🌡 Instruments
Instruments used in meterology, weather modification, important terms and isopleths.
Weather Modification
👉🏻 Weather modification refers to willful manipulation of the climate or local weather.
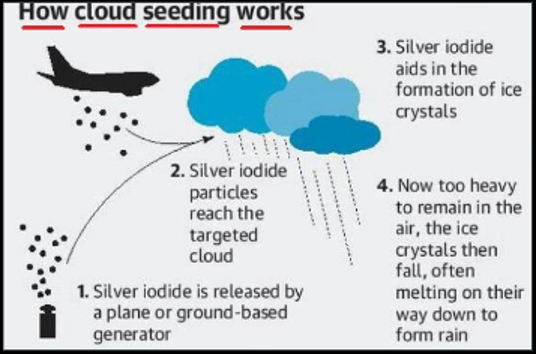
Cloud Seeding
- Exploding demand of water resources and continued population growth has given rise to the problem of water scarcity in many regions of our planet.
- To meet the demand of water resources scientist have started using weather modification commonly called as cloud seeding.
- Cloud seeding is a weather modification technique which involves the introduction of material into a cloud (using aircraft or ground-based generators) with a view to encouraging the formation and growth of ice crystals or raindrops and, in turn, enhancing the precipitation (snow and/or rain) falling from the cloud.
👉🏻 There are two basic types of cloud seeding - Cold and Warm:
- Cold cloud seeding (glaciogenic seeding) involves adding particles such as
silver iodide crystalsordry ice pelletsto the super-cooled (below freezing point) water already present in clouds to promote the formation of ice crystals. The ice crystals grow, fall and melt to below the freezing level to become raindrops. - Warm cloud seeding (hygroscopic seeding) involves adding
salt particles(sodium chlorides, magnesium chlorides and calcium chlorides), which attract water into or just below the base of suitable clouds to enhance the growth of cloud droplets by coalescence.
Important terminologies:
Growing degree days (GDD)
- Growing degree days (GDD) is a weather-based indicator for assessing crop development.
