🏥 Disease Management
Common Cattle Diseases and their control measures, Vaccination Schedule
Which of the following statment is not wrong?
- The Condition in which all the organs and tissues in the system functions normally and harmoniously.
- Any change from normal state either to single or great extent is called disease stage. Health is fundamental for a sound enterprise.
- Most of the disease can be avoided by proper attention, sanitation, hygiene, nutrition and management practices.
- Once outbreak of disease complicated – strain – financial loss – dual – production expenditure on medicines.
- So the farmer – vigilant – day to day activities- to avoid or prevent spreading of disease and to have a check on financial loss.
General Precautions
- Strict hygiene and sanitation of animal houses.
- Adhere regular and routine ‘vaccination’ schedule
- Provide well ventilated and proper housing.
- Provide balanced nutritious diet.
- Avoid entry of outsiders within the farm-premises.
- Prevention is better than cure.
- Quarantine.
- Follow up of latest scientific know how and management practices.
Bacterial
Anthrax

- Anthrax is caused by Bacillus anthracis, a bacteria found in the environment in soil.
Symptoms:
- An abrupt fever and a period of excitement followed by depression, respiratory or cardiac distress, staggering, convulsions, and death.
- Peracute - death occurs within minutes.
- High temperature and splen is enlarged 10-15 times its normal size. Therefore also known as
Splenic fever. - Convolutions and collapsing before death.
- Often blood does not clot after death resulting in
bloody dischargefrom anybody openings (rectum, mouth, nostrils, etc.) - Often, the course of disease is so rapid that illness is not observed and animals are found dead,
sudden death. - Humans are also susceptible to this disease. Therefore also known as Wool sorters’ Disease or Ragpickers’ Disease.
- The transmission of disease from animal to human is known as
Zoonosis.
Control:
- Annual vaccination: A live spore vaccine prepared from a virulent uncapsulated strain of B. anthracis dose 1 ml.
- Hygiene and sanitation for prevention and Careful disposal of infected material is most important.
👨🏻🎓 Also Watch: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=AYBleZZmmHo
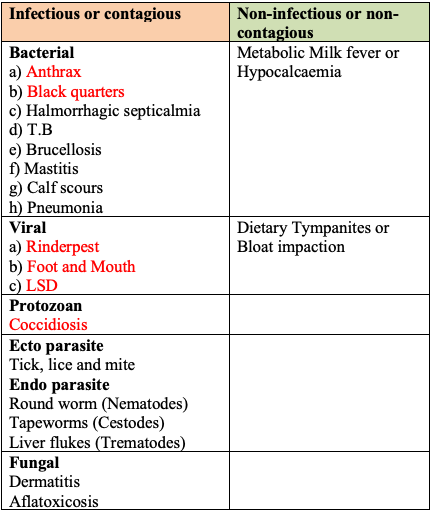
Haemorrhagic Septicaemia (HS)
- HS is bacterial disease spread by Pasteurella multocida bacteria.
- Fever with high temperature usually occurs during monsoon.
- Difficult breathing, Salivation and serious nasal discharge.
- Watery faeces dehydration, prostration (lying) and death.
- Vaccination once 1 year - before - rainy season.
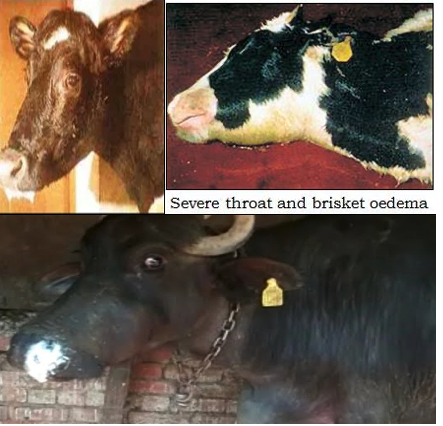
Black Quarter (BQ)
- The characteristic crepitant swellings in hind and fore quarters muscles which
crackleswhen rubbed due to gas accumulation in the muscle and which causes lameness. - When pressed, a crackling sound is heard because of the gas accumulation in the swellings.
Brucellosis (Contagious Abortion)

Abortionof pregnant animal.- 30 to 60 days incubation period.
Mastitis
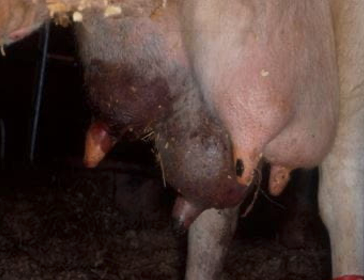
- Mastitis causes a persistant inflammation of the udders.
- The clear sign of mastitis is inflammation of the udder that turns into a red and hard mass.
👨🏻🎓 Also Watch: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=HBFMfbMPl3s
Calf Scours

