🐖 Basics
Important Terms and Concepts related to piggery
Which of the following statement is incorrect?
Introduction
- Swine Husbandry or Pig Farming or Hog Farming is the branch of animal husbandry which deals with the rearing of dometic pigs.
- The highest pig population is in state of
Assam.
Advantages
- Successfully maintained on discarded feed, garden waste and kitchen waste.
- Pigs produce more live weight gain from a given weight of feed than any other class of meat producing animals except broilers. That means pigs has the
highest feed conversion efficiencyafter the broiler. - FCR (Feed Conversion Ratio) -
1 : 2.5 - 3(Lowest). - High growth rate: 10 Kg/month
- Pigs are prolific breeder and have shorter generation intervals. A sow can be bred as early as 8-9 months of age and can farrow twice in a year. They produce 6-12 piglets in each farrowing.
- High dressing percentage: Meat yield in terms of dressing percentage ranges from 65 - 80% in comparison to other livestock species whose dressing yields may not exceed 65%.
- Pork is most nutritious with high fat and low water content and has got better energy value than that of other meats. It is rich in vitamins like Thiamine, Niacin, and Riboflavin.
- Pigs manure is widely used as fertilizer for agriculture farms and fishponds.
- Pig farming provides quick returns since the marketable weight of fatteners can be achieved within a period of 6-8 months.
- There is good demand from domestic as well as the export market for pig products such as pork, bacon, ham, sausages, lard etc.
- With a small investment on building and equipment, proper feeding, and a sound disease control program the farmer can profitably utilize his time and labour in this subsidiary occupation.
Nomenclature
- Group: Stock/Drove.
Farrowing: Process of parturition in pigs.Coupling: Process of mating in pigs.- Piglets: Young pigs.
- Boar:
Uncastrated adult male pig. - Boarling: Young male is called
boarling. - Barrow: Male pig castrated before reaching sexual maturity.
- Hog/Stage: Male pig which is castrated.
- Castrated/Sterilised Female: Spayed
- Gilt: Young
femaleswine that has not yet produced a litter. - Sow: Female swine which has farrowed at least once.
- Meat
- Meat of pig is known as
pork. - Salted smoked meat of pig is k/w
bacon.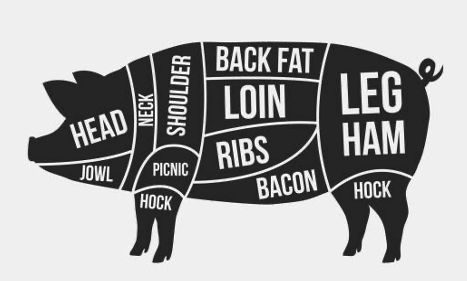
- Meat of pig is known as
Nutrition
- Monogastric (have single stomach)
- Omnivorous – low fibre, high quality protein (Animal sources)
- Requirement: Energy, protein, mineral, vitamins and additives.
Creed Feeding

- Creep feeding is the practice of introducing solid concentrate feed to the piglets before they are weaned.
- The suckling piglets are provided with solid feed behind a barrier to ease the transition from sow’s milk to solid pig starter feed.
- It started when piglets are
2 weeks old.
Flushing
- Flushing is the method of feeding sows and gilts before breeding.
- A good grower ration fed to sows and gilts seven to ten days before breeding helps in increased ovulation rates in them.
- After breeding, sows and gilts should be fed at a limited but well-balanced ration until the last six weeks of pregnancy and then full feeding should be resumed.
Weaning
- Piglets are generally weaned at 7-8 weeks old.
- Sow is separated from the piglets for a few hours each day to prevent stress of weaning and its feed is reduced gradually.
Care

- Feed on mothers’ milk for first 6-8 weeks along with creep feed.
- Supplementation of Iron to prevent piglet anemia is necessary.
- Protect the piglets against extreme weather conditions, particularly during the first two months.
- Needle teeth should be clipped shortly after birth.
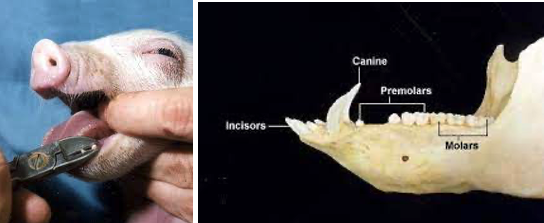
- Male piglets not selected for breeding should be castrated preferably at the age of 3-4 weeks which will prevent the boar odour in the cooked meat thus it enables production of quality meat.
References
- G.C. Banerjee: A Textbook of Animal Husbandry
- https://agritech.tnau.ac.in/
- https://www.breedslist.com/
- https://nbagr.icar.gov.in/
- Wikipedia
Which of the following statement is incorrect?
Introduction
- Swine Husbandry or Pig Farming or Hog Farming is the branch of animal husbandry which deals with the rearing of dometic pigs.
- The highest pig population is in state of
Assam.
Advantages
- Successfully maintained on discarded feed, garden waste and kitchen waste.
- Pigs produce more live weight gain from a given weight of feed than any other class of meat producing animals except broilers. That means pigs has the
highest feed conversion efficiencyafter the broiler. - FCR (Feed Conversion Ratio) -
1 : 2.5 - 3(Lowest). - High growth rate: 10 Kg/month
- Pigs are prolific breeder and have shorter generation intervals. A sow can be bred as early as 8-9 months of age and can farrow twice in a year. They produce 6-12 piglets in each …
Become Successful With AgriDots
Learn the essential skills for getting a seat in the Exam with
🦄 You are a pro member!
Only use this page if purchasing a gift or enterprise account
Plan
Rs
- Unlimited access to PRO courses
- Quizzes with hand-picked meme prizes
- Invite to private Discord chat
- Free Sticker emailed
Lifetime
Rs
1,499
once
- All PRO-tier benefits
- Single payment, lifetime access
- 4,200 bonus xp points
- Next Level
T-shirt shipped worldwide

Yo! You just found a 20% discount using 👉 EASTEREGG

High-quality fitted cotton shirt produced by Next Level Apparel