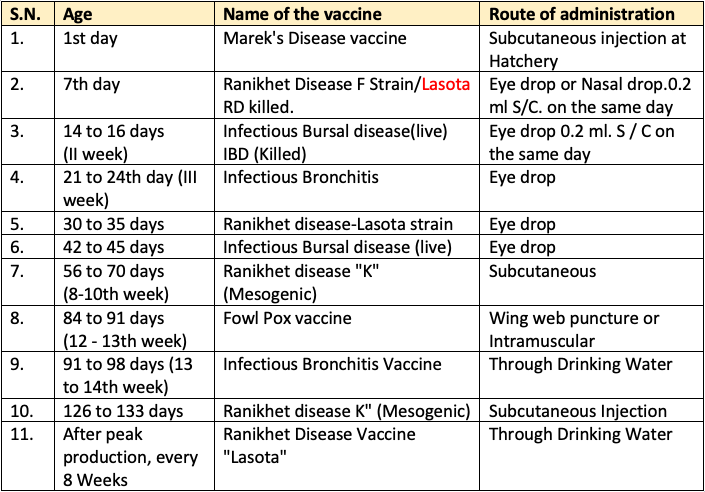
🦠 Diseases
Viral, Bacterial and Protozoan Diseases, Nutritional Disorders
Which of the following statment is not correct?
Viral
Ranikhet
- Most dangerous
viraldisease of chicken. - Ranikhet disease, also known in the West as
New Castle diseaseis a contagious and highly fatal diseases of flows. - One of the most serious virus diseases of poultry.
- The disease is also suspected to cause conjunctivitis among laboratory workers and persons handling infected birds.

- The first symptoms usually observed in young birds are sneezing, gasping and often droopiness.
- Within a short time after appearance of respiratory symptoms, deaths occur in a flock in quick succession and in increasing numbers from day to day.
- The affected birds are full and depressed with ruffled feathers.
- These symptoms are accompanied by diarrhea, characterize by the passing of a watery stool with an offensive smell.
- There is profuse salivation.
- Indian Veterinary Research Institute (IVRI) discovered vaccine named
Lasotafor Ranikhet disease.
Infectious Bursal Disease (IBD)

- Caused by IBD virus. Means
Viraldisease. - Also called
Gumborodisease. - Highly contagious
- Bursa disease causes immuno suppresion and which affects humoral antibodies production.
- Usually chicks of 2-6 weeks old affected
- Symptoms: whitish diarrohoea, the feathers around the vent are usually stained with faeces containing plenty of urates.
- Prevention: Vaccination at 2nd & 3rd weeks of age.
Fowl Pox
- It is
viraldisease. - The dry form of fowl pox is characterized by raised, wart-like lesions on unfeathered areas (head, legs, vent, etc.).
- In laying hens, infection results in a transient decline in egg production.
- In the wet form there are canker-like lesions in the mouth.
- The wet form may cause respiratory distress by obstructing the upper air passages.
- No treatment is available. However, fowl pox is relatively slow- spreading. Thus, it is possible to vaccinate to stop an outbreak.
- Fowl pox outbreaks in poultry confined to houses can be controlled by spraying to kill mosquitoes. However, if fowl pox is endemic in the area, vaccination is recommended.

Avian Influenza
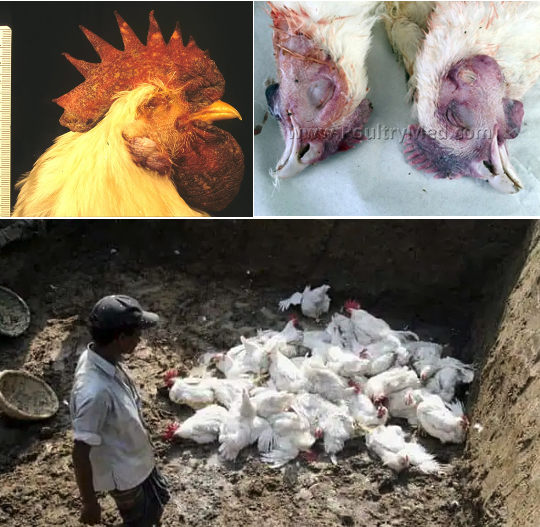

Viraldisease.- Also knonw as Bird Flu.
- Avian influenza is categorized as mild or highly pathogenic.
- The mild form produces listlessness, loss of appetite, respiratory distress, diarrhea, drop in egg production.
- The highly pathogenic form produces facial swelling, blue comb and wattles, and dehydration with respiratory distress.
- There can be blood-tinged discharge from the nostrils. Mortality can range from low to near 100 per cent.
- A vaccination programme used in conjunction with a strict quarantine has been used to control mild forms of the disease.
- With the more lethal forms, strict quarantine and rapid destruction of all infected flocks remains the only effective method of stopping an avian influenza outbreak.
Blue Comb (Viral)
- Disease primarily of young laying hens.
- It is also called pullet disease.
- Blue colour of combs.