- It is a calculation used by crop producers that is a measure of heat accumulation used to predict plant and pest development rates such as the date that a crop reaches maturity.
- In the absence of extreme conditions such as drought or disease, plants grow in a cumulative stepwise manner which is strongly influenced by the ambient temperature.
- The Growing Degree Days calculation allows producers to predict the plants’ pace toward maturity.
- Daily growing degree day values are added together from the beginning of the season, providing an indication of the energy available for plant growth.
- Growing degree day totals are used for comparing the progress of a growing season to the long-term average and are useful for estimating crop development stages and maturity dates.
- Growing Degrees (GDs) is defined as the mean daily temperature (average of daily maximum and minimum temperatures) above a certain threshold base temperature accumulated on a daily basis over a period of time.
- Negative values are treated as zeros and ignored.
- The base temperature varies among crops and the value is derived from the growth habits of each specific crop.
- The base temperature is that temperature below which plant growth is zero. For example, cereal and forage crops show little growth or development when average temperatures are below 5°C.
GDD Calculation
- GDs are calculated each day as maximum temperature plus the minimum temperature divided by 2 (or the mean temperature), minus the base temperature.
- GDDs are accumulated by adding each day’s GDs contribution as the season progresses.
- If the average temperature is below the base temperature, the growing degree day value for that day is zero.
- GDD = (Tmax + Tmin)/2 - Tbase
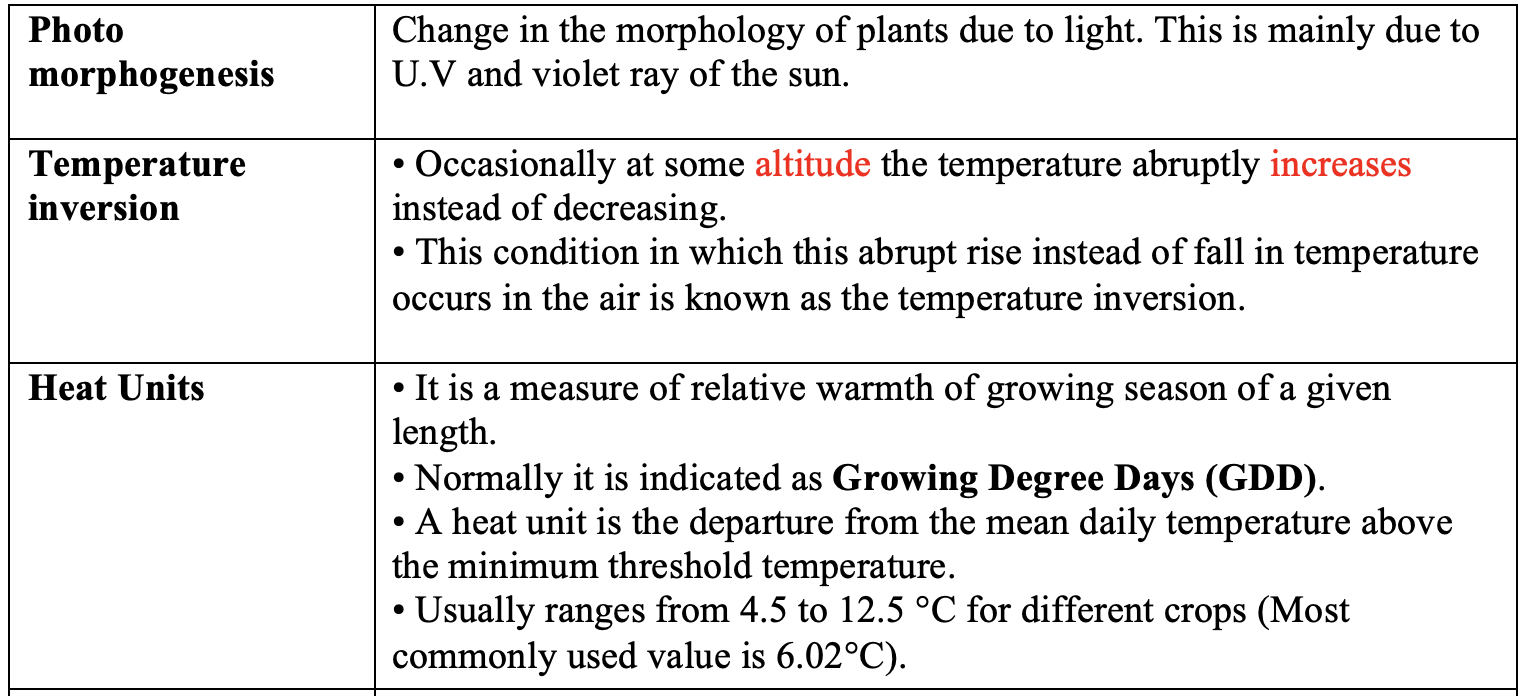
Thermal Death Point
- The temperature at which the plant cell gets killed when the temperature ranges from
50-60°C. - This varies with plant species.
- The aquatic and shade loving plants are killed at comparatively lower temperature (40°C).
Sun Clad
- Injury caused on the
barks of stemby high temperature during daytime and low temperature during the night time.
Stem Griddle
- The stem at ground level scorches around due to high soil temperature.
- It causes death of plant by destroying conductive tissue.
- Eg. This type of injury is very common in young seedlings of cotton in sandy soil when soil temperature exceeds 60°C.
Storm
- Low pressure centre surrounded by winds having their velocities in the range of
40 to 120 km/hour.
Hurricanes
- A severe tropical cyclone with wind speed
exceeding 120 km per hour. - The name hurricane is given to the tropical cyclones in the North Atlantic and the eastern North Pacific Ocean.
Tornadoes
- Defined as a violently rotating column of air attended by a funnel-shaped or tubular cloud extending downward from the base of
cumulonimbus cloud.
Chilling
- Plants which are adapted to hot climate, if exposed to low temperature for sometime, are found to be killed or severely injured or development of chloratic condition (yellowing) (eg.) cholratic bands on the leaves of sugarcane, sorghum and maize in winter months when the night temperature is below 20°C.
Freezing Injury
