🌏 History
Entomological Historical Developments, Important scientists & their contributions, Important Research Institutes
Entomology
- Greek word:
Entomomeans insect (cut-into section) +Logosmeans discourse.
Entomology is the biological science dealing with a specific group of organisms, the insects.
The branch of zoology that deals with the study of insects is known as entomology.
- The person who studies entomology is known as entomologist.
🔭 Explore More: https://youtu.be/Q-38ocCB0ss0
Application of Entomology
- Study and use of insects in agriculture is known as
Agricultural Entomology. - Study and use of insects in forestry is known as
Forest Entomology. - Study and use of insects in crime investigations is known as
Forensic Entomology. - Study of insects related to livestock and veterinary animals is known as
Veterinary Entomology. - Study of insects in relation to Human beings is known as
Medical Entomology.
History of Entomology in India
- 1758:
Carl Lennaueuspublished 10th edition of Systema Naturae which includes only 12 Indian insects. It was the earliest record. He is regarded as Father of Binomial Nomenclature.

- The first entomologist who made any extensive study of Indian Insects was
J.C. Fabricius. He was Danish Professor of Political Economy turned into a systematist and classified the insects into 13 orders based on types of mouth parts.

- 1767-1779:
Dr. J.G. Koeniga Medical Officer initiated the work on Indian insects on scientific lines. He also published a special account of the termites of Thanjavur District.

- 1782:
Dr. KerrPublished on account of lac insect. - 1815–26:
William Kirby(England Entomologist).

- Born in 1759. During his life he published many books on insects including his first major work, Monographia Apum Angliae (Monograph on the Bees of England) in 1802 and the Introduction to Entomology, which was the first popular entomological work in English.
- Because of his significant contributions to the science of entomology he is known as
Father of Entomology. He is considered as the “Founder of Modern Entomology”. - He helped to found the Royal Entomological Society in London in 1833.
- 1875: Foundation of the Indian Museum at
Calcutta.
- 1883: Bombay Natural History Society,
Bombaywas started. After the foundation of these two organisations scientific studies received greater attention in India. Numerous contributions of Indian insects were published in the Journal of the Bombay Natural History.

- 1892: Hampson issued four volumes on moths of India
- 1893: Rothney published on Indian Ants (earliest record of biological pest control in India) i.e. White ants attach on stationary items was kept free by red ants.
- 1897: Bingham’s issued volumes on “Hymenoptera” (Ants, bees and wasps). Since than volumes on other groups of insects like Coleoptera (beetles), Hemiptera (bugs), Odonata (dragonfly and damselfly), etc., were published.
- 1889: Indian Museum, Calcutta published the Indian Museum Notes in five volumes.
- 19th Century marks the major progress and expansions in the field of applied entomology.
- 1901:
Lionel de Nicevelleposting of the first entomologist to the Government of India.

- 1903: Professor
Maxwell Lefroysucceeded Nicevelle as Government Entomologist

- 1905: Establishment of Imperial Agricultural Research Institute at
Pusa (Bihar). Subsequently this Institute was shifted toNew Delhias Indian Agricultural Research Institute.- Maxwell-Lefroy became the first person to be appointed Imperial Entomologist to the government of India in 1903 and stayed in the post until 1912.
- Maxwell Lefroy also set up the entomology department in the newly created Indian Agricultural Research Institute (IARI) at Pusa in Bihar in 1905, now relocated to New Delhi.
- Professor Maxwell Lefroy, also published two important books “Indian Insect Pests” & “Indian Insect Life” when he was Heading the Division of Entomology, at Imperial Agricultural Research Institute, Pusa, Bihar.
- Subsequently State Governments also took up entomological work.
Madras, Punjab and Uttar Pradesh appointed their first Government Entomologists in 1912, 1919 and 1922 respectively. - 1912: Plant Quarantine Act was enforced in USA.
- 1914:
T.B. Fletcher, the first Government Entomologist ofMadras State, published book “Some South Indian Insects”.
- 1914: “Indian Forest Insects of Economic Importance: Coleoptera” was published by the first Imperial Forest Entomologist
E.P. Stebbing.

- 1916: Imperial Forest Research Institute was established at
Dehradun(Uttrakhand), andE.P. Stebbingwas appointed as Forest Zoologist. - 1916: The Natural History Section of the Indian Museum was formed as the Zoological Survey of India (ZSI).
- 1921:
Indian Central Cotton Committeeto investigate on pests of cotton. - 1925: Indian Lac Research Institute. Now known as
National Institute of Secondary Agriculture(Formerly Indian Institute of Natural Resins and Gums)Ranchi, Jharkhand.

- 1934:
Hem Singh Pruthiwho succeeded Fletcher as Imperial Entomologist, made efforts to bring all the entomological workers still closer which resulted into the foundation of “Entomological Society of India” in1938.

