🩺 Management
Housing Management of Poultry
Which of the following statment is not correct?
- Open-sided poultry houses are very popular in our country.
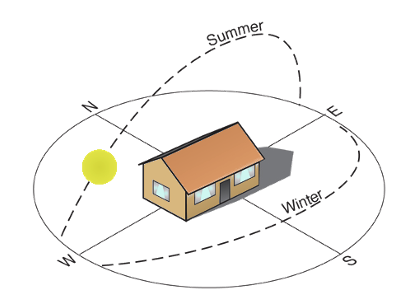
- In hotter parts of the country, the long axis of the house should run from East to West and the sides should face north-south to prevent direct sunshine falling in to the house.
- In colder parts of the country houses facing south or south-east to get maximum sunlight.
- Feeder (Feed Hopper:) It is a specially designed trough or utensil where feed for chicken is kept.
Types
- Chick/Brooder House: Used to brood and egg type chick from day-old-chick to
8 weeks age. - Grower House: Grow birds which age between
9 to 18 weeks. - Brooder cum Grower House: Birds are reared from
0 to 18 weeks. - Layer House: A house in which layer chickens of
18 to 72 weeksage birds reared. - Laying Nest - A box or cage where the chickens lay eggs.
- Broiler House: Broilers are reared up to 6 weeks of age.
- Breeder House: Both male and female birds reared with appropriate ratio of breeding purpose.
- Environmentally controlled (EC) house:
- In which, entire environment is manipulated in such a way that is optimum for the birds growth.
- The optium temperature for broiler is
24°Cand layer is13-20°C. The optium relative humidity for both broiler and layer is60%.
Poultry Housing System
I. Extensive system

- Also called
Free Range System. - Birds are allowed free range, such that it can wander at will, over the allotted paddock or field and are not controlled by fences.
- Stocking density rage 250 birds per ha.
- They received their bulk quantity of feed from the land in the form of herbage, seeds, insects etc. besides in small quantity by hand feeding.
- It is preferred for organic production.
- A small housing is provided for night shelter.
II. Semi-intensive system

- The birds are provided with a night shelter surrounded by open but fence runs for the day. This system is usually adopted for duck rearing.
- Birds are provided with a pen and run. Pen is an enclosed house and run is an enclosed grass area with fence.
- The stocking density rate on an average for adult birds is 500-750 per hectare.
- 3 to 4 sq.ft / bird in the pen.
III. Intensive system
- Birds are rearing in cages/slats.
- Therefore birds are totally confined with arrangements for feeding, watering, nesting etc. inside the house itself.
- This system is most widely practiced in India and around the world.
- Intensive system is sub-divided in four types:
Deep litter system
- In this system birds are kept inside the house all time.
- Litter material is of organic in nature capable of absorbing moisture and releasing moisture to the atmosphere and also to serve as a bedding material for the birds.
- Coirpith
- Paddy husk
- Ground Nut
- Saw dust
- Wood shavings
- Straw chopping
- Paper straw chopping
- Sugarcane baggase
- Birds are kept suitable later materials of about 5 to 12 inch depth.
- The major disadvantage of this system is if the management is bad, liberation and accumulation of ammonia, wet litter problem dirty eggs, disease problems may result.
- As per NABARD Norms, the floor space rquired for layer Hen in deep litter system:
1 Sq. Feet. ⭐️
Slatted floor system
- In this system, iron rods or wood reaper are used as floor which are placed 2-3 feet above the ground level to facilitate fall of droppings through slats.

Slat cum litter system
- 60% floor space cover with rods rest with litter.
- In this system less floor space per bird is needed when compared to solid floor system.
- Higher initial cost than conventional solid floors is the major disadvantage of this system.
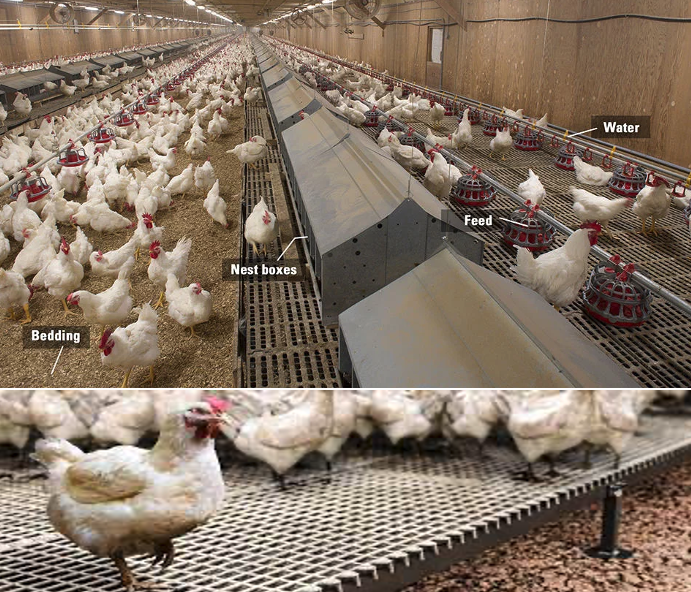

Cage system
- AKA
Battery Cage Systemor Californian Cage System. - Present in world 75 %
commercial layersreared in cage system. - In cage system — cage layers fatigue may occur (it is system in which lameness occur in birds, it may be due to Ca and P deficiency but exact reason in not known).
- In broilers case, incidence of breast blisters more especially when broilers weight above 1.5 kg.
- Birds are kept under total confinement with minimum space feed and water provided from outside.
- Eggs laid will get rolled out by the inclined floor bottom.
- Very limited movement is allowed by the birds to sit and stand properly.
- Minimum area is required/bird:
- Single:
1 per sq.ft - Multiple: 0.75 sq.ft
- Colony: 0.5 sq.ft
- Single:
- Generally the cage floor space is 14x16 inches and height of 17 inches is allowed in battery system.

