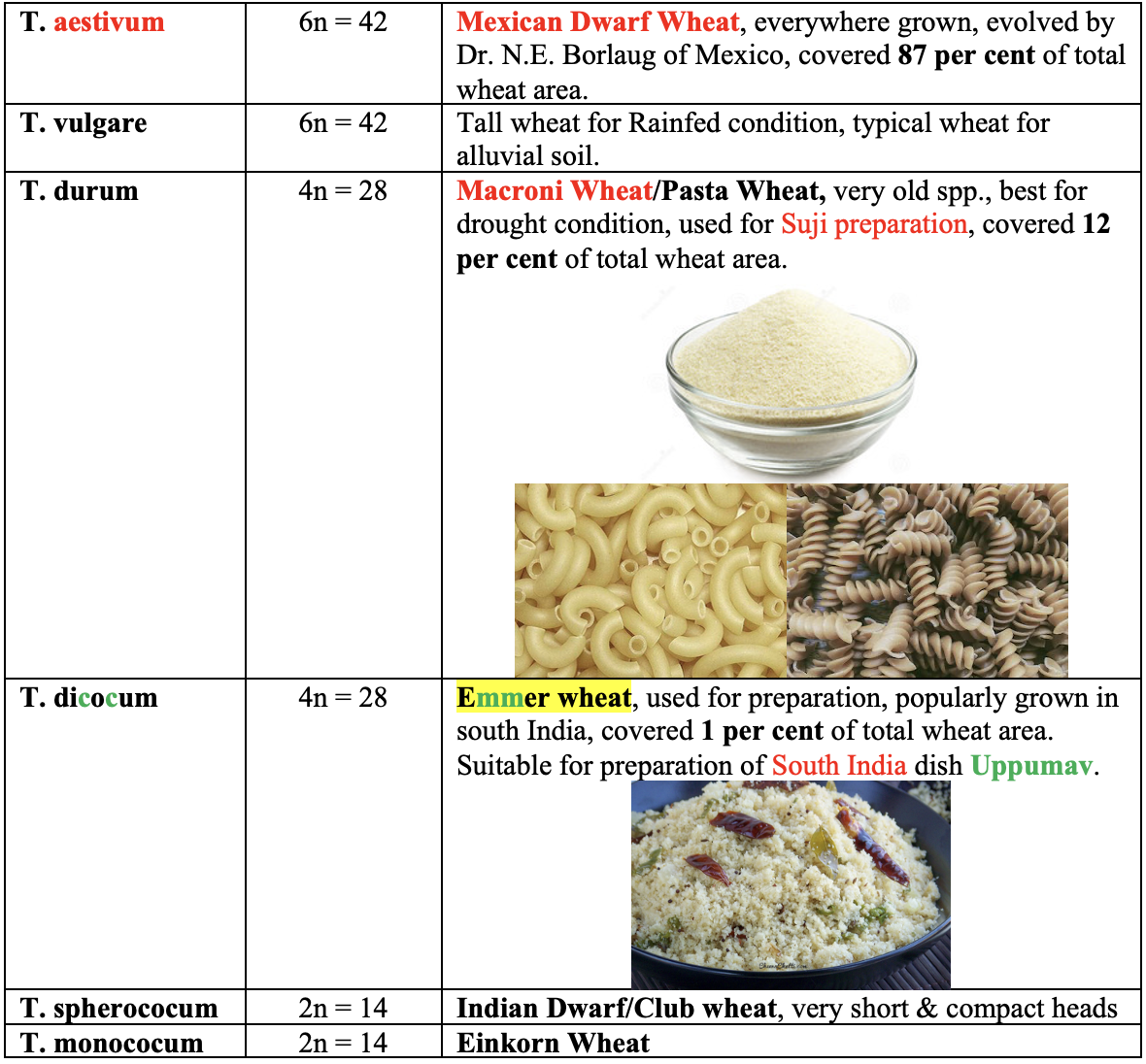
-
T. aestivum, is the most important species, occupying more than 90 per cent of the wheat area and 87 per cent of the total wheat production in the country. -
Research station:
- Modern/Common bread wheat:
CIMMYT, Mexico
- Indian Institute of Wheat and Barley Research,
Karnal - AICRP on Wheat & Barley Improvement Project,
Karnal
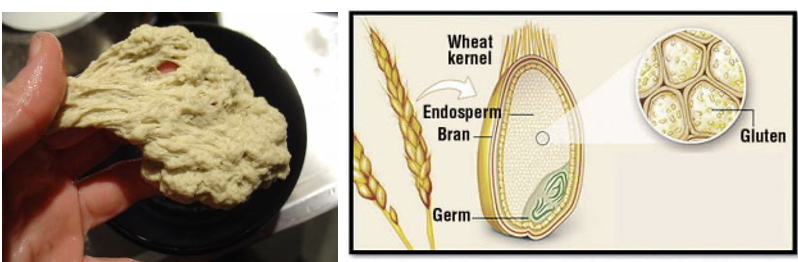
- Modern/Common bread wheat:
-
Protein content in wheat is
10-11%(Gluten). -
Chapatti making/backing quality of wheat is mainly affected by
Gluten strength.