- A type of cold injury which is commonly observed in plants of temperate regions. When the plants are exposed to very low temperature, water freezes into
ice crystals in the intercellular spacesof plants. - The protoplasm of cell is dehydrated resulting in the death of cells. • (E.g.) Frost damage in potato, tea etc.
Suffocation
- In temperature regions, usually during the winter season, the ice or snow forms a thick cover on the soil surface.
- As a result, the entry of oxygen is prevented and crop suffers for want of oxygen.
Heaving
- This is a kind of injury caused by lifting up of the plants along with soil from its normal position.
- This type of injury is commonly seen in temperate regions.
- The presence of ice crystals increases the volume of soil.
- This causes mechanical lifting of the soil.
Oasis Effect
- The oasis effect refers to the creation of a
local microclimate that is coolerthan the surrounding dry area due to evaporation or evapotranspiration of a water source or plant life and higher albedo of plant life than bare ground. - It is the exchange of heat whereby air over crop is cooled to supply heat for evaporation.
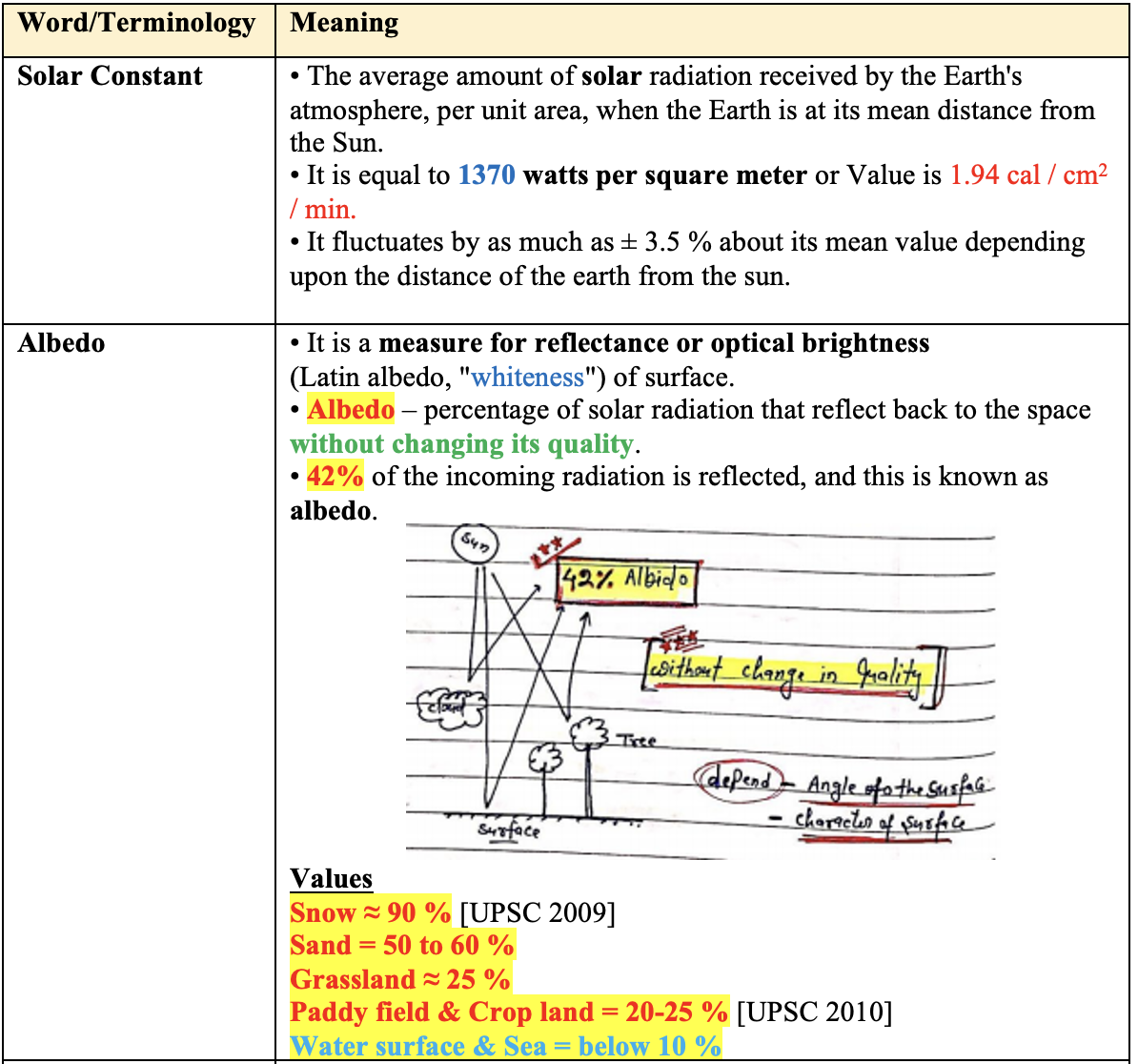
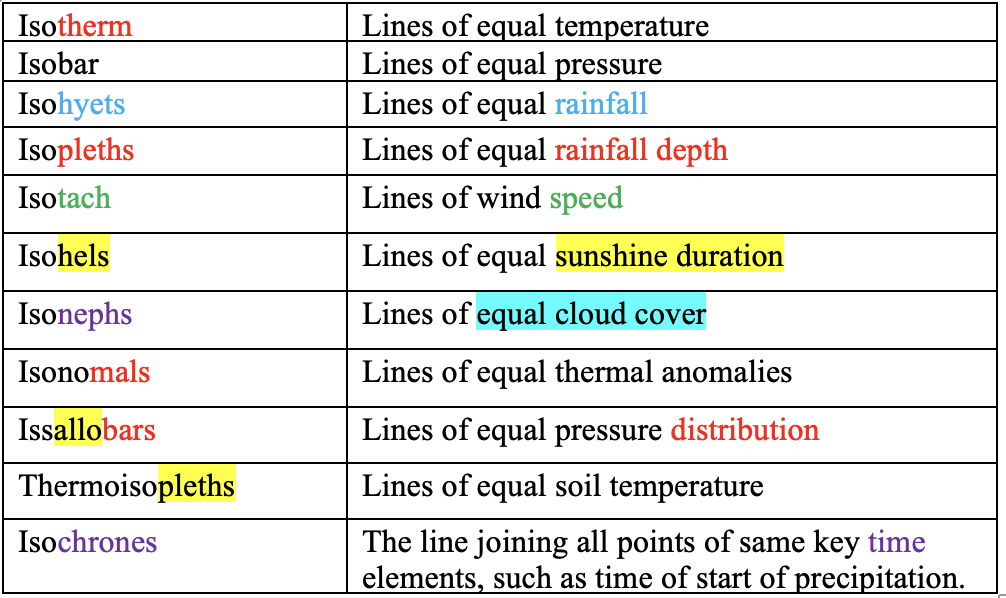
Isopleths for different Weather Parameters
👉🏻 Isopleth is a line on a map connecting points having equal incidence of a specified meteorological feature.
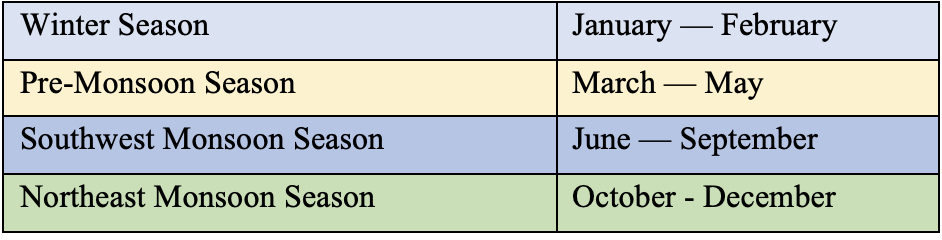
Seasons demarcated as per the Indian Meteorological Department
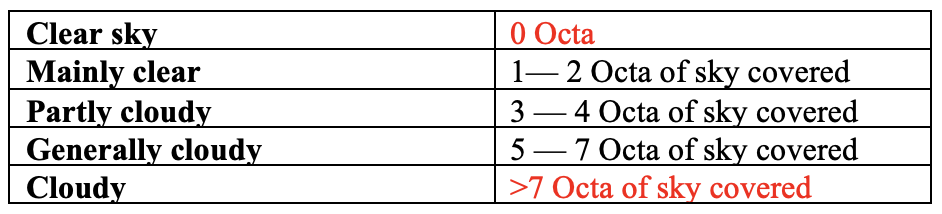
Sky Conditions:
Reported in terms of Octa wherein the sky is divided into 8 equal parts:
Instruments used in Meterology
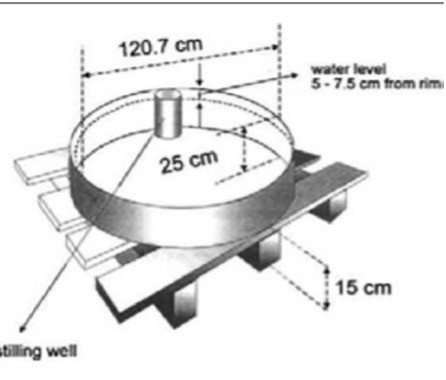
Evaporimeter