Rearing of broilers
- All in all out system: Farm will have only one batch of broilers.
- Multiple batch system
- Consist more than 1 batch of broilers with batch interval 1 to 4 weeks.
- The ideal system in India at present is having
5 to 6 batchof broilers at any time and birds will market daily from 40 – 54 of age.
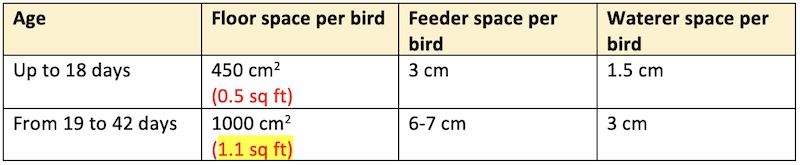
- Floor space and water requirement of broilers
Nutrition
- Poultry being simple stomached species, cannot synthesise most of the nutrients required for them and so the nutrients become dietary essentials chicken has to be fed adequate quantities of balanced diet for its growth, livability and to exhibit its genetic potential to the full extent.
- Excess energy is stored as body fat.
- Poultry feed is composed of
- 60-65% Energy giving materials
- 30-35% of Protein source (Both animal and vegetable protein)
- 2-8% Minerals source (Calcium supplements)
- Cannibalism is seen in poultry due to
NaCldeficiency.
- Feed Efficiency:
- It is ratio of feed consumption to weight gained.
- Highest FCR (Feed conversion ratio) is found in
PoultryandSwine. - Feed conversion ratio in broiler chicken:
1.5 to 1.9
Brooding of Chick
- Day-old chick: Hatched out chick is called as day-old-chick up to 24 hours.
- Brooding: This is a process of rearing the young chickens from 1-day old stage to 5 to 6 weeks of age during which, heat is to be provided to keep them warm.
- Brood: A group of chicks of same age raised in one batch is called as a brood.
- Brooder: Basically, this is a device for providing artificial heat. Also, brooder house.

- Hover: An apparatus used for keeping chicken warm. It is a heat source and placed inside brooder.
- Maintain temperature of
90 to 95 °Ffor the first week and then reduce 5°F every week. 24 hourslighting should be adopted during 0 – 8 weeks of age.
Incubation of Eggs
- Egg incubation is the process by which an egg, of oviparous (egg-laying) animals, develops an embryo within the egg.
- Incubation period for chicken eggs is
21 days. - Providing temperature and humidity for normal development of embryo in egg. It may be artificial or natural.
- A machine which provides all these is called an incubator.
- Temperature requirement for incubation is 37.2 - 37.7 °C.
- Hatching: Process of breaking out of an eggshell after completion of incubation.
Care
Culling
- Removal of unwanted bird from the flock is known as culling.
- E.g. old non-laying birds, sick birds and masculine hens are removed.
Debeaking
- It is recommended to debeak the layer birds to control feather pecking and cannibalism, bullying. It is carried out by means of electrocautery.
- It is important to remove only one third of the upper beak taking care to avoiding tongue.
- It is usually practiced at the age of
10-14 daysand repeated at the age of 14-16 weeks.
Deworming
- It is the process of removing worms from digestive tract of the birds.
- It is practiced at intervals of 45 days in layer birds.
- Chemical used
piprazinecompound.
Delicing
- Removal of external parasites like ticks, mites and fleas which suck the blood from the bird.
Moulting
- The process of shading old feathers and growth of new feather in their place moulting normally occurs once in a year.
Explore More 🔭
🟢 https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=CHMY4G9gTPA
References
- G.C. Banerjee: A Textbook of Animal Husbandry
- https://www.poultryindia.co.in/
- https://nbagr.icar.gov.in/
- Wikipedia
Which of the following statment is not correct?
- Open-sided poultry houses are very popular in our country.

- In hotter parts of the country, the long axis of the house should run from East to West and the sides should face north-south to prevent direct sunshine falling in to the house.
- In colder parts of the country houses facing south or south-east to get maximum sunlight.
- Feeder (Feed Hopper:) It is a specially designed trough or utensil where feed for chicken is kept.
Types
- Chick/Brooder House: Used to brood and egg type chick from day-old-chick to
8 weeks age. - Grower House: Grow birds which age between
9 to 18 weeks. - Brooder cum Grower House: Birds are reared from
0 to 18 weeks. - Layer House: A house in which layer chickens of
18 to 72 weeksage birds reared. - Laying Nest - A box …
Become Successful With AgriDots
Learn the essential skills for getting a seat in the Exam with
🦄 You are a pro member!
Only use this page if purchasing a gift or enterprise account
Plan
Rs
- Unlimited access to PRO courses
- Quizzes with hand-picked meme prizes
- Invite to private Discord chat
- Free Sticker emailed
Lifetime
Rs
1,499
once
- All PRO-tier benefits
- Single payment, lifetime access
- 4,200 bonus xp points
- Next Level
T-shirt shipped worldwide

Yo! You just found a 20% discount using 👉 EASTEREGG

High-quality fitted cotton shirt produced by Next Level Apparel