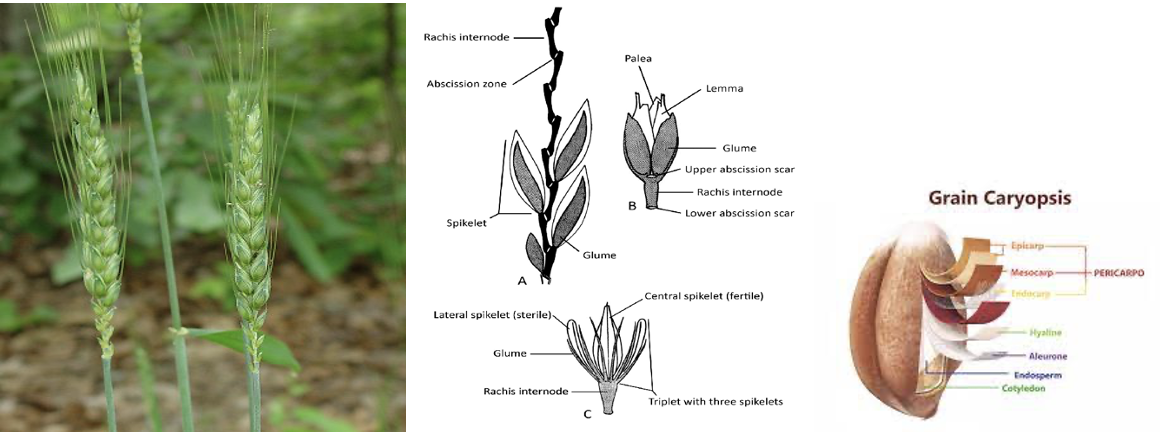
- The inflorescence of wheat is known as
Spike/Spikeletsand the central zigzag axis is called asRachis. Spikelets are composed flowers calledFlorets. - Fruit of wheat is
caryopsis. - The flower of wheat is closed by
LemmaandPaleaand the extending portion of lemma is known asawn. - Wheat plant has:
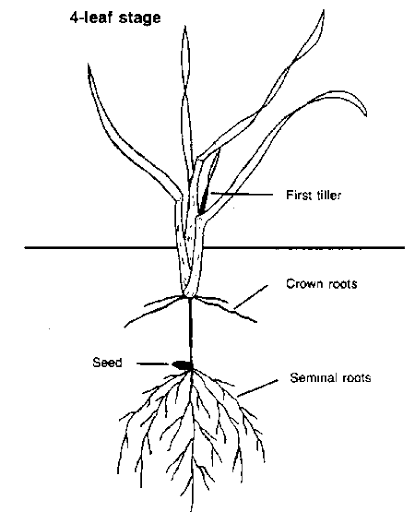
- Seminal roots (Primary roots) –
Temporaryroots, responsible for nourishment the plants during early stage of crop. - Crown roots (Secondry roots)–
Permanentroots, appeared20-22 daysafter sowing (after or attillering stage).
