🥨 Life Cycle
Learn about Lac, Current Status, Strains, Hosts and Life Cyle of Lac Insect
Which of the following statement is correct?
Status

- Lac culture is the scientific management of lac insects to obtain a high amount of quality lac. This involves selection and maintenance of host plants, inoculation of host plants with healthy lac insects, collection and processing of lac and protection against enemies.
- Lac is the
resinoussecretion of lac insects. - It is cultivated mainly by the tribal communities and a little quantity is collected by the forest dwellers in India.
- Lac is an important Non-Wood Forest Products (NWFPs).
Indiais the largest producer of lac in the world and contributes to about 70-80% of the world’s need.18,944 MTproduction in 2018-19.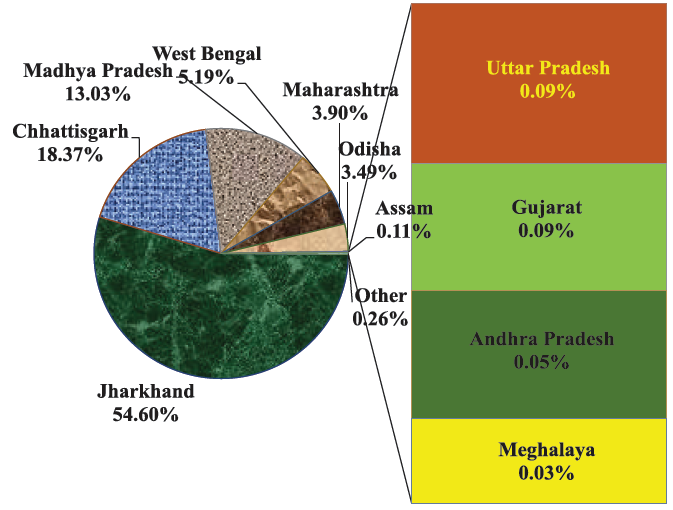
- Within India, the state of
Jharkhandhas the largest number of host trees and ranks first in the country for production. - The lac is a resin not gum and produced by tiny insect, is a soft-bodied insect belonging to order,
Hemiptera. - Two genera and 19 species of lac insects have been observed in India and most common Indian lac insect of commercial importance is Kerria lacca (Earlier Known as Laccifer lacca).
- The first scientific account of lac insect (Laccifer lacca, Lacciferidae, Homoptera) was given by Dr. J. Kerr in 1782.
- Phylam: Arthropoda
- Class: Insecta
- Order: Hemiptera
- Super family: Coccidae
- Family: Kerriidae
- Genus: Laccifer
- Species: Lacca
- Detailed account of lac insect is given by Roxburgh.
- Lac is a natural resin secreted by the tiny lac insects, mainly
Kerria lacca(Kerr), for protection of young ones and self. - The insects are cultured on tender shoots of several plants called hosts. It derives its nutrition by sucking the saps from the host plants.
- Rangeeni and Kusami are two strains of lac insect which are classified based on preference of the insect for specific host plants.
- Each of these strain, produce two crops in a year (
bi-Voltine).
Host
-
The insects live as a parasite, feeding on the sap of certain trees and shrubs.
Strain Host Plant Quality Production Share Kusami Kusum (Schleichera oleosa) Good 10% Rangeeni Palash (Butea monosperma), Ber (Zizvphus mauritiana), Acacia nilotica, A. catechu, Shorea talura etc. Average 90% -
Kusami insect grows well mainly on Kusum (Schleichera oleosa) and also on a few other trees but not on palash (Butea monosperma), whereas Rangeeni strain grows well mainly on palash and also on a few other trees but not on Kusum.
-
Kusum lac is good quality lac due to lighter colour of resin but contributes 10% of total production.
-
Rangeeni lac contributes 90 % of the total production.
-
Kusumi brood (6 months)
- Baisakhi: Summer season crop of rangeeni
- Katki: Rainy season crop of rangeeni
