🐏 Sheep
Important Terms, Concepts, Housing & Management
Which of the following statment is not correct?
- Ovis aries
- Family: Bovidae
- Sheep are mostly reared for meat and wool.
- Wool potential:
- Exotic breeds: 3.5-5 kg
- Indian breeds: 1-2 kg
- Two types of wool obtained from sheep:
- Carpet Wool: Use for manufacturing of carpets.
- Apparel Wool: Use for manufacturing of cloths.

- Meat of sheep is
Mutton, Hogget (A domestic sheep between one and two years of age) and Lamb. - Nutrition:
- Sheep prefer ground vegetarian grasses, legumes, and wide varieties of forages. water requirement adult sheep 2 – 4 liters.
- Lambs and kids will suckle from the mother until they are 4 months old but they will start to show an interest in green plants
from 3 weeks of age. Flushingis feeding extra concentrates to pregnant sheep to increases the lambing rate.
Nomenclature
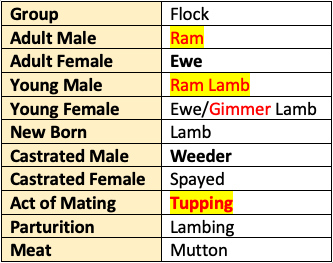
- Cosset: Lamb raised without help of its mother.

Breeds
👉🏻 Sheep breeds can be classified on the basis of Agro-ecological regions viz.
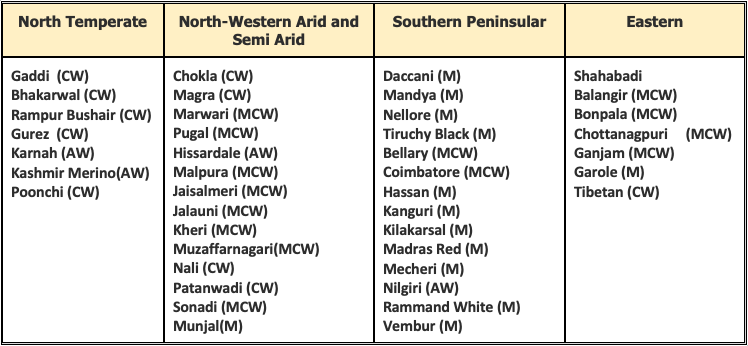
Bikaneri

- AKA
Magra. - The Magra sheep is known as the only lustrous carpet wool-producing breed.
Best Carpet Wool⭐️
Chokla

- This breed is distributed in Churu, Jhunjhunu, Sikar (Shekawati Region) & Bikaner districts of Rajasthan.
- It is famous for Best fine Carpet wool breed.
- AKA
Merino of Rajasthan. - Staple length is about 5-6 cm.
Marwari

- This sheep breed is mainly distributed all over Jodhpur and parts of Jaipur districts of Rajasthan.
- This sheep breed possess long legs, black face and a prominent nose.
- This sheep breed has high disease tolerance, which increases the survival rate.
Shahabadi

- Distribution/Origin: The Shahabadi sheep breed, is native to the erstwhile Shahabad (subsequently bifurcated into the Bhojpur, Rohtas and Buxar districts), Patna and Gaya districts of Bihar.
Best wool producing breedin India.
Deccani

- The Deccani breed derives its name from the region Dakkan (Deccan) corresponding to its original spread across the Semi-arid & Deccan plateau of Telangana, Parts of AP, Northern Karnataka, Maharashtra, and parts of Northern Tamil Nadu.
- Fit for weaving Kambal as wool is of low grade. Hence, mostly used for the manufacture of rough blankets (Kambals).
- Deccani is a recognised meat breed.
Trichy black

- These are distributed in Trichy, Perambalur, Dharmapuri and Salem districts of Tamilnadu.
- It is wool purpose breed.
- These are smaller breeds.
- Black coloured all over the body.
Mandya

- Mainly found in Mandya district of Karnataka.
- Relatively small animals colour white - sometimes face is black coloured which may extend up to neck.
- Best mutton type conformation among the Indian breeds.
Nellore

- It is distributed in Nellore and Ongole districts of Andhra Pradesh.
- It is the tallest breed of sheep in India.
- Resembling goats in appearance.
- They have little hair and no wool is obtained from them.
- Rams are horned ewes are polled.
Neelagiri

- These are distributed in Neelagiri district of Tamilnadu.
- It is wool purpose breed.
- Majority are found in white colors.
Gaddi

- Sheep are small in size, and are found in Kishtwar and Bhadarwah tehsils of Jammu. (Himalayan Region Breed)
- A large number inhabit the Kulu valleys in HP winter, and in summer they graze the highest elevations of them Pir Panjal Mountains, mostly in the Paddar range.
- Rams are horned, ewes hornless; fleece is generally white with brown coloured hair on the face.
- Wool is fine and lustrous; average annual yield is 1.13 kg per sheep, clipped thrice a year.
- Undercoat is used for the manufacture of high quality Kulu shawls and blankets.
Avikalin

