🌡 Weather Parameters
Parameters related to weather, clouds, precipitation, solar radition, latitude.
Weather Parameters
Atmospheric Pressure
- Atmospheric pressure is the weight of the carbon of air at any given place and time.
- It is measured by means of an instrument called
Aneroid Barometeras force per unit area. - The units used are millibars (mb). A pressure 1000 mb = weight of 1.053 kg.sq.cm.
- The pressure at sea level is 76 cm (1013.25 mb).
Wind
Horizontalmovement of air is calledWind. TheVerticalmovement of air is calledAir Current.- Wind movement for
4 – 6 km/houris suitable for most crops. - Winds of high speed are called
Squalls. - Due to horizontal difference in air pressure, air flows from the areas of high pressure to the areas of low pressure.
- Wind direction is determined with the help of a
Wind Vaneand the speed or velocity of the wind byRobinson's Cup Anemometer. - In the
Wind Vane, theheaddenotes the directionfrom which the air is blown, and thetaildenotes the direction to which the air blows.

- The two most significant winds for climate and human activities are the ‘trade winds’ and the ‘westerly winds’.
Trade Windsare the winds blowing from sub-tropical high-pressure areas (30 N and 30 S latitude) towards the equatorial low-pressure belts.Westerly Windsare the winds blowing from sub-tropical high-pressure areas towards the polar low-pressure belts. They blow from southwest to northeast in the Northern Hemisphere and from northwest to southeast in the Southern Hemisphere.Periodic Windsare the winds that reverse their direction periodically with season.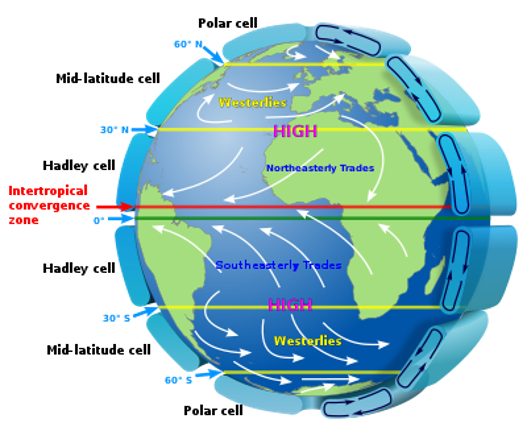
Temperature
- Temperature is the degree of hotness of a substance.
- High humidity and warm temperatures are conductive to most plant pest and diseases.
- The Principles of mercury barometer was discovered by
Torricelli. - Lowest temperature in a day is observed during just before sunshine, whereas highest temperature is after
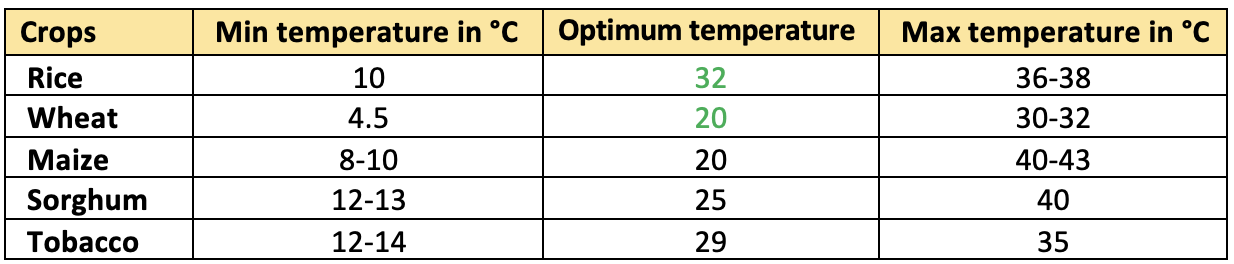
2 P.M.. - The range of temperature for maximum growth of most of the agricultural plants is
between 15 and 40°C. Cardinal temperatureis temperature range of maximum, optimum and minimum temperature of a crop for its optimum growth and development.
