🌡 Basics of Meteorology
Meterology, Climate, Weather, Agrometerology, Weather vs Climate, Sun and Earth, Atmosphere
Meteorology

- “Meteorology is the study of envelope of air surrounding the planet and of the phenomenon associated with atmosphere”.
- It is derived from the
Greekword “meteoron” which means “in the sky” or “high in the sky”.
Climate
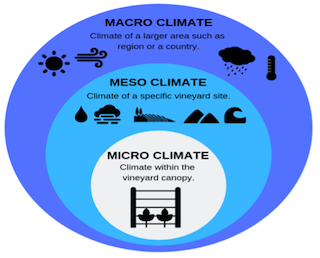
- Climate (Greek Word) is a weather condition over a given region during a longest period.
- Climatology: “The study of long-term manifestations of the weather represented by a statistical collection of weather conditions over a specified length of period usually at least a few decades”.
- Micro climatology deals with pertinent factors (solar radiation, temperature, wind, vapour pressure, CO2) of the environment in the zone lying between the highest level reached by the plant and the lowest depth to which air penetrates into the soil.
Agrometeorology
- Agrometeorology (abbreviate from Agricultural Meteorology) is the branch of meteorology which investigates the relationship of plants and animals to the physical environment.
- The use of science of Meteorology for agriculture is called Agricultural Meteorology.
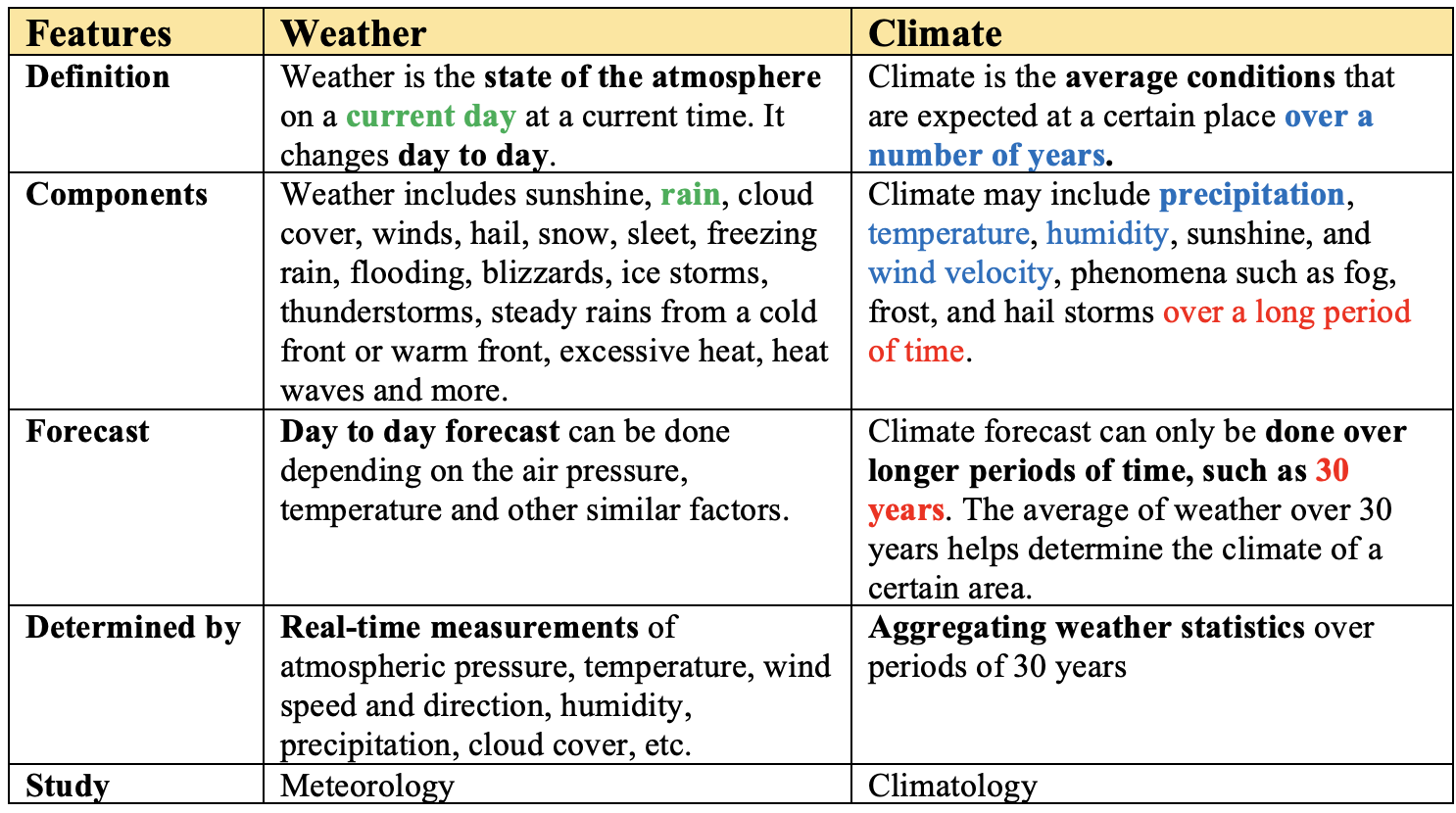
Weather vs Climate