Rambouillet x Malpur- This breed is quite suitable as a dual-purpose sheep for carpet wool and mutton production.
Hissardale
- Hissardale was evolved at the Government Livestock Farm,
Hissar, through crossbreeding AustralianMerino rams⚦ withBikaneri (Magra) ewes♀. - The rams of this breed were earlier distributed in the hilly regions of Kullu, Kangra etc.
Exotic Breeds
Merino

- Native of
Spain - Fine wool breed
- About 80% of wool that is produced in the world comes from Merino and its cross.
Rambouillet

- This sheep breed was developed in France.
- This sheep also known as Rambouillet Merino or
French Merino. - It produces an excellent fine-wool fleece.
Dorset

- The
Dorset Hornis an endangered British breed of domestic sheep.
Corriedale

- Native of New Zealand.
- Corriedale sheep are a dual-purpose breed, meaning they are used both in the production of wool and meat.
- The Corriedale is the oldest of all the crossbred breeds, a Merino-Lincoln cross developed almost simultaneously in Australia and New Zealand and first brought to the United States in 1914.
Sheep Clone

- Cloned
sheepproduced named asDolly. - Dolly the sheep was the first mammal to be cloned from an adult cell.
- She was born on July 5, 1996 at the Roslin Institute in Scotland.
- Dolly was produced by British developmental biologist Ian Wilmut, who earned the title of “Father of Cloning”.
🔭 https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=fqeCUY42A-E
Dagging (Crutching)
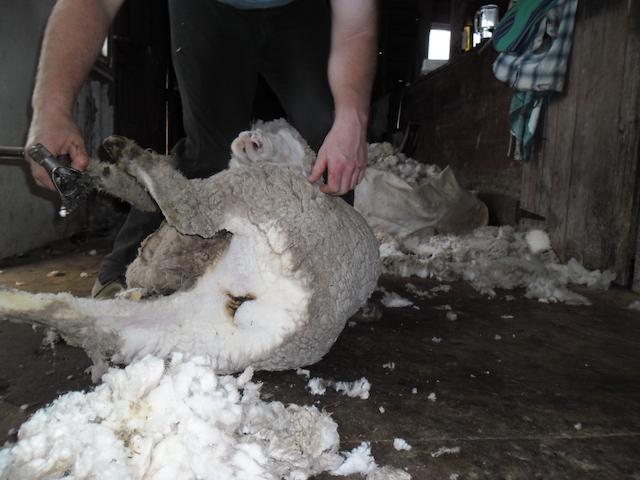

- Dagging or crutching is the cutting away of dirty, wet wool from around the tail and anus (crutch) of the sheep.
- The wet, dirty wool attracts flies especially the blow flies (bright green or blue in colour).
- The flies lay their eggs on the wool and in one or two days maggots hatch from them.

Ringing in Sheep
- Ringing - trimming wool around the sheath of the penis of the rams to facilitate mating.

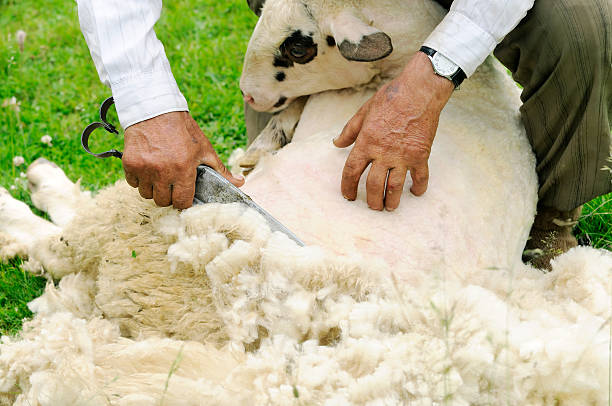
Shearing
- Shearing is the complete removal of the wool and is carried out using machine or hand shears.

Docking
- The removal of tail in sheep is called docking.
- Done in
sheepat the age of 7 to 14 days.
Seasonal Breeding in Sheeps
Most sheep are seasonally polyestrus and short-day breeders. They start their estrus when the length of the day begins to decrease.
Photoperiod: the period of time during the day when there is daylight. Photoperiod regulates reproductive cyclicity in seasonal breeders. (Pathways to Pregnancy and Parturition).
Sheep are seasonal breeders that enter into the breeding season during shorter photoperiods; thus, they are short-day breeders.