- Normal sea surface temperature is
23 °C. - Lapse rate —
temperature decreasealong with height (Vertically), expressed as LR. The normal lapse rate is6.5°C/kmor3.5°F/1000 feet. - Absolute zero is
-273°C.
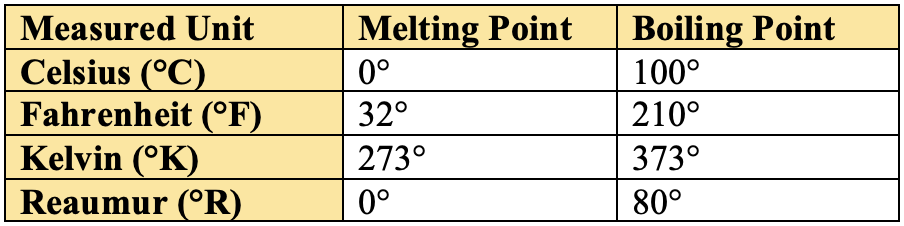
Melting and Boiling points of water
Relationship between: Celsius, Fahrenheit and Kelvin:
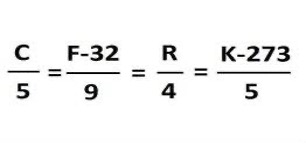
Humidity
- Relative humidity is ratio between the amounts of moisture presenting the air to the saturation capacity of the air at a particular temperature.

- Low relative humidity includes both more evaporation and transpiration.
- Relative humidity of
40 – 60%IBPS 2018 is suitable for most of the crop plants, whereas higher RH increases pest and disease incidence.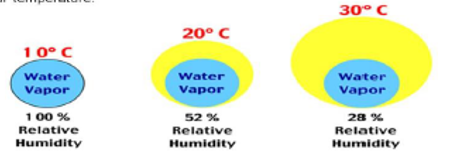
Clouds
- Cloud can be defined as a mass of tiny water droplets ice crystals or both condensed on hygroscopic nuclei and suspending in the atmosphere.
- Forms of Clouds (
10): Cirrus, Cirro-cumulus, Cirro-stratus, Alto-stratus, Alto-cumulus, Stratus, Nimbo-stratus, Strato-cumulus, Cumulus, Cumulo-nimbus
Classification of Clouds
- The World Meteorological Organization (WMO) is an intergovernmental organization with a membership of 191 Member States and Territories.
- It originated from the International Meteorological Organization (IMO), which was founded in 1873.
- Established by the ratification of the WMO Convention on
