🧠 Nervous system
Structure and Classification of neuron, Mechanism of impulse conduction, Types of Nervous System
Which of the following statment is incorrect?
- Insects show co-ordination in behaviour, memory and possess intelligence due to well distributed nervous system.
- The nervous system functions as a link between the sense organs which respond to various external and internal stimuli and the effector organs such as muscles, glands etc.
- The sense organs include the structures with various sensilla that respond to sounds, weather factors, smell etc.
- Nervous system consists of elongated cells which form the physiologically functional elements that are known as
neurons. - These neurons carry the information in the form of electrical impulses.
Structure of a neuron
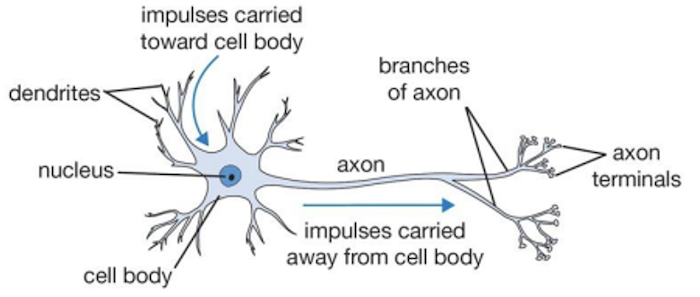
- The nerve cells are called neurons which are derived from ectoderm.
- Each neuron consists of a prominent nucleated cell body known as perikaryon or soma and an elongated cytoplasmic thin fibre called the ‘axon’ and group of small branches called the ‘dendrites’. The axon gives lateral branches called collaterals.
- Both the axon and collaterals end in fine fibrils known as terminal arborizations.
- The neurons get connected with each other by having a link between the terminal arborizations of the axon of one neuron and dendrites of the soma of another neuron through a
synapse.
Classification of Neurons
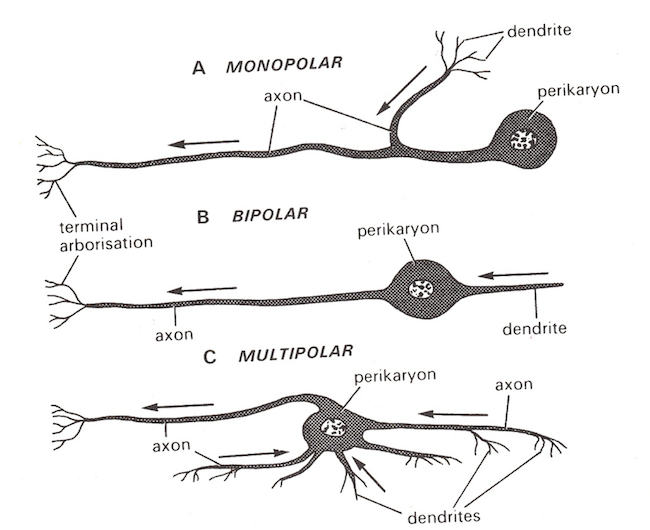
I. Based on their structure
- Unipolar / monopolar: Have a single axon without collaterals and dendrites
- Biopolar: Have either collateral or dendrites in addition to axon
- Multipolar: Neurons have an axon with several collaterals and dendrites.
II. Based on function: 3 kinds of neurons.
- Sensory / afferent: Present just beneath the integument and associated with sensory organs. Carry impulses from sense organs to the central nervous system.
- Motor / efferent neurons: Always unipolar / monopolar carry impulses from central nervous system to the organs.
- Association / internuncial neurons: Associated in between sensory and motor neurons, usually present in ganglia, consists of axons of sensory neurons and soma of motor neurons.
Mechanism of impulse conduction:
- Impulses are conducted by the neurons by two means.
- Axonic conduction: lonic composition varies between inside and outside of axon resulting in excitable conditions which leads to impulse conduction as electrical response.
- Synaptic conduction: Neurochemical transmitters are involved in the impulse conduction through the synaptic gap.
Types
👉🏻 Nervous system can be divided in to three major sub-system as
1. Central nervous system (CNS)
- Central nervous system consists of brain, sub-oesophageal ganglion and ventral nerve cord.
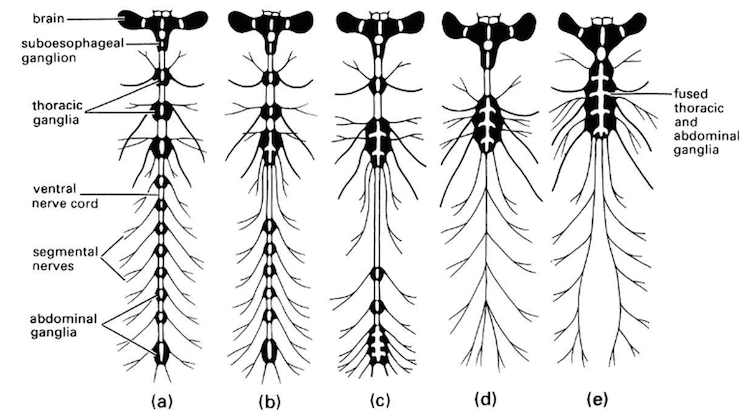
The central nervous system of various insects showing the diversity of arrangement of ganglia in the ventral nerve cord
2. Visceral or sympathetic nervous system (SNS)
👉🏻 It is divided in to three systems:
- Oesophageal sympathetic/ stomatogastric which includes the frontal ganglion and associated with the brain, aorta and foregut.
- Ventral visceral, associated with the ventral nerve cord; and
- Caudal visceral, associated with the posterior segments of abdomen.
3. Peripheral nervous system (PNS)
The peripheral nervous system consists of all the motor neuron axons that radiate to the muscles from the ganglia of the CNS and visceral nervous system plus the sensory neurons of the cuticular sensory structures (the sense organs) that receive mechanical, chemical, thermal or visual stimuli from an environment.
References
- Insecta - Introduction: K.N. Ragumoorithi, V. Balasurbramani & N. Natarajan
- A General Textbook of Entomology (9th edition, 1960) – A.D. Imms (Revised by Professor O.W. Richards and R.G. Davies). Butler & Tanner Ltd., Frome and London.
- The Insects- Structure and Function (4th Edition, 1998) – R.F. Chapman. Cambridge University Press
- https://www.amentsoc.org/
- Researchgate
- Wikipedia
Which of the following statment is incorrect?
- Insects show co-ordination in behaviour, memory and possess intelligence due to well distributed nervous system.
- The nervous system functions as a link between the sense organs which respond to various external and internal stimuli and the effector organs such as muscles, glands etc.
- The sense organs include the structures with various sensilla that respond to sounds, weather factors, smell etc.
- Nervous system consists of elongated cells which form the physiologically functional elements that are known as
neurons. - These neurons carry the information in the form of electrical impulses.
Structure of a neuron

- The nerve cells are called neurons which are derived from ectoderm.
- Each neuron consists of a prominent nucleated cell body known …
Become Successful With AgriDots
Learn the essential skills for getting a seat in the Exam with
🦄 You are a pro member!
Only use this page if purchasing a gift or enterprise account
Plan
- Unlimited access to PRO courses
- Quizzes with hand-picked meme prizes
- Invite to private Discord chat
- Free Sticker emailed
Lifetime
- All PRO-tier benefits
- Single payment, lifetime access
- 4,200 bonus xp points
- Next Level
T-shirt shipped worldwide

Yo! You just found a 20% discount using 👉 EASTEREGG

High-quality fitted cotton shirt produced by Next Level Apparel