🍯 Bee Products
Honey, Bees Wax, Royal Jelly, Bee Venom, Propolis, Pollen
Which of the following is correct regarding honey?
1. Honey

- A sweet, viscous fluid - Produced by honeybees.
- Collected as nectar from nectaries at base of flower.
- Also collected from extra floral nectaries (nectar secreted by parts other than flowers).
- Collected also from fruit juice, cane juice.
- About 2 million flowers must be visited to make half kg of honey.
- Bee draws nectar by its tongue (proboscis).
- Collected by hive bees - Deposited in cells in comb.
- Honey is very nutritious and have many medicinal property.
- Used in India since ancient times. Used in Ayurveda.
Ripening of Honey
- Nectar contains 20-40% sucrose whereas fully ripened honey contains < 2% sucrose.
- Sucrose (disaccharide) in nectar is converted by enzyme invertase to Glucose (dextrose) and Fructose (Levulose) (which are monosaccharides), to form honey.
- Invertase is present in nectar itself and in saliva of honey.
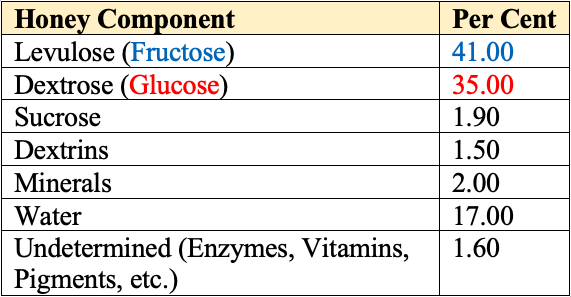
Fully Riped Honey Contains
- Ripening of honey is by action of enzyme and by evaporation of water by fanning of wings.
- Unripe honey is processed artificially by indirect heating to 145-160 °F for 30 minutes.
Properties of Honey
- Percentage of sugar in honey is 78 %.
- According to FSSAI what can be the maximum sucrose content in honey is 5%.
- Honey containing more than 20% moisture at raw stage is not considered pure. Because honey with a high moisture content has a thin texture and eventually tastes sour as a moisture level of 20% or more will ferment into alcohol.
- Vitamin E is not present in honey.
- Honey of little bee, Apis florea has high content of dextrins and is of medicinal importance.
- An antioxidant called pinocembrin is found in honey.
- Below 14°C dextrose of honey gets granulated.
- pH range of honey is 3.4 to 6.1 i.e. acidic in nature.
- Test for invert sugar is done by Resorcinol and Aniline Chloride Test.
Purity test for honey
- Measure specific gravity of honey using hydrometer.
- If the specific gravity is between
1.25 - 1.44 g/ccit is pure honey
2. Bees Wax

- Wax glands are present in worker honey bees in the sternum of segment no. 4, 5, 6 and 7.
- Bee wax is Myristyl Palmitate.
- 20 Kg of honey is consumed by honey bees to produce 1 kg of wax.
- Rock bee, Apis dorsata yields more bee wax.
- It is valuable, used in candle, pharmaceutical and cosmetic industry.
3. Royal Jelly
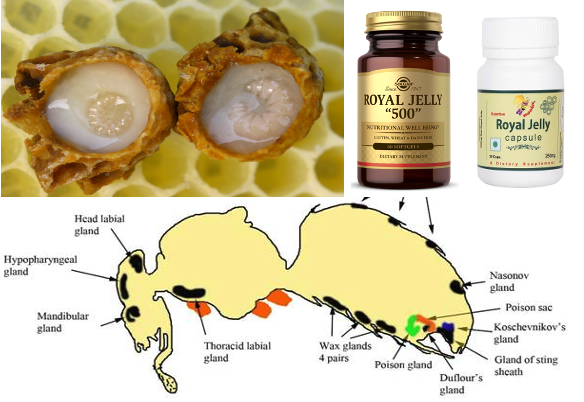
- Hypopharyngeal glands of
workerssecrete royal jelly. - Royal jelly contains vitamins like panthothenic acid.
- Nutritious, increase vigor and vitality/fertility.
👀 Explore More: https://youtu.be/L4cth57-66k
4. Bee Venom

- Sting of honeybee is modified ovipositor.
- Bee venom produced is formic acid. An alkaine gland, Dufour’s gland also opens at the base of the sting.
- Bee venom is used to cure rheumatism. Treatment known as Apitherapy.
- Specific odour of the colony is due to the secretion of Vasnov’s gland present in the last abdominal segment of workers.
5. Propolis

- Propolis is a resinous substance collected by bees from resinous exudates of trees and leaves used for sealing cracks and unwanted spaces in the hive.
- It is used as gum.
6. Pollen

- Collects pollen by passing flower to flower. Pollen sticking to body removed.
- Using pollen comb - Packed using pollen press into corbicula.
- A single bee carries 10-30 mg pollen (25% of bee’s wt)
- Dislodge by middle log into cell.
- Mix with honey and store.
- It is considered as Super Food.
References
- https://nbb.gov.in/
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bee
- The Insects - Structure and Function (4th Edition, 1998) – R.F. Chapman. Cambridge University Press
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Apiary
- https://agritech.tnau.ac.in/farm_enterprises/fe_api_typesofhoneybee.html
Which of the following is correct regarding honey?
1. Honey

- A sweet, viscous fluid - Produced by honeybees.
- Collected as nectar from nectaries at base of flower.
- Also collected from extra floral nectaries (nectar secreted by parts other than flowers).
- Collected also from fruit juice, cane juice.
- About 2 million flowers must be visited to make half kg of honey.
- Bee draws nectar by its tongue (proboscis).
- Collected by hive bees - Deposited in cells in comb.
- Honey is very nutritious and have many medicinal property.
- Used in India since ancient times. Used in Ayurveda.
Ripening of Honey
- Nectar contains 20-40% sucrose whereas fully ripened honey contains < 2% sucrose.
- Sucrose (disaccharide) in nectar is converted by enzyme invertase to Glucose (dextrose) and Fructose (Levulose) …
Become Successful With AgriDots
Learn the essential skills for getting a seat in the Exam with
🦄 You are a pro member!
Only use this page if purchasing a gift or enterprise account
Plan
Rs
- Unlimited access to PRO courses
- Quizzes with hand-picked meme prizes
- Invite to private Discord chat
- Free Sticker emailed
Lifetime
Rs
1,499
once
- All PRO-tier benefits
- Single payment, lifetime access
- 4,200 bonus xp points
- Next Level
T-shirt shipped worldwide

Yo! You just found a 20% discount using 👉 EASTEREGG

High-quality fitted cotton shirt produced by Next Level Apparel