23 March 1950, WMO became the specialized agency of the United Nations for meteorology (weather and climate), operational hydrology and related geophysical sciences a year later. - It’s foundation day is celebrated as World Meterological Day on
23rd Marcheach year. - The Secretariat, headquartered in
Geneva, is headed by the Secretary-General. Its supreme body is the World Meteorological Congress.
👉🏻 Classification of Clouds by The World Meteorological Organization
- The World Meteorological Organization (WMO) comes out with this classification in
The International Cloud Atlas. - The table given below gives a list of approximate heights of each level and the genera occurring in each:
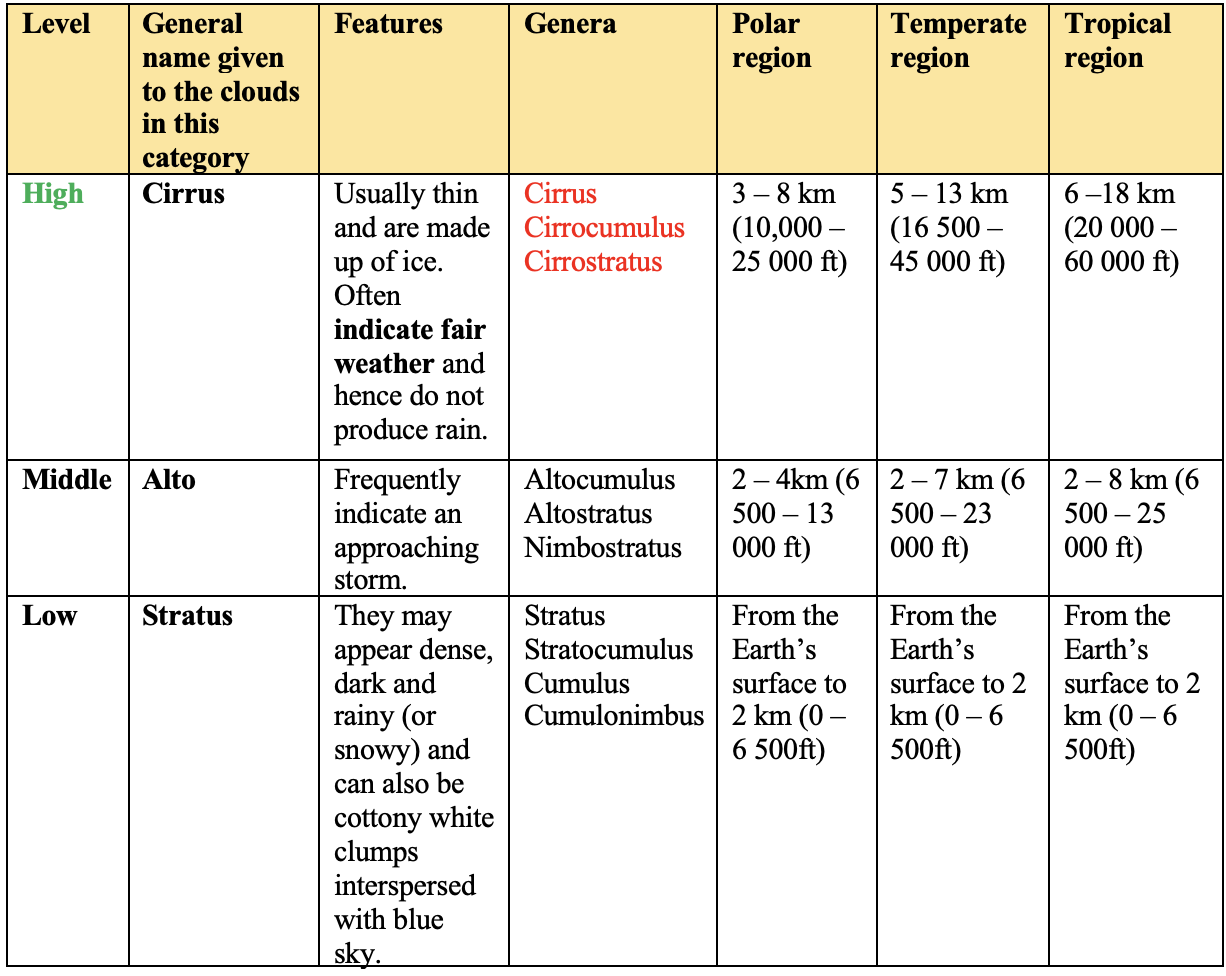
-
There is another category which is known as
Great Vertical Extent Clouds. The GeneraCumulusandCumulonimbuscan be placed under it. Hails occurs in Cumulonimbus clouds. -
These clouds are most dramatic types of clouds. They are also known as the
Storm Clouds. They rise to dramatic heights, and sometimes well above the level of transcontinental jetliner flights. -
The word ’nimbus’ is derived from Latin meaning rainstorm or cloud. Nimbus clouds are clouds that produce precipitation that reach the ground in the form of rain, snow and hail.
-
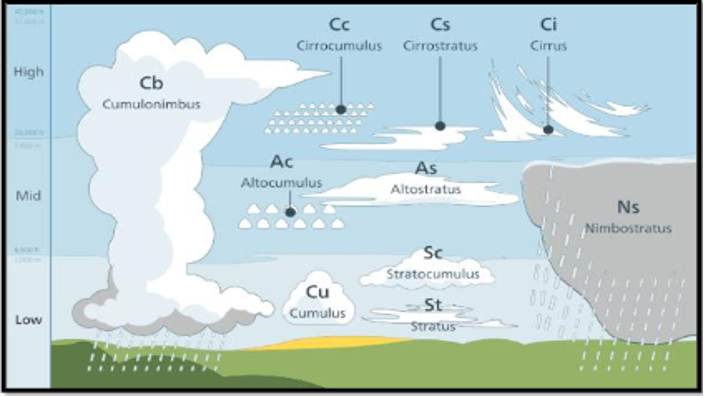
Altostratus is usually found in the middle level, but it often extends higher.