Marek’s Disease
ViralDisease found inpoultry.- Marek’s Disease will cause inflammation and tumors in the nerves, spinal column, and brain. In this form, birds will become paralyzed in the legs, or wings or may develop head tremors.
- There is no treatment for Marek’s disease.
- Diseased birds should be promptly removed from the flock and humanely destroyed (Culling).

Infectious Bronchitis (IB)
- IB is one of the most important viral diseases of poultry.
- It causes major economic losses to the poultry industry.
- IB is an acute, highly contagious, viral respiratory disease of chickens. characterized by tracheal rales, coughing, and sneezing.
- Symptoms: Nasal discharge, rales, coughing and sneezing.
- Spread by aerosol, ingestion of contaminated feed and water, contact with contaminated equipment and clothing.

Turkey Rhinotracheitis
Viraldisease.- Swollen head syndrome (SHS) is an acute, highly contagious upper respiratory tract infection of poultry.
- The typical clinical signs seen in chickens infected with the virus include swelling of the periorbital and infraorbital sinuses, particularly around the eye, coupled with mild conjunctivitis.

Vaccination
- “Prevention is better than Cure”.
- Many viral diseases cannot be treated but can be controlled only by preventive vaccination.
Bacterial
- Pullorum
- Fowl Cholera
- Fowl Typhoid
- Colibacillosis
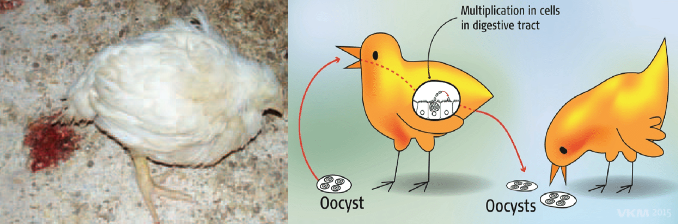
Protozoan
- Coccidiosis: Severe upto 10 weeks of age, due to poor litter management, bloody droppings, high mortality, production performance is hampered.
Nutritional Disorders
- Vitamin E Deficiency:
Encephalomalacia- Crazy chick disease
- It causes paralysis of leg, retraction of head, convulsions, death.
- Provide vegetable oils, synthetic Vit E etc to the birds.

- Vitamin B2 (Riboflavin) Deficiency:
Curled toe paralysis- Tendency to walk on hocks, dermatitis on corners of mouth, vent and foot pads.
- Provide fish products, Vit B2, rice bran.
- Vitamin D Deficiency:
Rickets - Vitamin Mn Deficiency:
Perosis - Vitamin Zn Deficiency:
Parakeratosis
References
- G.C. Banerjee: A Textbook of Animal Husbandry
- https://www.poultryindia.co.in/
- https://nbagr.icar.gov.in/
- Wikipedia
Which of the following statment is not correct?
Viral
Ranikhet
- Most dangerous
viraldisease of chicken. - Ranikhet disease, also known in the West as
New Castle diseaseis a contagious and highly fatal diseases of flows. - One of the most serious virus diseases of poultry.
- The disease is also suspected to cause conjunctivitis among laboratory workers and persons handling infected birds.

- The first symptoms usually observed in young birds are sneezing, gasping and often droopiness.
- Within a short time after appearance of respiratory symptoms, deaths occur in a flock in quick succession and in increasing numbers from day to day.
- The affected birds are full and depressed with ruffled feathers.
- These symptoms are accompanied by diarrhea, characterize by the passing of a watery stool with an …
Become Successful With AgriDots
Learn the essential skills for getting a seat in the Exam with
🦄 You are a pro member!
Only use this page if purchasing a gift or enterprise account
Plan
Rs
- Unlimited access to PRO courses
- Quizzes with hand-picked meme prizes
- Invite to private Discord chat
- Free Sticker emailed
Lifetime
Rs
1,499
once
- All PRO-tier benefits
- Single payment, lifetime access
- 4,200 bonus xp points
- Next Level
T-shirt shipped worldwide

Yo! You just found a 20% discount using 👉 EASTEREGG

High-quality fitted cotton shirt produced by Next Level Apparel