🪱 Aphelenchid Nematodes
Species, Biology, Symptoms, Integrated Management
Which of the following is not wrong regarding aphelenchoides nematodes?
Leaf and bud nematode
- Aphelenchoides sp.
- Aphelenchoides means ‘resembling Aphelenchus’; which in turn is derived from apheles means smooth + enchus means stylet.
- Aphelenchid nematodes are commonly known as Leaf and Bud Nematodes.
- Also known as foliar nematode.
White Tip Nematod or Rice Leaf Nematode
- Aphelenchoides besseyi
- Dastur (1934) first reported this nematode as Aphelenchoides sp. Associated with a disease of rice occurring in epidemic form in the then Central Province of India. The nematode was later reported from Japan under the name Aphelenchoides oryzae in 1940. Allen in 1952 identified it as A. besseyi.
- This nematode associated with serious epidemic of rice in MP.
- This is
seed bornenematode. The immature nematodes (usually preadults) are present in between the glumes and the grain in a quiescent stage. - It feed as ectoparasite.
- Humidity favors infestation.
- It causes white tip diease of rice, which is a typical seed-born disease.
- The most diagnostic symptom, it the upper 3-5 cm portion of leaf tip turning white or pale yellow at the tillering stage.

- Management: Hot Water treatment: 52-55 °C for about 10-15 minutes.
Mushroom Nematode
- Aphelenchoides composticola
- Important nematode of mushroom. It is a mycophagous nematode and feed on the fungus mycelium.
- The growth of Agaricus bisporus (button mushroom) is adversely affected and fruiting is drastically reduced.
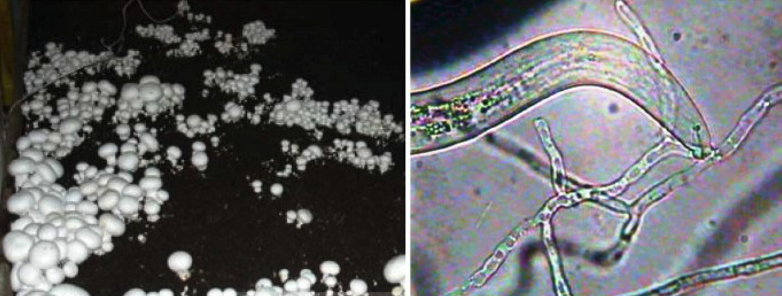
Foliar Nematodes
- Aphelenchoides ritzemabosi and Aphelenchoides fragariae.
- Both the species feed ectoparasitically on buds and endoparasitically on leaves.
Chrysanthemum Nematode
- Aphelenchoides ritzemabosi
- Nematode feeding on undersized and distorted flowers of chrysanthemum.

Strawberry Nematode
- Aphelenchoides fragariae known as
Spring crimporstrawberry nematode. It is associated with strawberry disease known as “spring crimp” and “summer crimp” - Nematode feeding on buds results in a blind strawberry plant.
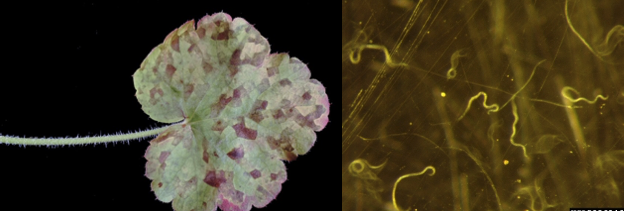
Red Ring Nematode
- Rhadinaphelenchus cocophilus
- This nematode causes red ring diseases of coconut in central and south America and Caribbean islands. It is not reported from India so far.

- The nematode along with the diseased tissues are transmitted by palm weevil, Rhynchophorus palmarum and deposited in the leaf axils of healthy plants. (Insect transmitted)

- Stem show characteristic symptom. About 3 cm beneath the stem surface, a ring of reddish necrotic tissue.
References
- Dropkin, V.H. 1980. Introduction to plant nematology. John Wiley and sons, INC. New York.
- Singh, R.S and Sitaramaiah, K. 1994. Plant pathogens. The plant parasitic nematodes. Oxford & IBH Pub. Co. Pvt. Ltd. New Delhi.
- Parvata Reddy, P. 1983. Plant nematology. Agricole Pub. Co., New Delhi.
- Southey, J. F. Laboratory methods for work with plant and soil nematodes Tech.
- Bull. Min. Agric. Fish. Food. Her Majesty’s Stationary Office, London.
- Walia, R. K and Bajaj, H. K (2014). Textbook of Introductory Plant Nematology. Directorate of Knowledge Management in Agriculture, ICAR, New Delhi.
- Kumar, V., Khan, M.R. & Walia, R.K. Crop Loss Estimations due to Plant-Parasitic Nematodes in Major Crops in India. Natl. Acad. Sci. Lett. 43, 409–412 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40009-020-00895-2
- Figure 1: Source: A: Maggenti, 1981, B-E: Franklin, 1973
Which of the following is not wrong regarding aphelenchoides nematodes?
Leaf and bud nematode
- Aphelenchoides sp.
- Aphelenchoides means ‘resembling Aphelenchus’; which in turn is derived from apheles means smooth + enchus means stylet.
- Aphelenchid nematodes are commonly known as Leaf and Bud Nematodes.
- Also known as foliar nematode.
White Tip Nematod or Rice Leaf Nematode
- Aphelenchoides besseyi
- Dastur (1934) first reported this nematode as Aphelenchoides sp. Associated with a disease of rice occurring in epidemic form in the then Central Province of India. The nematode was later reported from Japan under the name Aphelenchoides oryzae in 1940. Allen in 1952 identified it as A. besseyi.
- This nematode associated with serious epidemic of rice in MP.
- This is
seed bornenematode. The …
Become Successful With AgriDots
Learn the essential skills for getting a seat in the Exam with
🦄 You are a pro member!
Only use this page if purchasing a gift or enterprise account
Plan
Rs
- Unlimited access to PRO courses
- Quizzes with hand-picked meme prizes
- Invite to private Discord chat
- Free Sticker emailed
Lifetime
Rs
1,499
once
- All PRO-tier benefits
- Single payment, lifetime access
- 4,200 bonus xp points
- Next Level
T-shirt shipped worldwide

Yo! You just found a 20% discount using 👉 EASTEREGG

High-quality fitted cotton shirt produced by Next Level Apparel