-
Nimbostratus is almost always found in the middle level, but it usually extends into the other two levels.
-
Fibrous cloud:
Cirrus
-
Occurrence at low height:
Cumulus -
Occasional drizzling:
Stratus -
Cloud associated with heavy rainfall:
Nimbostratus -
Good RF at high latitude:
Alto-stratus
- Size of Cloud droplets – 20 µm (dia.)
- Size of Rain droplets – 2 mm (dia.)
Precipitation
- In heavy and evenly distributed rainfall areas, crops like rice in plains and tea, coffee and rubber in Western Ghats are grown.
- Low and uneven distribution of rainfall is common in dry-land farming where drought resistance crops like pearl millet, sorghum and minor millets are grown.
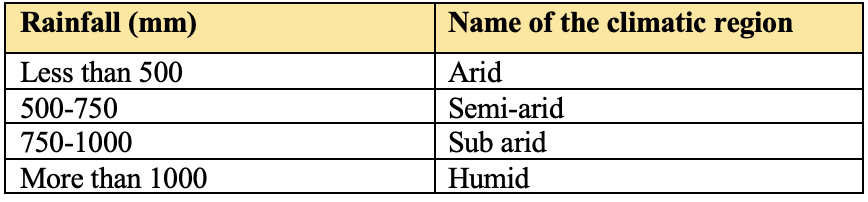
The crop regions are classified on the basis of average rainfall which is as follows.
Southwest Monsoon (SW)
- Covers
75 per cent rainfall, about300 m-hastarts in1st Junein extreme south of India (Kerala), at the end of the June it spreads to entire country and last at 31st Sept.
North East monsoon (NE)
- Starts at
Nov 15and last atDec(25 per cent RF) covers about100 mha.
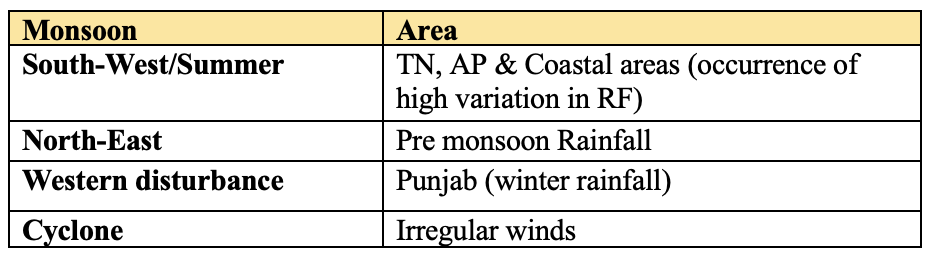
👉🏻 El Nino: Phenomena of Warming of Eastern Pacific.
👉🏻 La Nino: Phenomena of Cooling of Eastern Pacific.
In forecasting of Rainfall
- The word ‘isolated rain’ denotes
1/3 areareceives rain. - The word ‘scattered rain’ denotes
2/3 areareceives rain. -Rainy Day: If the rainfall receivedmore than 2.5mmin24 hours, it is called rainy day.
Types of Precipitation:


Forms of Condensation


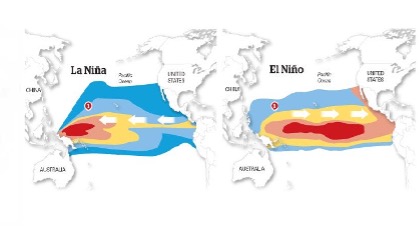
Solar Radiation
- Photoperiodism is a response of plant to day length.
