🎎 Bee Castes
Honey Bees as Social Insects
Which of the following statement is not correct realted to honeybees?
- Honey bees are fascinating social insects known for their complex social structure and cooperative behavior. They live in organized colonies or hives, which consist of three main castes:
- The Queen
- The Workers
- The Drones
- Every honey bee colony comprises of a single queen, a few hundred drones and several thousand worker castes of honey bees.
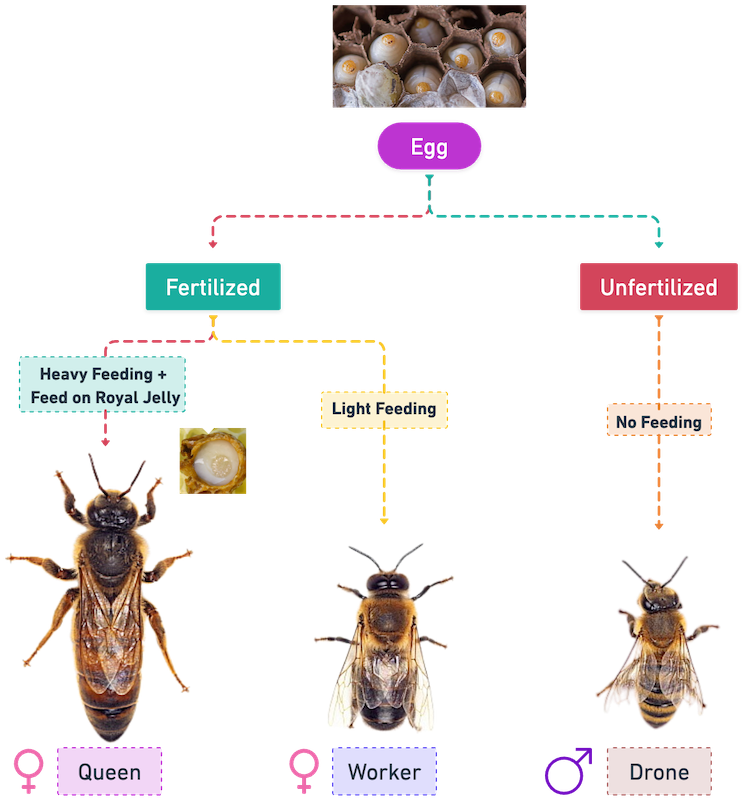
- Queen is a fertile, functional female.
- Worker is a
sterilefemale. - Drone is a
fertilemaleinsect.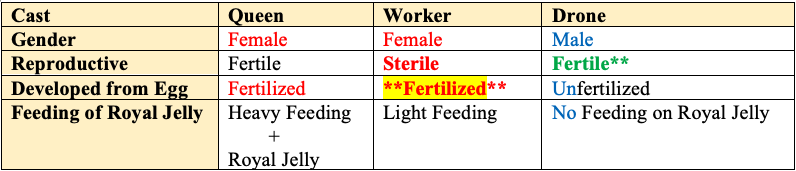
- The queen bee is the largest member of the colony and her primary role is reproduction. She is responsible for laying eggs, which ensure the colony’s survival.
- The queen emits
pheromonesthat regulate the behavior and development of the other bees in the colony. It also attact male drone during mating season. - Queen secretes an antiqueen substance which is a pheromone, from its glands. It inhibits worker bees to build another royal brood chamber and produce royal jelly for others.
- In honey bees, unfertilized eggs (haploid eggs) give raise to drones (males) whereas from
fertilized eggs(diploid eggs), queen and workers (females) are produced. - Sex is determined by the fertilization of eggs.
- In honey bees, males are produced by parthenogenesis.
- Workers are female bees that make up the majority of the colony. They perform various tasks such as foraging for food, building and maintaining the hive, caring for the queen and the brood (developing young bees), and defending the colony. Workers progress through different stages of tasks as they age, transitioning from cleaning cells and feeding larvae to guarding the hive and collecting nectar and pollen.
- Drones are male bees whose sole purpose is to mate with the queen. They do not possess stingers and are not involved in any other activities within the colony.
- Drones usually emerge during the spring and summer seasons when the queen requires mating flights.
- Communication is crucial within a honey bee colony. Bees communicate through a complex system of chemical signals, vibrations, and dances. For example, the waggle dance is performed by forager bees to communicate the location of food sources to their nest mates.
- Honey bees are highly efficient pollinators and play a vital role in the ecosystem by pollinating a wide variety of flowering plants. They collect nectar and pollen, and in the process, transfer pollen from male to female flowers, facilitating fertilization and the production of fruits and seeds.
- Overall, the social structure and behaviors of honey bees exemplify remarkable coordination and division of labor, enabling them to thrive as a cohesive unit and contribute significantly to both ecological balance and the production of honey and other bee products.
Bee Hive
- The place where bee colonies are maintained is called an Apiary (beehouse).
- Aka Comb or Bee Hive.
- In comb, upper cells are honey cells followed by pollen cells, worker cells, drone cells and queen cells (bottom).
- Brood cells of worker are hexagonal with a flat cap, drone cell is spherical with a convex cap and central hole, queen cells are cylindrical and large.
- Apis cerana indica and Apis mellifera contructs parallel combs, accordingly bee hive is designed.
- The bees which make single vertical combs are Apis dorsata and Apis florea.
- Bee hive temperature is 32-36°C.