- Pan Evaporimeter: used for estimating
Evaporationunder field condition and scheduling of irrigation. - Portable Evaporimeter: developed in Israel, used to measure evaporation for short period.
Altimeter
👉🏻 It is used to measure - Height

Aneroid barometer
👉🏻 It is used to measure - Atmospheric Pressure

Barograph
👉🏻 It is used to measure - Continuous atmospheric pressure

Wind vane
👉🏻 It is used to measure - Wind direction
- Lee Ward: to which wind is flowing
- Wind Ward: from wind is coming

Anemometer
👉🏻 It is used to measure - Wind speed/velocity

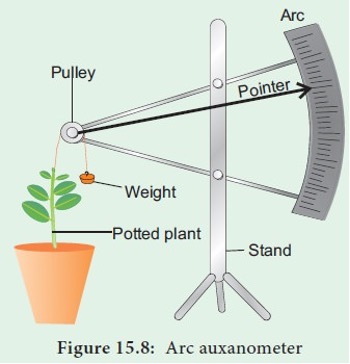
Auxanometer
👉🏻 It is used to measure - Growth of plant
Crescograph
👉🏻 It is used to measure - Growth of plant

Cryometer
👉🏻 It is used to measure - Measuring temp. below 0°C

Drosometer
👉🏻 It is used to measure - Dew
Hygrometer/Psychrometer
👉🏻 It is used to measure - Relative humidity (RH)

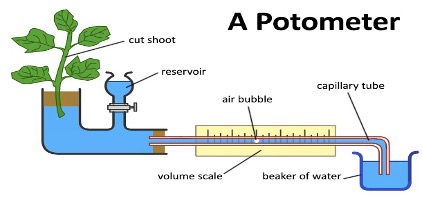
Potometer
👉🏻 It is used to measure - Transpiration
Lysimetre
👉🏻 It is used to measure - Evapotranspiration (ET)
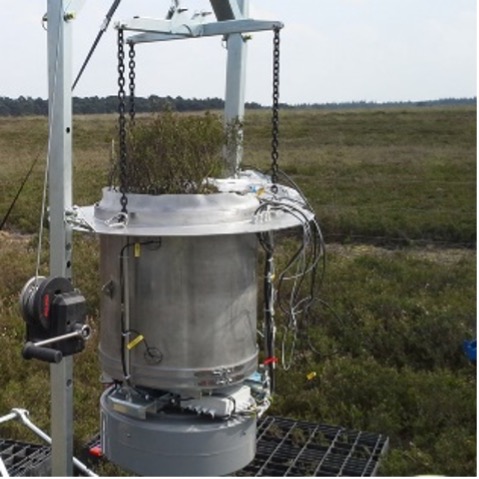