- Photosynthetically Active Radiation (
PAR - 0.4 – 0.7μ) is essential for production of carbohydrates and ultimately biomass. - Short day – Day length is <12 hours (Rice)
- Long day – Day length is >12 hours (Barley, oat, radish, sugar beet, carrot and cabbage)
- Day neutral – There is no or less influence on day length (Tomato, Maize).
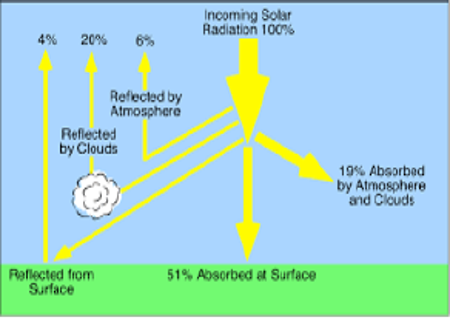
Latitude
- The distance from the equator, either south or north, largely creates variations in the Climate.
- Based on the latitude, the climate has been classified as:
- Tropical
- Sub-tropical
- Temperate
- Polar
Tropical Zone
- In the regions between the equator and the tropics (equatorial region), the solar radiation reaches the ground nearly vertically at noontime during almost the entire year.
- Thereby, it is very warm in these regions.
- Through high temperatures, more water evaporates, and the air is often moist.
- The resulting frequent and dense cloud cover reduces the effect of solar radiation on ground temperature.
Sub-Tropics (23.5° to 40°)
- The subtropics receive the highest radiation in summer, since the Sun’s angle at noon is almost vertical to the Earth, whilst the cloud cover is relatively thin.
- These regions receive less moisture which increases the effect of radiation. Therefore,
most of the desertsin the world are situated in this zone. - In winter, the radiation in these regions decreases significantly, and it can temporarily be very cool and moist.
Temperate Zone (40° to 65.5°)
- In the temperate zone, the solar radiation arrives with a smaller angle, and the average temperatures here are much cooler than in the subtropics.
- The seasons and day length differ significantly in the course of a year.
- The climate is characterized by less frequent extremes (
mild temperatures), a more regular distribution of the precipitation over the year and a longer vegetation period - therefore the name “temperate”.
Polar Zones
- The polar areas between 60° latitude and the poles receive less heat through solar radiation, since the Sun has a very flat angle toward the ground.
- Because of the changes of the Earth axis angle to the Sun, the day length varies most in this zone.
- In the summer, polar days occur.
- Vegetation is only possible during a few months per year and even then, is often sparse.
- The conditions for life in these regions are very hard.
Altitude:
- The
height from the MSL(Mean Sea Level) creates variation in climate. - Even in the tropical regions, the high mountains have temperate climate.
- The temperature decreases by 6.5 ºC/Km from the sea level.
Explore More 🔭
Weather Parameters
Atmospheric Pressure
- Atmospheric pressure is the weight of the carbon of air at any given place and time.
- It is measured by means of an instrument called
Aneroid Barometeras force per unit area. - The units used are millibars (mb). A pressure 1000 mb = weight of 1.053 kg.sq.cm.
- The pressure at sea level is 76 cm (1013.25 mb).
Wind
Horizontalmovement of air is calledWind. TheVerticalmovement of air is calledAir Current.- Wind movement for
4 – 6 km/houris suitable for most crops. - Winds of high speed are called
Squalls. - Due to horizontal difference in air pressure, air flows from the areas of high pressure to the areas of low pressure.
- Wind direction is determined with the help of a
Wind Vaneand the speed or velocity of the wind byRobinson's Cup Anemometer. - In the …
Become Successful With AgriDots
Learn the essential skills for getting a seat in the Exam with
🦄 You are a pro member!
Only use this page if purchasing a gift or enterprise account
Plan
- Unlimited access to PRO courses
- Quizzes with hand-picked meme prizes
- Invite to private Discord chat
- Free Sticker emailed
Lifetime
- All PRO-tier benefits
- Single payment, lifetime access
- 4,200 bonus xp points
- Next Level
T-shirt shipped worldwide

Yo! You just found a 20% discount using 👉 EASTEREGG

High-quality fitted cotton shirt produced by Next Level Apparel