- Seminal roots (Primary roots) –
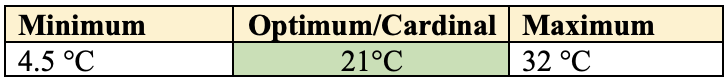
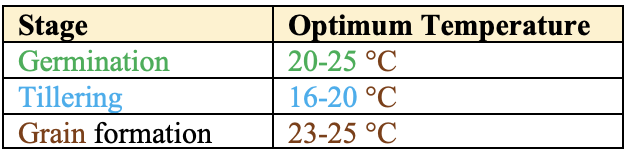
Climate
RabiSeason Crop.- Wheat crop favours
cold🥶 andmoist weather💦 during the vegetative growth period. - Warm and dry climate 🥵 during grain formation.
- Wheat is a
C3,self-pollinatedandlong day plant. - Water requirement for proper growth is
600-900 mm. Indo-gangetic plainis the most suitable region for wheat cultivation.
Sowing
- 90 per cent of the wheat seed germination takes place after 4 to 8 days of sowing.
- Germination:
Hypogeal
Sowing Date
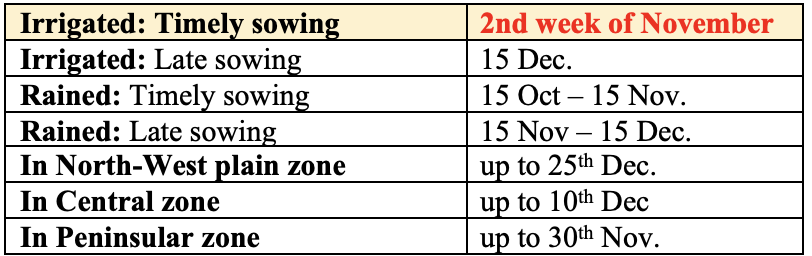
Sowing Depth
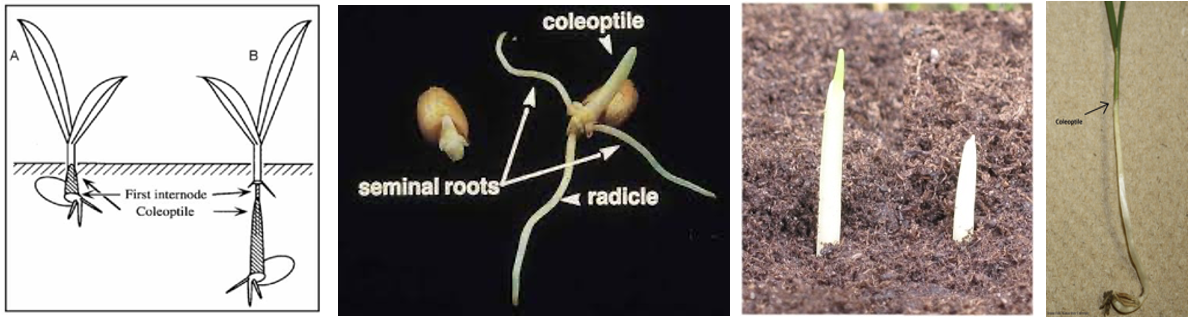
- The dwarf wheat should be sown only at
5-6 cmdepth as they have shorter coleoptiles. Seeding depth of 8-10 cm results in poor germination and reduced yield. - Sowing depth of dwarf wheat is shallow, directly depend upon length of coleoptyle.
- Coleoptyle (main part of wheat seed) is immediately seen after germination.
FIRB

- Recent work shows that system of raised bed planting of crops may be particularly advantageous in areas where groundwater levels are falling and herbicide-resistant weeds are becoming a problem.
- Management of irrigation water is improved in simpler, and more efficient. On an average it uses,
25 to 40 %less water than flatbed methods and improves crop yields bymore than 20%. FIRB planting saves 30% to 50% wheat seed compared to flatbed planting.
Zero Tillage

- Zero till drill seed-cum-fertilizer machine, developed from GBPUAT, Pantnagar (Uttarakhand) is used in
rice-wheatsystem for wheat cultivationwithout any ploughingi.e. direct seed sowing in wheat to save ploughing cost. - The requirement of seed under zero tillage has been found to be around
20-25% higheras compared to conventional practices and the optimum seed rate is 140-150 kg/ha. - Rice should be harvested near the ground and the left-over stubble should not be more than 15 cm in height.
Surface seeded Technology
- In parts of North-Eastern India soil remains wet for a long time after harvesting of rice crop and it is not possible to undertake tillage operations for growing wheat. In such areas dry or soaked wheat seeds can be broadcasted a few days before or immediately after harvest of the rice crop under wet/ saturated soil conditions.