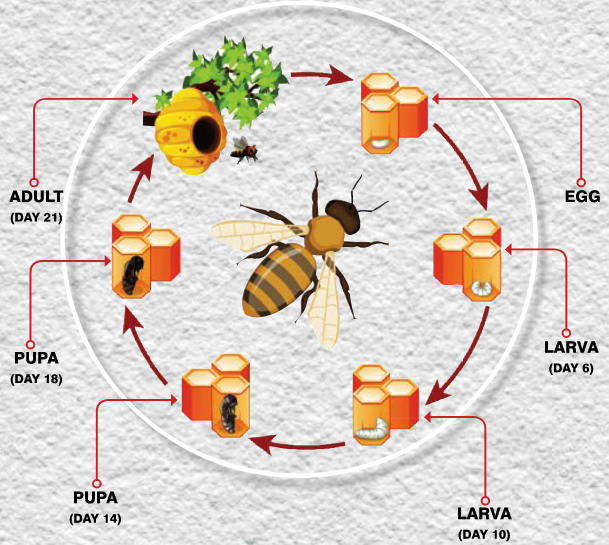
Life Cycle
👉🏻 Duration (Period) in days:
Duration of Different Casts Life Cycle of a Honey Bee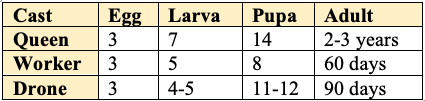
Duties of a queen
- The only individual which lays eggs in a colony. (Mother of all bees).
- Queen of Apis mellifera lays 2,000 - 3,000 eggs/day while A. cerana indica lays 500-600 eggs/day.
- Five to Ten days after emergence, she mates with drones in one or more nuptial flights.

- When her spermatheca is filled with sperms, she will start laying eggs and will not mate any more.
- She lives for
2-3 years. - The secretion from mandibular gland of the queen is called queen’s substance.
- Queen’s substance was isolated by Butler et. al. (1962) and identified is as 9-Oxodec-trans-2-enoic acid.
- The queen substance if present in sufficient quantity performs following functions:
- Prevent swarming and absconding of colonies.
- Prevent development of ovary in workers.
- Colony cohesion is maintained.
- The queen can lay either fertilized (laid in worker or queen cells) or unfertilized eggs (laid in drone cells) depending on the requirement.
- During the summer months, the queen bee is very busy because the hive is most active and needs to be as strong as possible. During this time, the queen bee lays around 2500 eggs every day.
Duties of a drone
- Their important duty is to fertilize the queen.
- They also help in maintenance of hive temperature.
- They cannot collect nectar / pollen and they do not possess a sting.
Duties of a worker
- Their adult life span of around
6 weekscan be divided into- First three weeks worker bees are confined to the hive called house or nurse bees.
- Rest of the life-out door duty.
- House hold duty includes:
- Build comb with wax secretion from wax glands.
- Feed the young larvae with royal jelly secreted from hypopharyngeal gland.
- Feed older larvae with bee-bread (pollen + honey)
- Feeding and attending queen.
- Feeding drones.
- Cleaning, ventilating and cooling the hive.
- Guarding the hive. 👮♂️
- Evaporating nectar and storing honey.
- Outdoor duties:
- Collecting nectar, pollen, propolis and water.
- Ripening honey in honey stomach.
- This Division of labour related to age is called Polytheism in worker bees.
Days Work 1-2 days Cleaning 3-5 days Nursing bees (feeds old larvae with bee bread (pollen and honey) 6-10 days Nursing bees (feeds young larvae with royal jelly) 11-12 days Orientation flight 12-18 days Produce royal jelly and wax, constructs combs, receive honey, ripens and stores 20-21 days Guarding entrance From day 21st onwards Field collection of honey - A worker bee makes 19,000 trips per day.
- A worker bee during there complete lifecycle can produce honey as much as 1/12th of a spoon.
- Honey bees wing stroke is 11,000 per minute.
- Bee travels 9 km/hr.
- Bee visits 2 million flowers to collect 500 g of honey.
- If 50% of the nectar collected are from the same plant then it is called Unifloral honey otherwise Mixed honey.
🧚🏼♀️ Other Social Insects:
- Ants
- Wasps
- Termites

References
- https://nbb.gov.in/
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bee
- The Insects - Structure and Function (4th Edition, 1998) – R.F. Chapman. Cambridge University Press
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Apiary
- https://agritech.tnau.ac.in/farm_enterprises/fe_api_typesofhoneybee.html
- https://wgbis.ces.iisc.ac.in/
Which of the following statement is not correct realted to honeybees?
- Honey bees are fascinating social insects known for their complex social structure and cooperative behavior. They live in organized colonies or hives, which consist of three main castes:
- The Queen
- The Workers
- The Drones
- Every honey bee colony comprises of a single queen, a few hundred drones and several thousand worker castes of honey bees.

- Queen is a fertile, functional female.
- Worker is a
sterilefemale. - Drone is a
fertilemaleinsect.
- The queen bee is the largest member of the colony and her primary role is reproduction. She is responsible for laying eggs, which ensure the colony’s survival.
- The queen emits
pheromonesthat regulate the behavior and development of the other bees in the colony. …
Become Successful With AgriDots
Learn the essential skills for getting a seat in the Exam with
🦄 You are a pro member!
Only use this page if purchasing a gift or enterprise account
Plan
Rs
- Unlimited access to PRO courses
- Quizzes with hand-picked meme prizes
- Invite to private Discord chat
- Free Sticker emailed
Lifetime
Rs
1,499
once
- All PRO-tier benefits
- Single payment, lifetime access
- 4,200 bonus xp points
- Next Level
T-shirt shipped worldwide

Yo! You just found a 20% discount using 👉 EASTEREGG

High-quality fitted cotton shirt produced by Next Level Apparel