💇🏻♂️ Apiary Management
Good Beekeeping Practices (GBPs)
Which of the following is not considered as good beekeeping practice?
- There is vast potential for beekeeping in the country. However, due to lack of knowledge, scientific beekeeping is not being practiced by the beekeepers.
- It is necessary for beekeepers to participate in the trainings / other capacity building programmes on the subject to gain scientific knowledge on the subject.
- Selection of good apiary site, good quality bees and proper management are the main keys for success of beekeeping.
Selection of good apiary site
👉🏻 Select apiary site by considering the following:
- The apiary must be located in well- drained open area, preferably near orchards, with profuse source of nectar, pollen and water.
- Protection from sunlight is important in order to maintain an optimum temperature in the hive.
- Ant wells are fixed around the hive stand.
- The colonies must be directed towards east, with slight changes in the directions of the bee box as a protection from rain and sun.
- Site should receive early morning and afternoon sunshine
- Keep the colonies away from the reach of cattle, other animal, busy roads and streetlights.
- Area should be rich in bee flora
- Site should be open & at dry place having shade
- There should not be other commercial apiary within 2-3 kilometers from the apiary site
- There should not be any source of stagnant / dirty water, chemical industry/ sugar mill, etc., nearby the apiary
Placement of colonies in apiary
- Hives should be as per specification of BIS/ISI and should be of locally available seasoned light weight wood.
- Unseasoned and heavy wood should be avoided.
- Avoid nailing the bottom board with the brood chamber.
- Restrict number of bee colonies in an apiary from 50 to 100.
- Keep row to row and box to box distance as 10 and 3 feet, respectively.
- Avoid over-stocking of colonies in the apiary.
Selection of good quality bees
- Beekeeping can be done by domesticating two species of honey bees viz. Apis cerena and Apis mellifera depending upon floral conditions.
Provision of fresh water in the apiary
- Ensure availability of fresh water preferably in shallow containers near the apiary to maintain a healthy apiary.
- Water is needed for the following:
- Maintenance of adequate humidity in a colony to ensure proper incubation of eggs.
- For feeding bee bread by nurse bees, the mixture of honey and pollen of certain consistency is required for which water is needed.
- When temperature in the apiary increases beyond 37°C, water is used by bees to evaporate and cool the colony.
Dearth period management
- Provide 50 % sugar syrup to the colonies during dearth periods when honey stores in the colonies is not adequate and nectar is not available in the area. The syrup should be prepared by boiling clean water in the vessel and sugar added with slow stirring for few minutes. Cover the vessel with lid and let it cool. Feed cooled syrup.
- Sugar syrup should be kept in such a way that the bees should not drown in it. This should be ensured by using shallow vessels with straw to facilitate easy feeding.
Honey Extraction

- Harvest the honey by smoking the bees off the parts which needs to be harvested and cut the combs carefully.
- Harvests are normally possible during and shortly after the two main flowering seasons:
- October to November
- February to June.
- A ripe comb is light in colour and filled with honey.
- Exctract honey from frame which is having more than half of the honey cells (recommended 75% of honey cells) on both the sides are sealed with wax.
- Wash all the equipments / containers etc. thoroughly with warm water before honey extraction
- Extract honey from super chambers only
Bee Pasturage
- Plants that yield pollen and nectar are collectively called bee pasturage or bee forage.
- Floral Fidelity:
- A bee visits or restrict themselves to smae species of plant for pollen/nectar collection until exhausted.
- Bees travel 2-3 km distance to collect pollen/nectar.
- Scope of beekeeping for pollination in India:
- Total area under bee dependent crops - 50 million ha
- At the rate of 3 colonies/ha - 150 million colonies needed
- In India only 1.2 million colonies exist - There is huge scope.
Mylettophylly

- Pollination by bees is called Mylettophylly.
80 %of total insect pollination is by honey bees.- The bee is capable of carrying pollen loads of 26 - 35% of its body weight.
Management of Bees for Pollination
- Place hives very near the field (source) - to save bee’s energy.
- Migrate colonies near field at 10% flowering.
- For pollination of crops, place Italian bee @
3 colonies/haor Indian bee @5 colonies/ha. - The colonies should have 5-6 frame strength of bees, possess sealed brood, have young mated queen.
- Allow sufficient space for pollen and honey storage.
Crops benefited by Bee Pollination
- It increases yield (seed yield, fruit yield) in many crops
- It improves quality of fruits and seeds
- Bee pollination increases oil content of seeds in sunflower
- Bee pollination is a must in some self-incompatible crops for seed set
Crops benefited by Bee Pollination
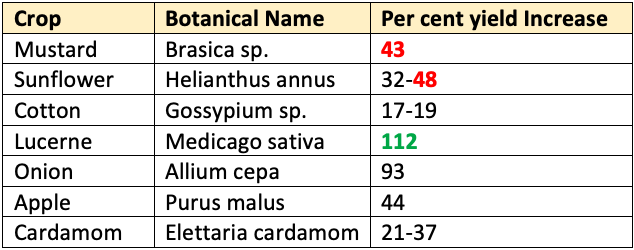
Per cent increase in yield due to Bee Pollination
References
- https://nbb.gov.in/
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bee
- The Insects - Structure and Function (4th Edition, 1998) – R.F. Chapman. Cambridge University Press
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Apiary
- https://agritech.tnau.ac.in/
Which of the following is not considered as good beekeeping practice?
- There is vast potential for beekeeping in the country. However, due to lack of knowledge, scientific beekeeping is not being practiced by the beekeepers.
- It is necessary for beekeepers to participate in the trainings / other capacity building programmes on the subject to gain scientific knowledge on the subject.
- Selection of good apiary site, good quality bees and proper management are the main keys for success of beekeeping.
Selection of good apiary site
👉🏻 Select apiary site by considering the following:
- The apiary must be located in well- drained open area, preferably near orchards, with profuse source of nectar, pollen and water.
- Protection from sunlight is important in order to maintain an optimum …
Become Successful With AgriDots
Learn the essential skills for getting a seat in the Exam with
🦄 You are a pro member!
Only use this page if purchasing a gift or enterprise account
Plan
Rs
- Unlimited access to PRO courses
- Quizzes with hand-picked meme prizes
- Invite to private Discord chat
- Free Sticker emailed
Lifetime
Rs
1,499
once
- All PRO-tier benefits
- Single payment, lifetime access
- 4,200 bonus xp points
- Next Level
T-shirt shipped worldwide

Yo! You just found a 20% discount using 👉 EASTEREGG

High-quality fitted cotton shirt produced by Next Level Apparel