Sun and Earth
- The distance between earth and sun is 1.5 x 108 km.
- Earth rotates in its axis at an angle of 23 ½°.
- Day and night are equal on both March 21 and September 23.
- Shortest day in north hemisphere is on
December 21. - Blue colour of the sky and red colour of sunset is due to
Dispersion. - Black colour absorbs more radiation as compared to others.
- Highly reflectivity is found in
Greencolour. - Reflected radiation (Albedo) is useful in remote sensing.
- Visible radiation is the range of
390-760 micron (0.39-0.7 micron). Red lightis most favourable for growth of plants.Photosynthetic active radiation (PAR)can be measured in Einstein units (EU).- Process responsible for heat flow:
Conduction,ConvectionandRadiation. - Radiation does not require medium for its heat flow.
What is Atmosphere?

- Atmosphere is the air surrounding the earth.
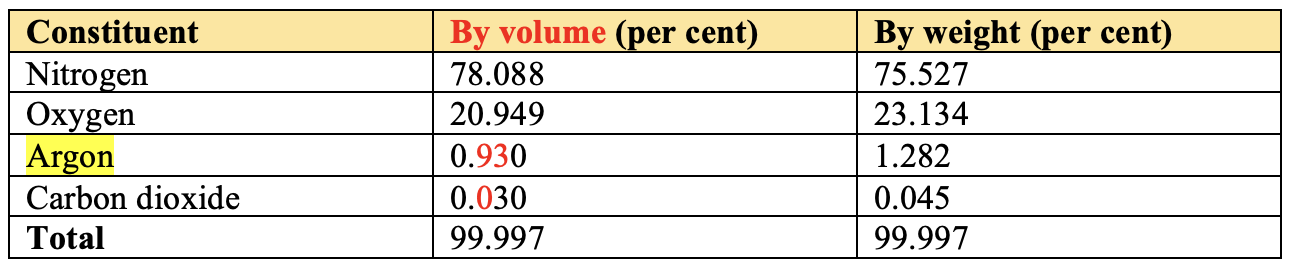
- The atmosphere is a mixture of different gases.
- It contains life-giving gases like oxygen for humans and animals and carbon dioxide for plants.
