👶 Animal Husbandry
Basic Concepts and Significance of Animal Husbandry
Select the odd statement from the following?
The branch of science, which deals with the study of various breeds of domesticated animals and their management for obtaining better products and services from them, is known as Animal Husbandry.
- The term husbandry derives from the word “husband” which means ‘one who takes care’. When it incorporates the study of proper utilisation of economically important domestic animals, it is called Livestock Management.
- Domesticated: Those that are of use at home and are easily bred and looked after by humans. Common domesticated animals are dog, horse, cow, sheep, buffalo, fowl etc.
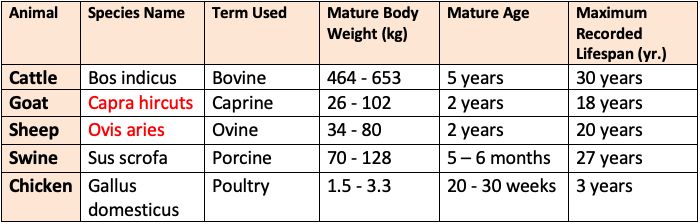
Mature Body Weight and Ages of Different Species
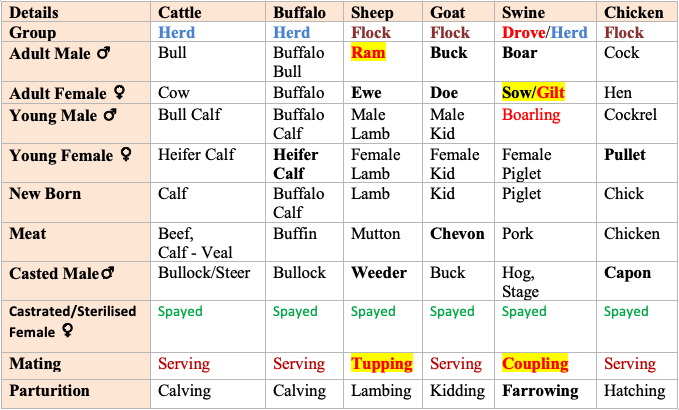
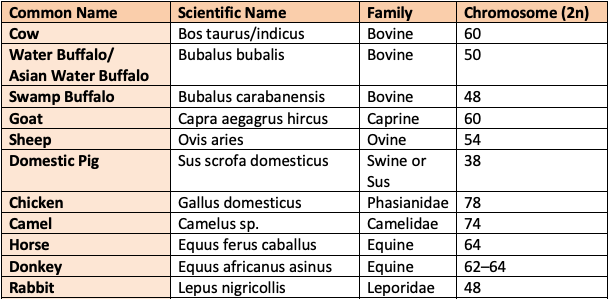
Common Names in Livestock Population
Body temperature & gestation period of domesticated animals
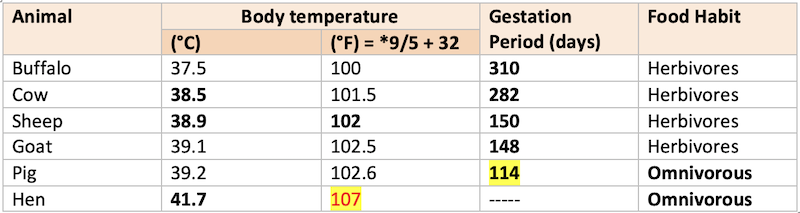
- Smaller the animal more is heat required to maintain the body metabolism.
- Body temperature may vary +1/-1 °C.
Significance of livestock and poultry in Indian economy
- Agricultural is the back bone of Indian Economy and within agriculture, livestock plays an importance role in providing sustainable income to farmers throughout the year.
- Livestock farming is an integral part of crop farming and contributes substantially to household nutritional security and poverty alleviation through increased household income.
- Dairy animals produce milk by converting the crop residues and by products from crops which otherwise would be wasted. Dairy sector contributes by way of cash income, draught power and manure. Livestock provides for human needs by way of
- Food
- Fibre
- Fuel
- Fertilizer
- Skin
- Traction
- It is a living bank providing flexible finance in time of emergencies and also serves as insurance against crop failure for survival. If Agriculture is the foundation of our national economy, Animal husbandry constitutes the sheet anchor of agriculture. Family income from livestock and poultry acts as Bankers cheque.
- Effective utilization of labour – family labour is effectively utilized in animal husbandry.
- Soil fertility: organic manure – promotes and maintain soil fertility.