- The cost of producing wheat is only 70-75 per cent as it eliminated the need for tillage operations.
Seed Rate
- Test weight of wheat grains is about
40 gm. While test weight of Phalaris minor is only2 gm.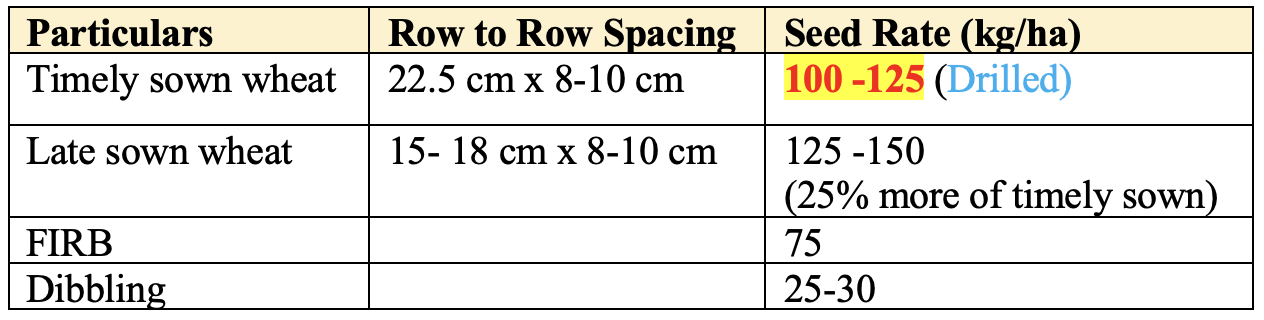
- To ward off threat to wheat production from the globally spreading menace of resistant varieties of
Wheat Stem Rust-Ug99, DBW 17, PBW 550, Lok 1, and Turja identified. - Most suitable cropping system for wheat crop is mixed cropping (Wheat + Mustard and Wheat + Chickpea).
- Four to Five rows of wheat grown in two rows of sugarcane is a popular intercrop practice.
- Relay copping of wheat in an early planted potato crop is a high bonus cropping system.
- To obtain maximum yield of wheat, 500 tillers per m2 is required.
Irrigation Management
😐 We will study about Irrigation Management in Wheat in Water Management Course.
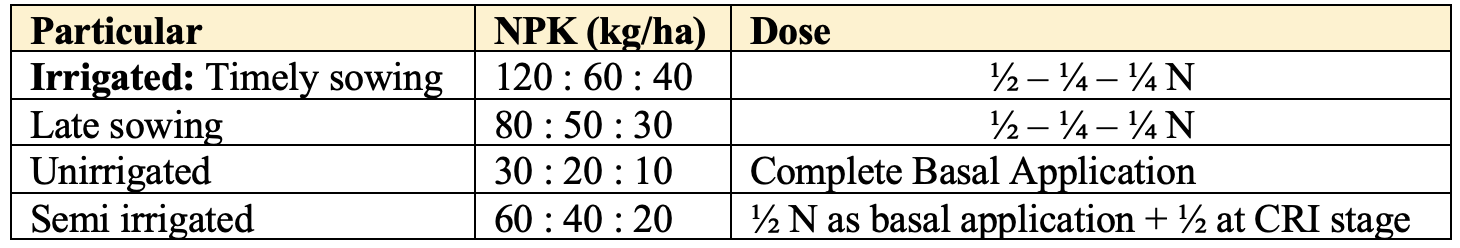