- Watery stools that may be brown, grey, green, yellow in colour.
- Calves are often weak and depressed, and may lose their desire to nurse.
- Calves develop a sunken-eyed appearance as a result of dehydration
Bovine Tuberculosis (bTB)
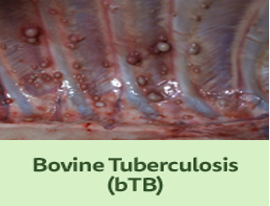
- Tuberculosis is caused by Mycobacterium bovis.
- Dry cough followed by wet cough is the major symptom.
Viral
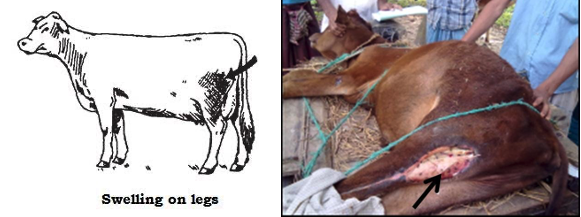
Foot and Mouth Disease (FMD)
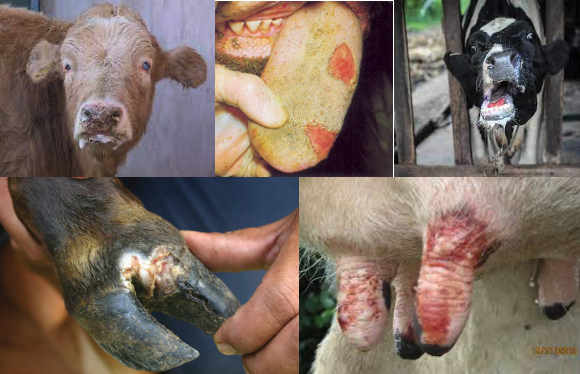
- Symptoms:
- A severe, highly contagious viral disease of livestock that has a significant economic impact.
- Incubation period is 6-7 days.
- High fever up to 104-106°F (41°C) and anorexia.
- Profuse salivation (saliva hanging in long ropy strings up to the ground).
- Animal stamps its feet and wounds in the interdigital space of legs followed by lameness.
- Oral ulcers and lesions.
- Smacking of lips.
- Vesicles in the mammary gland.
- Treatment:
- No treatment but it can be controlled.
- External application of anti septics contributes to the healing of ulcers and wards off attracts by flies.
- Antibiotics may be administered to counter bacterial infections.
- Prevention can be done thorough disinfection of shed, utensils, clothes of attendants.
- Vaccine: FMD vaccines is given at an interval of
6-months.
👨🏻🎓 Also Watch: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=My3fzEgiBRw
Rinderpest
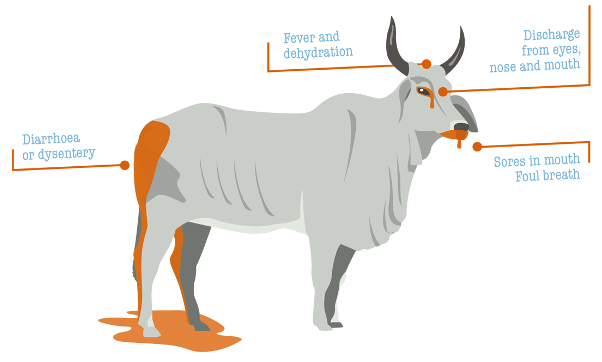
- Rinderpest is most destructive of the
virus disease. - Infected animals suffered from symptoms such as fever, wounds in the mouth, diarrhoea, discharge from the nose and eyes, and eventually death.
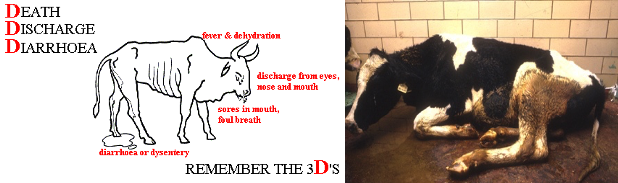
- 3 Ds of Rinderpest
- Diarrhoea
- Discharge
- Death
- Prevention and Control
- Segregation of affected animal.
- Disinfection of shed.
- Vaccine: TCRV (Tissue Culture Rinderpest Vaccine), GTV (Goat Tissue Vaccine)
- Vaccine for Rinderpest was formulated by
IVRI. - Test to identify: ELISA (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay)
Lumpy Skin Disease
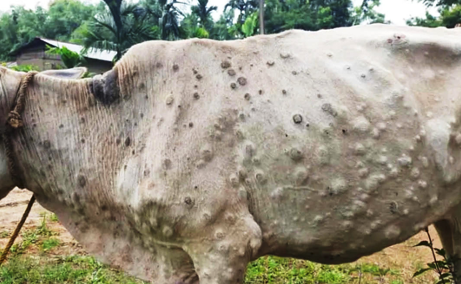
- Lumpy skin disease is caused by the lumpy skin disease virus (LSDV), a member of the Capripoxvirus (CaPV).
- Usually, high milk-producing, thin-skinned European cattle breeds are more susceptible to the disease compared to indigenous breeds.
- The characteristic symptom is nodules develop on the skin, nasal discharge and high fever.
- Vaccine:
Lumpi-Pro VacInd– jointly developed by NRC Equines at Hisar, Haryana and the IVRI, Izatnagar, UP — is a live attenuated vaccine.
Bluetongue Disease

