🥅 Housing Management
Site selection for Dairy shed, Loose and Conventional Housing of Dairy animals
Which of the following statment is not correct?
- An efficient housing of cattle requires a well-planned and adequate housing of cattle. Improper planning in the arrangement of animal housing may results in additional labour charges and curtail the profit of the owner.
- So during erection of a house for dairy cattle, following points should be considered:
- Topography & drainage: A dairy building should be on higher elevation than the surrounding ground to offer a good slope for rainfall & drainage for rainfall & drainage for the wastes of the dairy to avoid stagnation within.
- Soil type: Foundation soil should not be too hydrated or desiccated. Because such soils are susceptible to considerable swelling during rainy season and exhibit numerous cracks and fissures.
- Exposure to sun and protection from wind: As far as possible, the long axis of the dairy barns should be in north-south direction to have maximum benefit of the sun. Protection from cold & hot weather. Direction of Cow Shed: North-South (to get maximum sun-light)
- Accessibility: Easy accessible. Situation of the cattle shed by the side of the main road preferably at a distance 100 meters should be aimed.
- Water supply: Abundant, fresh, clean, soft water.
- Thermo-neutral Zone: The range of temperatures of the immediate environment in which a cattle maintain normal body temperature without needing to use energy above and beyond normal basal metabolic rate.
- Labour: Honest, economic, regular supply
- Marketing: Dairy should be at a place from where the owner can sell his products profitably and regularly.
- Electricity: Adequate supply for electric equipment in the dairy.
- Miscellaneous factors: Area should not be infested with diseases, wild animal, dacoits etc.
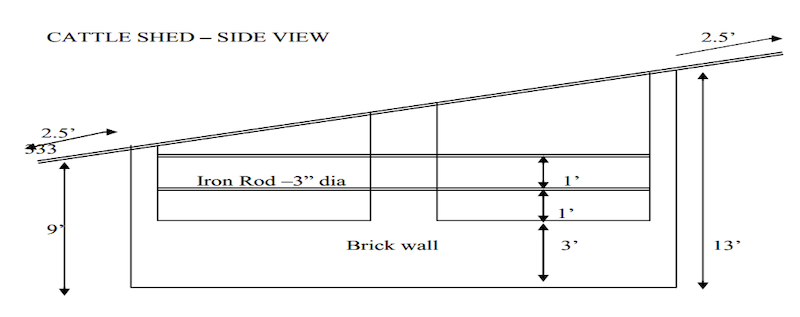
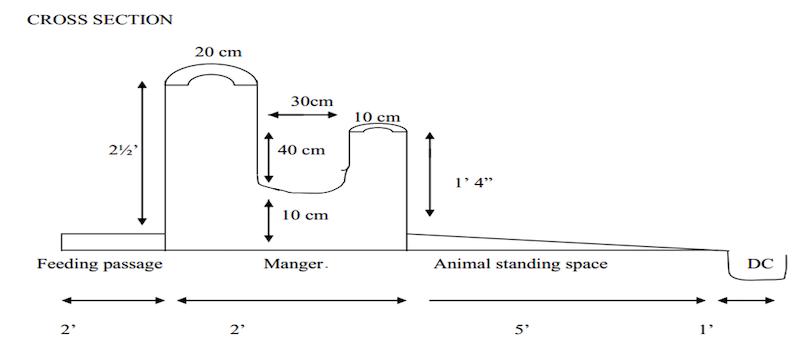
Floor space requirement per animal (ICAR)
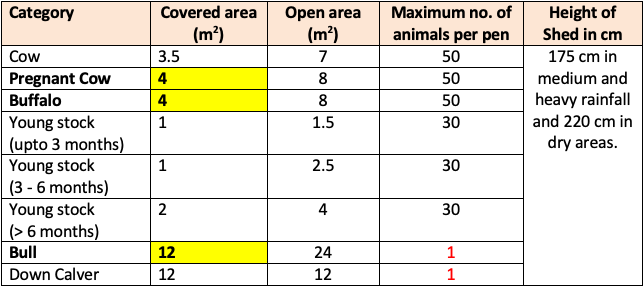
- Down Calver: Some time before calving
- For square feet → multiply the area value by 10.76
- As Murrah buffalo is large in size require
50 sq. feet.
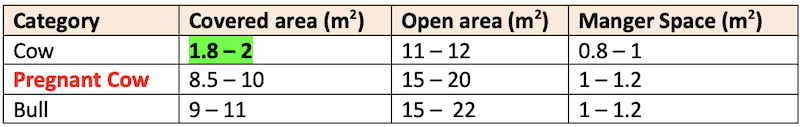
🤯 If specially mentioned according to NABARD norms for cross-breed cattle:
Types of Housing
👉🏻 There are two types of dairy barns in general use at present time:
Loose Housing System