Fertilizer Management
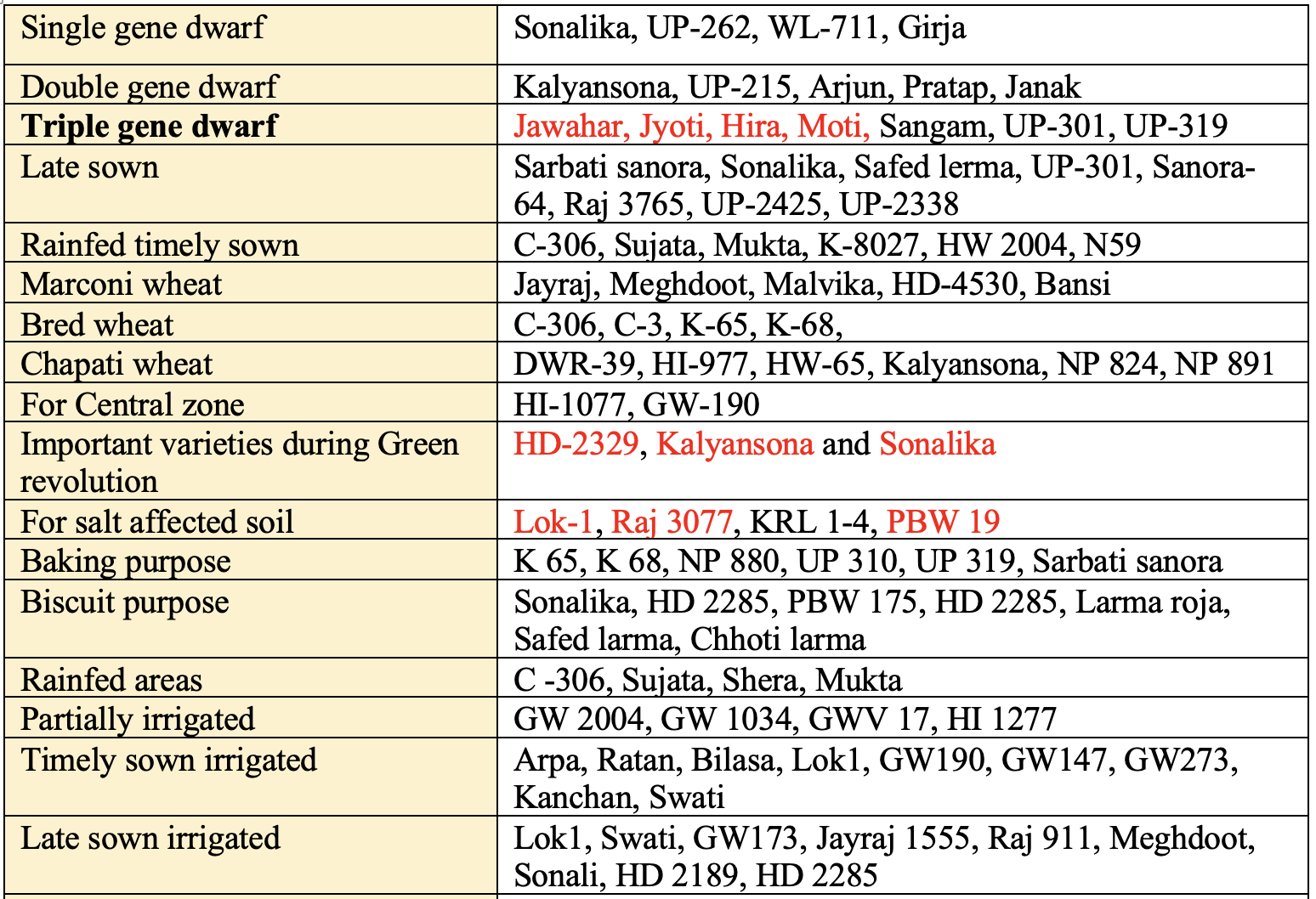
Wheat Varieties
-
- Dwarf gene introduced in wheat to develop dwarf wheat is
Norin.
- Dwarf gene introduced in wheat to develop dwarf wheat is
Norin👉🏻 Nor (Rht) = Reduced height (Genes 👉🏻 Rht1 and Rht2)- Source of dwarfing gene is
NorinfromJapanOlsen dwarffrom S. Rhodesia.
- 1st dwarf gene wheat variety is
Norin-10, developed by Dr. N.E. Borlaug in 1961-62. Larma rojois all three rust resistant variety of wheat.- 1st time, Govt of India imported 100 kg of Mexican dwarf wheat varieties (
Sanora-63,Sanora-64andLarma rojo) in1963. - Triple gene dwarf wheat varieties were released during 1970.
Pusa Yashasvi
- Recently, the Indian Agricultural Research Institute (
IARI) has released a new variety of wheat named Pusa Yashasvi. - It is also known as
HD-3226. - It has higher genetic yield potential (at 79.6 quintals) as compared to other varieties of wheat.