- Insect-borne,
viral disease. - It is a non-contagious disease which is spread by biting insects.
Protozoan
Surra (Trypanosomiasis)
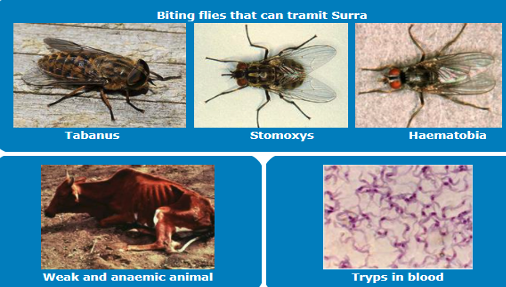
- An important disease of cattle and buffalo caused by protozoa.
- Transmitted mechanically by biting flies.
- Cattle and buffalo also are reservoir hosts to horses and camels.
- There is severe loss of productivity due to anaemia.
- Animals under stress are more susceptible to the disease.
- The incubation period after infection is approximately
5 to 30 days.
Metabolic Disorders
Partutient paresis (Milk Fever)
- Partutient paresis is a metabolic disease in cows occurs soon after calving caused due to
fall in calcium levels(Hypocalcaemia). There is actually no fever. - Occurs usually within 72 hours of calving.
- Complete milking during the first 48 hours of calving may precipitate milk fever in some cases.
- To avoid this do not fully empty the uder after calving.
Ketosis/ Acetonemia
- Disturbance in
carbohydratemetabolism.
Bloat (tympany)
- Characterised by an accumulation of gas in the stomach.
- Disorder of ruminant animals involving distention of the rumen.
- Sevear bloat is removed by
Trocar cannula.
Degnala disease
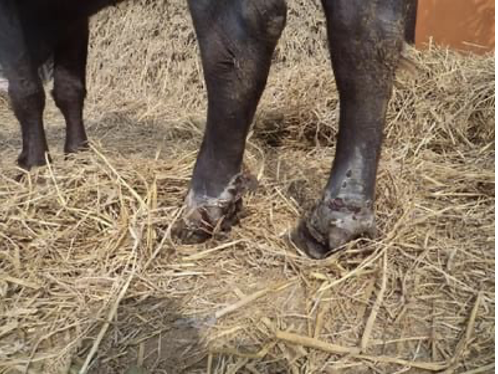
- It is a common infection, affecting cattle & buffaloes in Indian subcontinent.
- This is due to deficiency of
Selenium. - It occurs in animal, when they are exclusively feed on paddy straw get wet during the maturing stage on plant in field or during threshing period & stored without proper drying.
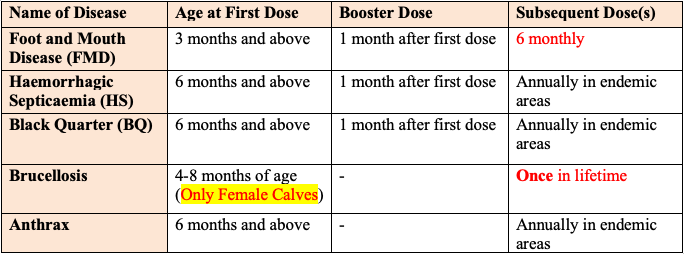
Vaccination for Cattles
References
- G.C. Banerjee: A Textbook of Animal Husbandry
- https://www.dairyknowledge.in
- https://buffalopedianew.cirb.res.in/godavari/
- https://nbagr.icar.gov.in/
- https://www.nddb.coop/
- Wikipedia
Which of the following statment is not wrong?
- The Condition in which all the organs and tissues in the system functions normally and harmoniously.
- Any change from normal state either to single or great extent is called disease stage. Health is fundamental for a sound enterprise.
- Most of the disease can be avoided by proper attention, sanitation, hygiene, nutrition and management practices.
- Once outbreak of disease complicated – strain – financial loss – dual – production expenditure on medicines.
- So the farmer – vigilant – day to day activities- to avoid or prevent spreading of disease and to have a check on financial loss.
General Precautions
- Strict hygiene and sanitation of animal houses.
- Adhere regular and routine ‘vaccination’ schedule
- Provide well ventilated and proper housing. …
Become Successful With AgriDots
Learn the essential skills for getting a seat in the Exam with
🦄 You are a pro member!
Only use this page if purchasing a gift or enterprise account
Plan
Rs
- Unlimited access to PRO courses
- Quizzes with hand-picked meme prizes
- Invite to private Discord chat
- Free Sticker emailed
Lifetime
Rs
1,499
once
- All PRO-tier benefits
- Single payment, lifetime access
- 4,200 bonus xp points
- Next Level
T-shirt shipped worldwide

Yo! You just found a 20% discount using 👉 EASTEREGG

High-quality fitted cotton shirt produced by Next Level Apparel