- It also contains water vapour and dust particles.
- It envelops the earth all round and is held in place by the gravity of the earth.
- It helps in stopping the ultraviolet rays harmful to the life and maintains the suitable temperature necessary for life.
- Generally, atmosphere extends up to about
1600 kmfrom the earth’s surface. However, 99 % of the total mass of the atmosphere is confined to the height of32 kmfrom the earth’s surface.
The composition of the atmosphere:
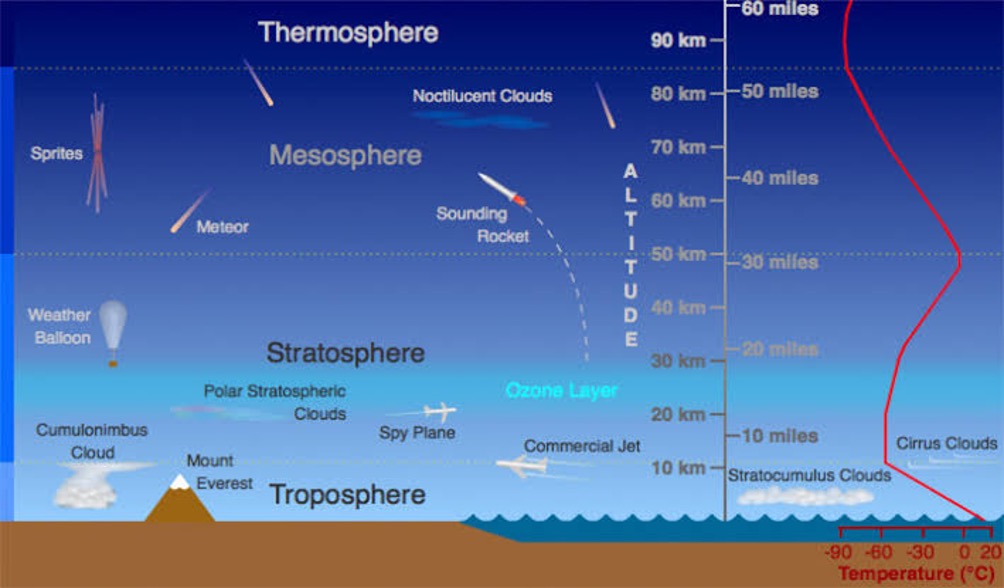
Structure of the atmosphere:
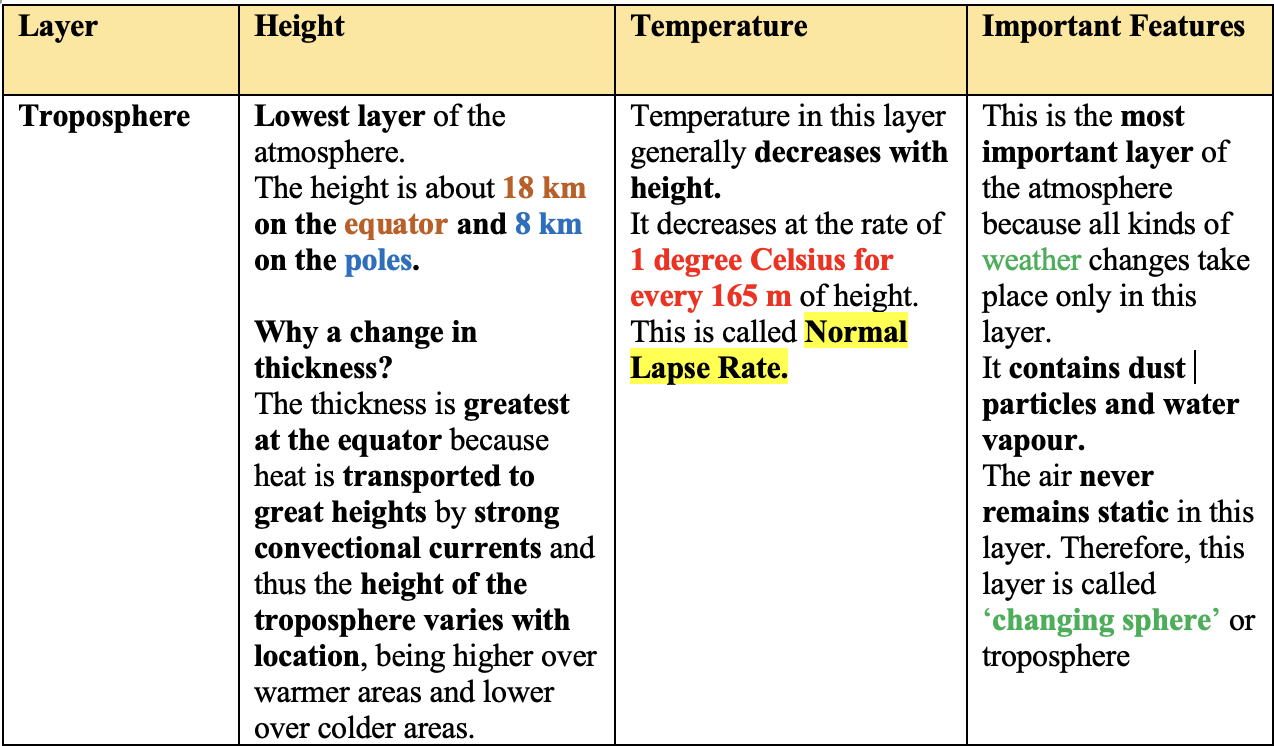
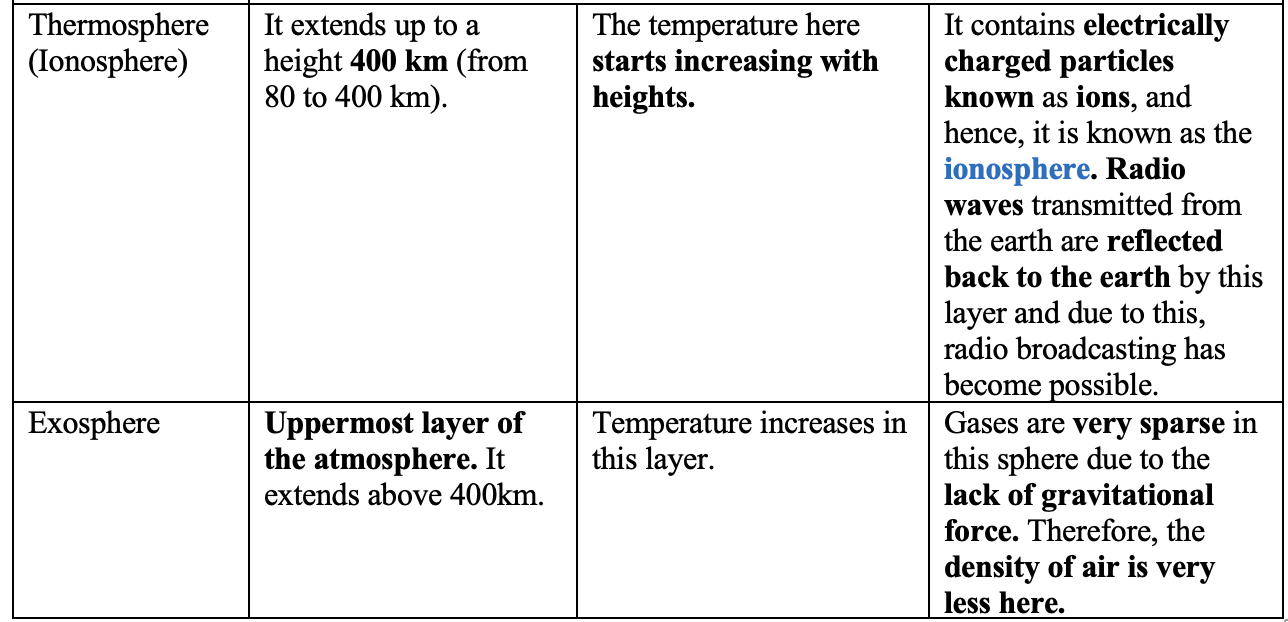
The atmosphere consists of 5 layers:
- Troposphere
- Stratosphere
- Mesosphere
- Thermosphere (Ionosphere)
- Exosphere
The following are the features of each of these layers:


Meteorology

- “Meteorology is the study of envelope of air surrounding the planet and of the phenomenon associated with atmosphere”.
- It is derived from the
Greekword “meteoron” which means “in the sky” or “high in the sky”.
Climate

- Climate (Greek Word) is a weather condition over a given region during a longest period.
- Climatology: “The study of long-term manifestations of the weather represented by a statistical collection of weather conditions over a specified length of period usually at least a few decades”.
- Micro climatology deals with pertinent factors (solar radiation, temperature, wind, vapour pressure, CO2) of the environment in the zone lying between the highest level reached by the plant and the lowest depth to which air penetrates into the soil. …
Become Successful With AgriDots
Learn the essential skills for getting a seat in the Exam with
🦄 You are a pro member!
Only use this page if purchasing a gift or enterprise account
Plan
Rs
- Unlimited access to PRO courses
- Quizzes with hand-picked meme prizes
- Invite to private Discord chat
- Free Sticker emailed
Lifetime
Rs
1,499
once
- All PRO-tier benefits
- Single payment, lifetime access
- 4,200 bonus xp points
- Next Level
T-shirt shipped worldwide

Yo! You just found a 20% discount using 👉 EASTEREGG

High-quality fitted cotton shirt produced by Next Level Apparel