Pusa Yashasvihas a higher content of zinc, protein, and gluten (which contributes to the strength and elasticity of the dough).- The best feature of this variety of wheat is that it is highly resistant against all major rust fungi viz. yellow/stripe, brown/leaf, and black/stem.
👉🏻 HD-2967 (Pusa Borlaug) & Pusa-3086 (Pusa Gautami): 40% Area of Wheat (IARI)
Weed Management
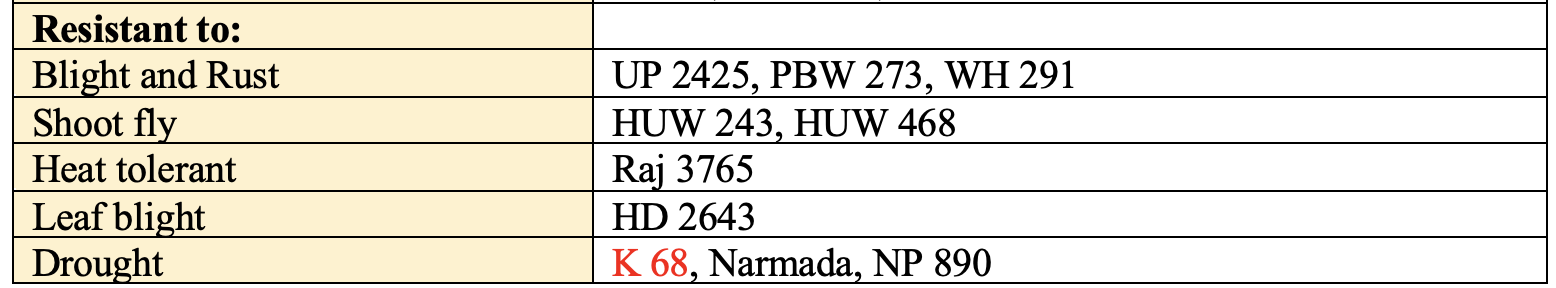
- Objectionable Weed –
Convolvulus arvensis - Associated Weed – Phalaris minor, Avena fatua and Chenopodium album
- Satelite Weed – Phalaris minor & Avena fatua
- Horrible Weed – Sorghum halepense
- Phalaris minor is found with dwarf wheat.
- Common herbicide used to control weeds is 2, 4-D. It is used as post-emergence herbicide.
Milking stageof wheat is sensitive to 2, 4-D.
Harvesting
- The shelling percentage of wheat is
60 per cent. - Harvest index =
40-45 per cent(0.4-0.45). - Grain and straw ratio in Mexican Dwarf Wheat is
1 : 1.5. - Grain moisture should be
20-25%. - Safe storage moisture content of grain should be in the range of
10-12%. - Irrigated condition:
40-45 q/ha. - Rainfed condition: 20-25 q/ha.
- Average Yield: 30 q/ha.
Basics
- Botanical name: Triticum spp.
- Family:
Poaceae(Gramineae) - Origin: South
WestAsia (Turkey) - Generally, wheat is a
self-pollinated,C3andhexaploid plant. - In India, it is
secondmost important staple food crop after rice. - Wheat is known as
King of Cereals.
World
- Wheat is the largest
staple food crop of world. - India stands
2ndposition in production of wheat after China. - Area:
India> Russia > China - Production:
China(18%) > India (10%) > Russia - Productivity:
Germany> China - India’s share in global wheat production was recorded at 11.78 per cent in the year 2015-16.
- Major exporting countries: USA > Canada > Russia in 2016-17.
- India’s share in global exports was around 0.40 per cent in the year 2015-16.
- Major importing countries: Indonesia > Algeria > …
Become Successful With AgriDots
Learn the essential skills for getting a seat in the Exam with
🦄 You are a pro member!
Only use this page if purchasing a gift or enterprise account
Plan
- Unlimited access to PRO courses
- Quizzes with hand-picked meme prizes
- Invite to private Discord chat
- Free Sticker emailed
Lifetime
- All PRO-tier benefits
- Single payment, lifetime access
- 4,200 bonus xp points
- Next Level
T-shirt shipped worldwide

Yo! You just found a 20% discount using 👉 EASTEREGG

High-quality fitted cotton shirt produced by Next Level Apparel