- Jethwi: Summer season crop of kusmi (January/February to June/July)
- Aghani:
Winterseason crop of kusmi (June/July to January/February)
Life Cycle
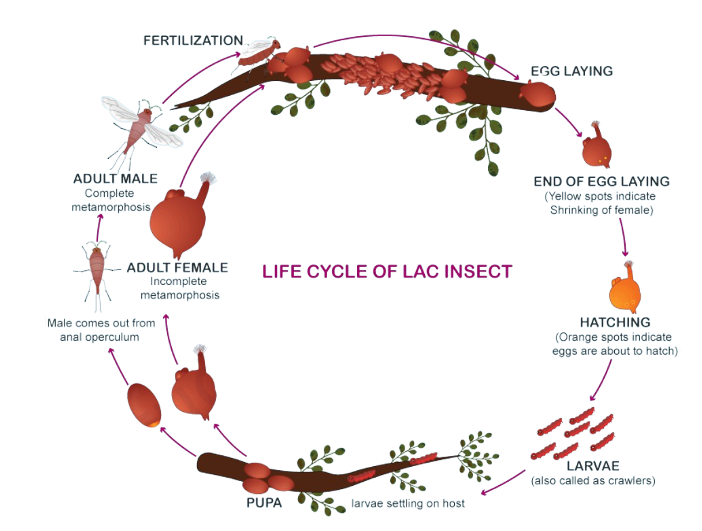
- The first instar nymphs are called crawlers and they fix themselves to the tree.
- These crawlers, crawl on the branches of their host plants and feed on the phloem. As they pierce the branches to reach the phloem, they cover the holes with their wax secretions.
- The dye originates in the hemolymph of the insect.
- The lac insect passes through 2 generations/year. (bi-voltine)
- The females reproduce ovovivparously and lays an average of 300 eggs.
- The body of lac insect covered by lac is called
Cell. - The host plant twig bearing lac along with eggs is called brood lac.
- Most common method of inoculation of brood lac is ‘Longitudinal method’.
- Lac sticks left after escape of nymphs is called
Phunkai. - Emergence of nymphs of lac is called swarming.
- Lac insect loses eyes, antenna and legs after first moult.
- The cells of male lac insect are slipper shaped.
- A mature lac has a yellow spot on the posterior cell.
- Most suitable temperature for lac cultivation is
27-30°C. - 1 kg of lac resin is obtained from 3,00,000 lac insects.
- The Hindi word “Lakh” for shellac possibly derives from such large number of insects required to produce lac.
References
- https://nisa.icar.gov.in/
- https://agritech.tnau.ac.in/
- Wikipedia
Which of the following statement is correct?
Status

- Lac culture is the scientific management of lac insects to obtain a high amount of quality lac. This involves selection and maintenance of host plants, inoculation of host plants with healthy lac insects, collection and processing of lac and protection against enemies.
- Lac is the
resinoussecretion of lac insects. - It is cultivated mainly by the tribal communities and a little quantity is collected by the forest dwellers in India.
- Lac is an important Non-Wood Forest Products (NWFPs).
Indiais the largest producer of lac in the world and contributes to about 70-80% of the world’s need.18,944 MTproduction in 2018-19.
- Within India, the state of
Jharkhandhas the largest number of host trees and ranks first in the country …
Become Successful With AgriDots
Learn the essential skills for getting a seat in the Exam with
🦄 You are a pro member!
Only use this page if purchasing a gift or enterprise account
Plan
- Unlimited access to PRO courses
- Quizzes with hand-picked meme prizes
- Invite to private Discord chat
- Free Sticker emailed
Lifetime
- All PRO-tier benefits
- Single payment, lifetime access
- 4,200 bonus xp points
- Next Level
T-shirt shipped worldwide

Yo! You just found a 20% discount using 👉 EASTEREGG

High-quality fitted cotton shirt produced by Next Level Apparel