Diseases in Sheep
Sheep Pox
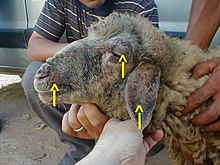
ViralDisease. It is highly contagious and spread by contact.- High fever – Dullness – Isolation from herd discharge from Natural orifices
- Eyes and Nostrils with swelling of eye lids – ‘Pox’ eruptions on the skin of ears, head, inside of thighs, scrotum, lower side of the base of the tail.
- Sheep pox vaccine developed from indigenous strain by
IVRI.
Blue Tongue
- Bluetongue is an insect-borne infectious non-contagious disease
viral diseaseto which all species of ruminants are susceptible, although sheep are most severely affected. - Cattle and goats which appear healthy can carry high levels of the virus and provide a source of further infection.
- It is caused by Bluetongue virus (BTV).
- The virus is transmitted by the transmitted by Culicoides midges.
- Major signs are high fever, excessive salivation, swelling of the face and tongue, and cyanosis of the tongue.
- Swelling of the lips and tongue gives the tongue its typical blue appearance, though this sign is confined to a minority of the animals.
- Nasal signs may be prominent, with nasal discharge and stertorous respiration.
- Some animals also develop foot lesions, beginning with coronitis, with consequent lameness.
- In sheep, this can lead to knee-walking.
- In cattle, constant changing of position of the feet gives bluetongue the nickname the dancing disease.
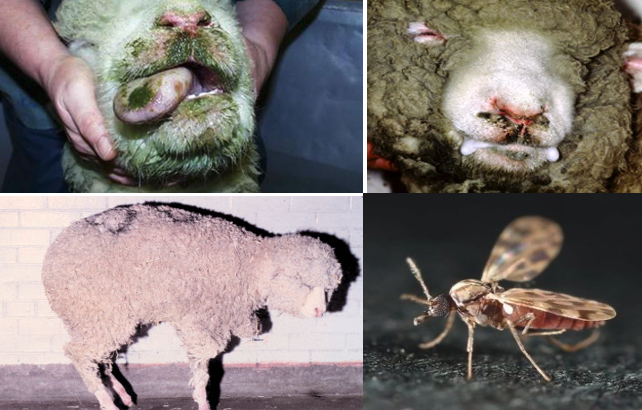
- Control:
- A live attenuated polyvalent vaccine prior to rainy season.
- Annual vaccination.
- Routine hygiene and sanitation.
- Vector control is very important in disease prevention.
Stargazing

- Stargazing is a term used to describe a deceptively innocuous behavior: the head and neck are raised almost straight up, as if the affected animal is gazing at the stars.
- This condition is common to several diseases that affect the central nervous system.
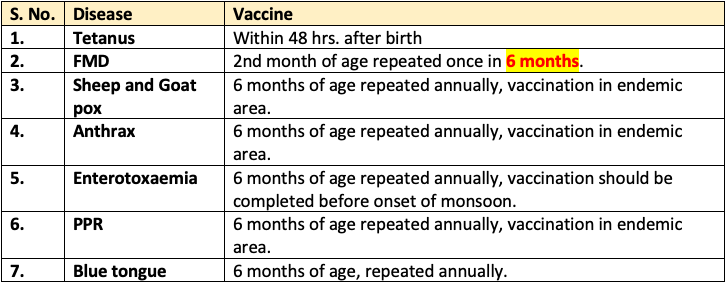
Vaccination in Goat and Sheep
References
- G.C. Banerjee: A Textbook of Animal Husbandry
- https://www.dairyknowledge.in
- https://www.breedslist.com/
- https://nbagr.icar.gov.in/
- https://www.nddb.coop/
- Wikipedia
Which of the following statment is not correct?
- Ovis aries
- Family: Bovidae
- Sheep are mostly reared for meat and wool.
- Wool potential:
- Exotic breeds: 3.5-5 kg
- Indian breeds: 1-2 kg
- Two types of wool obtained from sheep:
- Carpet Wool: Use for manufacturing of carpets.
- Apparel Wool: Use for manufacturing of cloths.

- Meat of sheep is
Mutton, Hogget (A domestic sheep between one and two years of age) and Lamb. - Nutrition:
- Sheep prefer ground vegetarian grasses, legumes, and wide varieties of forages. water requirement adult sheep 2 – 4 liters.
- Lambs and kids will suckle from the mother until they are 4 months old but they will start to show an interest in green plants
from 3 weeks of age. Flushingis feeding extra concentrates to pregnant sheep to increases the lambing rate. …
Become Successful With AgriDots
Learn the essential skills for getting a seat in the Exam with
🦄 You are a pro member!
Only use this page if purchasing a gift or enterprise account
Plan
- Unlimited access to PRO courses
- Quizzes with hand-picked meme prizes
- Invite to private Discord chat
- Free Sticker emailed
Lifetime
- All PRO-tier benefits
- Single payment, lifetime access
- 4,200 bonus xp points
- Next Level
T-shirt shipped worldwide

Yo! You just found a 20% discount using 👉 EASTEREGG

High-quality fitted cotton shirt produced by Next Level Apparel