🌱 Agronomy Basics
Learn basics of agronomy and basic principles of agronomy
What is Agronomy?
- It consists of two
Greekwords i.e., Agros means field, Nomos means to manage. - Agronomy is the science of manipulating the crop environment complex with dual aims of improving agricultural productivity and gaining a degree of understanding of the process involved.
- “Agronomy is the branch of agricultural science which deals with the principles and practices of crop production for obtaining maximum economic returns from a unit of area in a defined period without deteriorating the fertility status of soil”.
- Agronomy is considered as the mother or primary branch of agriculture. Like agriculture, it is nothing but an integrated and applied aspect of different discipline of pure sciences.
Pietro de’Crescenziis the father of Agronomy.
👉🏻 It has three distinct branches:
- Crop Science (mainly field crops)
- Soil science
- Environmental Science (that deals with applied aspects)
The central theme of agronomy is of soil-crop-environment relationship.
Scope of Agronomy
- Yield maximization with introduction of new cultivars/ HWs
- Reduced cost of production due to proper crop management
- Better water use efficiency due to agronomic knowledge
- Special tillage and intercultural operations for better crop growth and maximizing harvesting index
- Appropriate soil fertility management can increase crop yields with lesser use of fertilizer for increased profit
- Reduced post-harvest loss due to agronomic knowledge and practices
- Intensive cropping patterns and integrated farming systems for sustainable agricultural growth and increased food production per unit area to feed teeming millions every year.
Basic Principles of Agronomy
Agronomic principles are the ways and means for the better management of soil, plant and environment for economically maximum returns per unit area for years.
👉🏻 What are they?
- Planning, programming and executing measures for maximum utilization of resources (land, sunshine, rain water, temperature, humidity, winds) and inputs (labor, seeds, capital, irrigation water, fertilizer/ manures, farm equipment, marketing facilities etc) for increased yield and maximum profits.
- Choice of proper crop varieties adaptable to the particular agro-climate, land situation, soil fertility, season and befitting to the cropping systems
- Proper field management by tillage, preparing field channels and bunds for irrigation and drainage, checking soil erosion, leveling and adopting other suitable land improvement practices
- Adoption of multiple cropping and also mixed or intercropping to ensure harvest even under adverse environmental conditions.
- Proper water management /better water use efficiency
- Adoption of adequate Plant protection measures/Integrated Pest Management
- Adoption of suitable management practices/intercultural operations
- Adoption of suitable method of harvesting of crops as well as suitable post-harvest technologies
👉🏻 Crop Production: The quantity of agricultural output (grain, pods, fruits, straw etc) produced form our applied inputs (seeds, fertilizers, labour etc).
👉🏻 Crop Productivity: Production of crop per unit area is known as crop productivity. It is expressed in quintle/ha or Kg/ha or tonnes/ha.
Factors Affecting Crop Production
External Factors
The following are the external factors that affect the crop production:
- Climatic
- Edaphic
- Biotic
- Physiographic
- Socio-economic
Climatic factors
- Temperature
- Relative Humidity (RH)
- Precipitation
- Solar Radiation
- Wind Velocity
- Atmospheric Gases
👉🏻 We will discuss about these factors in Agrometerology course…
Edaphic Factors:
These are the factors which are related to soil.
- Soil Moisture
- Soil Temperature
- Soil Organism
- Soil Organic Matter
- Soil Mineral matter
- Soil pH
- Soil Air
👉🏻 We will discuss about these factors in Soil Science course…
Biotic Factors
These are the factors having life.
- Flora: 🌼 Competitive and complementary (synergistic effect) nature among field crops when grown together.
- Fauna: 🐝 🪱 Honey bees and wasps help in cross pollination and increases yield and considered as beneficial organisms.
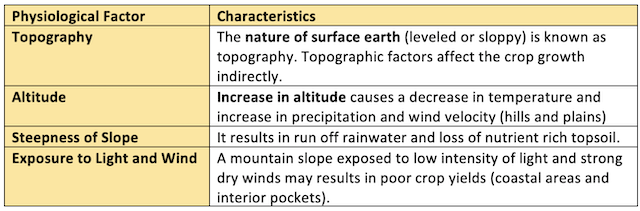
Physiographic Factor 🏔
Socio-Economic Factors 👨👩👧
Marginal, small, medium and large farmers.
👉🏻 We will discuss about these in detail in Extension and Economics courses…
Genetic Factors 🧬
These are those factors which affect plant growth and development involving genes, the chromosomes, the genomes, and all those which determine gene expression with the exclusion of environmental factors.
👉🏻 We will discuss about these in detail in genetics course…
What is Agronomy?
- It consists of two
Greekwords i.e., Agros means field, Nomos means to manage. - Agronomy is the science of manipulating the crop environment complex with dual aims of improving agricultural productivity and gaining a degree of understanding of the process involved.
- “Agronomy is the branch of agricultural science which deals with the principles and practices of crop production for obtaining maximum economic returns from a unit of area in a defined period without deteriorating the fertility status of soil”.
- Agronomy is considered as the mother or primary branch of agriculture. Like agriculture, it is nothing but an integrated and applied aspect of different discipline of pure sciences.
Pietro de’Crescenziis the father of Agronomy.
👉🏻 It has three distinct branches:
- Crop …
Become Successful With AgriDots
Learn the essential skills for getting a seat in the Exam with
🦄 You are a pro member!
Only use this page if purchasing a gift or enterprise account
Plan
- Unlimited access to PRO courses
- Quizzes with hand-picked meme prizes
- Invite to private Discord chat
- Free Sticker emailed
Lifetime
- All PRO-tier benefits
- Single payment, lifetime access
- 4,200 bonus xp points
- Next Level
T-shirt shipped worldwide

Yo! You just found a 20% discount using 👉 EASTEREGG

High-quality fitted cotton shirt produced by Next Level Apparel