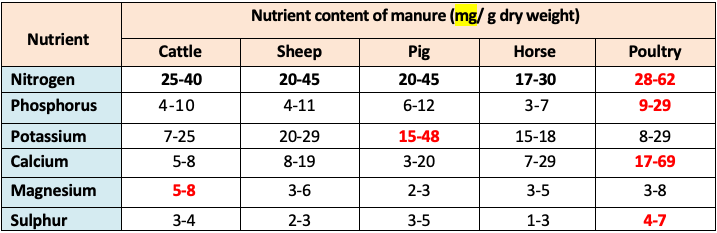
👉🏻 Poultry manure has highest nutrient but less used because release nutrients very fast. So, do not provide nutrients to plants for longer time.
- Apart from manurial value biogas can be produced from livestock dung and poultry droppings.
- Cow produces 8 tonnes of farm yard manure per year and farm biomass and farm products which includes fodder, feed, edible weed, tree fodder, bund grass are better utilized – and converted to Edible products like – Milk, Meat and Egg. .
- Inter relationship
- Man-animal-plant interrelation is interdependent (one cannot survive without the help of other). Man not only depends on plants and animals for food but also for income and other needs.
- He co-ordinates activities of the crop and other husbandry by proper planning.
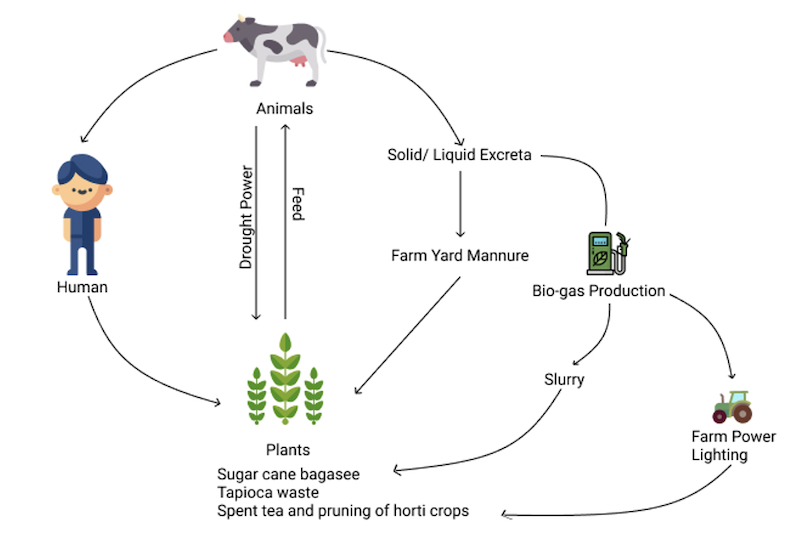
- The usage of draught animal power for ploughing of land.
- India owns nearly
15 %of the world livestock population, which is highest in the world with population of 535 million. 70 %of the livestock are owned by 67 % of small and marginal farmers.- 76 % of the milk is produced by weaker sections of society.
- India has nearly
57 %of the world’s buffalo population (first rank),16 %of the cattle population (second rank),20 %of goat population (second rank) and5 %of sheep population (third rank) although India constitutes2.4 %of the world’s total land area. - The contribution of livestock sector to the total Gross value added (GVA) was
4.90%in 2020-21, accounting for30.13 %of total GVA of Agricultural and Allied Sector. - During 2014-15 and 2020-21, the value addition of sector grew at a compound annual growth rate of
7.93%. - It is estimated that about 18 million people are employed in the livestock sector in principle or subsidiary status. Export earnings from livestock sector and related products are progressively rising.
Problems
- Though the cattle wealth is quite abundant in terms of population the production from these animals is very poor viz., 987 kgs per lactation whereas the world average is 2038 kgs per lactation.
- The main reasons for this shortcoming are the abundant population of nondescript cows, chronic shortage of feed and fodder, poor nutritive value of the available feed and fodder, low fertility rates, destruction of grazing land, increasing human population and competition between animals and man for the available feed resources.
Solutions
- To satisfy the nutrient requirement for the huge population of livestock the options are:
- To reduce the unproductive/ low productive animals.
- Feeding of non-conventional feed stuffs – among these are the horticultural by products like agriculture by products, vegetable wastes and horticulture industrial wastes.
References
- G.C. Banerjee: A Textbook of Animal Husbandry
- Wikipedia