- Afzal Hussain was the first President of the Entomological Society of India and the Vice-President were Hem Singh Pruthi and T.V. Ramakrishana Ayyar.

- The official publication of the Society is the “Indian Journal of Entomology”.
- He is known as
Father of Agricultural Entomologyin India
- 1937: A laboratory for storage pests was started at Hapur, U.P.
- 1937: Entomology division was started in IARI, New Delhi
- 1939: Locust Warning Organisation (LWO) established.
- India has the world’s oldest desert locust control programme. The British government established the Locust Warning Organisation (LWO) in 1939 in Karachi following a deadly locust plague between 1926 and 1931.
- In 1946, the LWO moved to
Delhiunder the directorate of plant protection, quarantine and storage under the ministry of agriculture and farmers welfare.
- 1940: Dr. T.V. Ramakrishna Ayyar published the book “Handbook of Economic Entomology” which met the long felt need of the students of Agriculture and agricultural scientists as well.
- 1968: Dr. M.S. Mani’s “General Entomology”
- 1969: Dr. H.S. Pruth’s “Textbook of Agricultural Entomology”. Dr. Pradhan’s “Insect Pests of Crops”
- 1946: “Directorate of Plant Protection, Quaraintine & Storage” establised in
Faridabad, Haryana.- It is headed by Plant Protection Advisor (PPA).
- The current PPA is Dr J.P. Singh.

- 1960: “The Desert Locust in India” monograph by Y.R. Rao.
- 1968: The Govt. of India enacted “
Central Insecticide Act - 1968which came into force in1st January, 1971.
An Act to regulate the import, manufacture, sale, transport, distribution and use of insecticides with a view to prevent risk to human beings or animals, and for matters connected therewith.
- 1969: “The monograph on Indian Thysanoptera” by Dr. T.N. Ananthakrishnan.
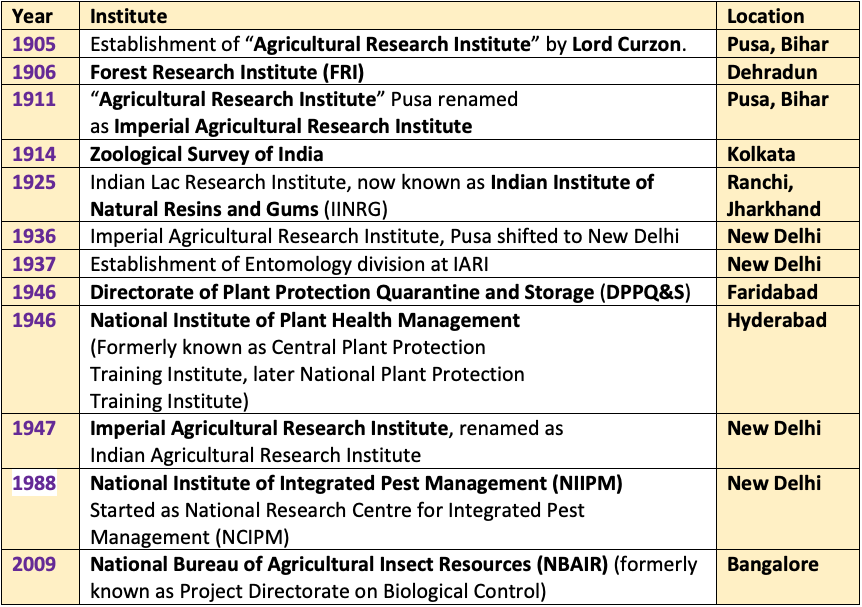
Important Institutes of Entomology in India
🟢 Explore More
🔭 https://youtu.be/iJlfBNyBKQA
References
- Insecta - Introduction: K.N. Ragumoorithi, V. Balasurbramani & N. Natarajan
- A General Textbook of Entomology (9th edition, 1960) – A.D. Imms (Revised by Professor O.W. Richards and R.G. Davies). Butler & Tanner Ltd., Frome and London.
- The Insects- Structure and Function (4th Edition, 1998) – R.F. Chapman. Cambridge University Press
- Wikipedia
-
Entomology
- Greek word:
Entomomeans insect (cut-into section) +Logosmeans discourse.
Entomology is the biological science dealing with a specific group of organisms, the insects.
The branch of zoology that deals with the study of insects is known as entomology.
- The person who studies entomology is known as entomologist.
🔭 Explore More: https://youtu.be/Q-38ocCB0ss0
Application of Entomology
- Study and use of insects in agriculture is known as
Agricultural Entomology. - Study and use of insects in forestry is known as
Forest Entomology. - Study and use of insects in crime investigations is known as
Forensic Entomology. - Study of insects related to livestock and veterinary animals is known as
Veterinary Entomology. - Study of insects in relation to Human beings is known …