Atmometer
👉🏻 It is used to measure - Evapotranspiration (ET) rates of crops at any field location
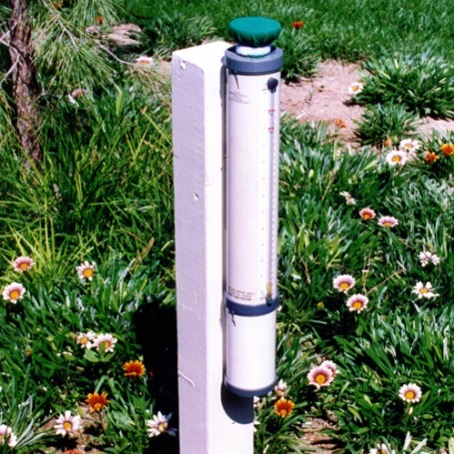

Hydrometer
👉🏻 It is used to measure - Relative density of liquids
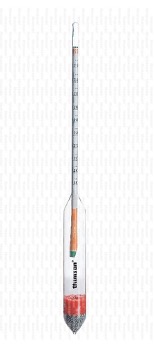
Lactometer
👉🏻 It is used to measure - Fat per cent in milk

Infra - Red thermometer
👉🏻 It is used to measure - Canopy temperature

Tensiometer
👉🏻 It is used to measure - Soil moisture tension (0.8 bar)

Infiltrometer
👉🏻 It is used to measure - Infiltration

Permeameter
👉🏻 It is used to measure - Hydraulic conductivity (HC)

Pycnometer
👉🏻 It is used to measure - Soil specific gravity

Cambel stokes recorder
👉🏻 It is used to measure - Sunshine duration

Heliograph
👉🏻 It is used to measure - Duration of bright sunshine hours

Pyranometer
👉🏻 It is used to measure - Total incoming solar radiation

Pyrheliometer
👉🏻 It is used to measure - Direct solar radiation

Pyradiometer
👉🏻 It is used to measure - Both long and short-wave radiation
Porometer
👉🏻 It is used to measure - Area of the stomatal openings

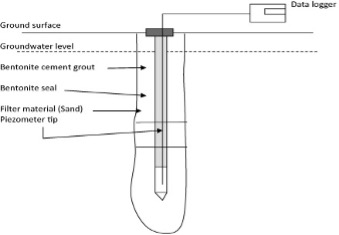
Peizometer
👉🏻 It is used to measure - Depth of water table, measuring hydrostatic pressure of ground water
Rain gauge
👉🏻 It is used to measure - Amount of rainfall

Pressure chamber/Thermocouple
👉🏻 It is used to measure - Leaf water potential
Pressure membrane apparatus
👉🏻 It is used to measure - Moisture Equivalents (ME)
Quantom Sensor
👉🏻 It is used to measure - PAR
Spectrophotometer
👉🏻 It is used to measure - Wavelength of light

Thermograph
👉🏻 It is used to measure - Continuous measuring temperature
Weather Modification
👉🏻 Weather modification refers to willful manipulation of the climate or local weather.

Cloud Seeding
- Exploding demand of water resources and continued population growth has given rise to the problem of water scarcity in many regions of our planet.
- To meet the demand of water resources scientist have started using weather modification commonly called as cloud seeding.
- Cloud seeding is a weather modification technique which involves the introduction of material into a cloud (using aircraft or ground-based generators) with a view to encouraging the formation and growth of ice crystals or raindrops and, in turn, enhancing the precipitation (snow and/or rain) falling from the cloud.
👉🏻 There are two basic types of cloud seeding - Cold and Warm:
- Cold cloud seeding …
Become Successful With AgriDots
Learn the essential skills for getting a seat in the Exam with
🦄 You are a pro member!
Only use this page if purchasing a gift or enterprise account
Plan
- Unlimited access to PRO courses
- Quizzes with hand-picked meme prizes
- Invite to private Discord chat
- Free Sticker emailed
Lifetime
- All PRO-tier benefits
- Single payment, lifetime access
- 4,200 bonus xp points
- Next Level
T-shirt shipped worldwide

Yo! You just found a 20% discount using 👉 EASTEREGG

High-quality fitted cotton shirt produced by Next Level Apparel