- Loose housing may be defined as a system where animals are kept loose except milking and at the time of treatment. The system is most economical.
- Some features of loose housing system are as follows:
- Cost of construction is significantly lower than conventional type.
- It is possible to make further expansion without much changes
- Facilitate easy detection of animals in heat
- Animals feel free and therefore, prove more profitable with even minimum grazing.
- Animals get optimum exercise which is extremely important for better health and production
- Overall better management can be rendered.
Conventional System
- The conventional dairy barns are comparatively costly and are now becoming less popular day by day. However, by this system cattle are more protected from adverse climatic conditions.
- The following barns are generally needed for proper housing of different classes of dairy-stocks on the farm.
Cow Sheds
- Cow sheds can be arranged in a single row if the numbers of cows are small (
less than 15) or in a double row if the herd is a large one (more than 15). - Ordinarily, not more than 80 to 100 cows should be placed in one building.
- In double row housing, the stable should be so arranged that the cows face out (tails to tail system) or face in (head to head system) as preferred.
Tail to Tail System

Advantages of tail to tail system
- In cleaning and milking the cows, the wide middle alley is of great advantage.
- Lesser danger of spread of diseases from animal to animal.
- Cows can always get more fresh air from outside.
- The head gowala can inspect a greater number of milkmen while milking. This is possible because milkmen will be milking on both sides of the gowala.
- Any sort of minor disease or any change in the hind quarters of the animals can be detected quickly and even automatically.
Disadvantages of tail to tail system
- Spreading of diseases through digestive and reproductive system is high.
- Drainage channel is not exposed to sunlight.
- Feeding of animals is laborious.
Head to Head System
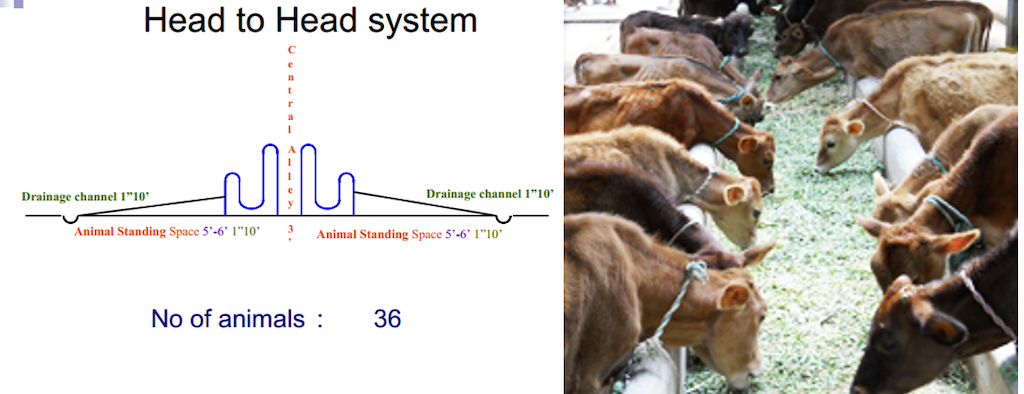
Advantages of Head to Head system
- Cows make a better showing for visitors when heads are together.
- The cows feel easier to get into their stalls.
- Sun rays shine in the gutter where they are needed most.
- Feeding of cows is easier, both rows can be fed without back tracking.
- It is better for narrow barns.
Disadvantages of tail to tail system
- All animals don’t get fresh air.
- Spreading diseases through respiratory system is maximum.
- Supervision of animals is not easy
- Cleaning is not easy
Insurance
- Always have a insurance for your animals.
- Generally the insurance premium is
5% of animal cost.
References
- G.C. Banerjee: A Textbook of Animal Husbandry
- https://www.dairyknowledge.in
- https://buffalopedianew.cirb.res.in/godavari/
- https://nbagr.icar.gov.in/
- https://www.nddb.coop/
- Wikipedia
Which of the following statment is not correct?
- An efficient housing of cattle requires a well-planned and adequate housing of cattle. Improper planning in the arrangement of animal housing may results in additional labour charges and curtail the profit of the owner.
- So during erection of a house for dairy cattle, following points should be considered:
- Topography & drainage: A dairy building should be on higher elevation than the surrounding ground to offer a good slope for rainfall & drainage for rainfall & drainage for the wastes of the dairy to avoid stagnation within.
- Soil type: Foundation soil should not be too hydrated or desiccated. Because such soils are susceptible to considerable swelling during rainy season and exhibit numerous cracks and fissures.
- Exposure to …
Become Successful With AgriDots
Learn the essential skills for getting a seat in the Exam with
🦄 You are a pro member!
Only use this page if purchasing a gift or enterprise account
Plan
Rs
- Unlimited access to PRO courses
- Quizzes with hand-picked meme prizes
- Invite to private Discord chat
- Free Sticker emailed
Lifetime
Rs
1,499
once
- All PRO-tier benefits
- Single payment, lifetime access
- 4,200 bonus xp points
- Next Level
T-shirt shipped worldwide

Yo! You just found a 20% discount using 👉 EASTEREGG

High-quality fitted cotton shirt produced by Next Level Apparel