🪱 Burrowing Nematodes
Species, Biology, Symptoms, Integrated Management
Which of the following is not wrong regarding burrowing nematodes?
- Radopholus similis
- The generic word Radopholus is derived from two Greek words:
- radix: root
- phelien: loving
- Denoting the endoparasitic mode of life.
- The common name “Burrowing Nematode” is coined because it causes extensive cavity formation in the roots due to migratory behaviour.
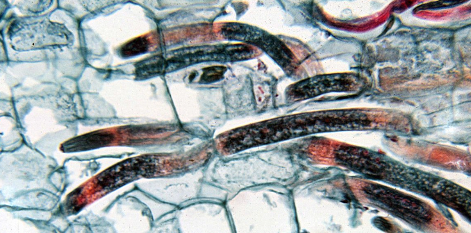
- The burrowing nematode was first observed by Cobb in 1890-91 while investigating a banana disease in Fiji.
- In India, it is believed to have been introduced into Kerala along with banana suckers from some other country.
- Although the host range of R. similis is very wide, yet it is considered to be a serious problem on banana, pepper, coffee, tea, cocoa, coconut, arcanum, sugarcane, turmeric, ginger etc.
Biology
- Females and all juvenile stages are infective.
- Males are non-parasitic and morphologically degenerate (without stylet).
- Penetration occurs mostly near the root tip. The nematode penetrates within 24 hours and the cells around the site of penetration becomes brown.
- After entering the roots, the nematodes occupy intercellular position in the cortical parenchyma where they feed on the cytoplasm of nearby cells causing cavities which coalesce to form tunnels. Nematodes do not enter the stellar portions of the root.
- Two distinct races of burrowing nematode were reported previously
- Banana race: Parasitic on banana but not on citrus
- Citrus race: Parasitic both on banana and citrus
- The citrus race which is confined to Florida is now recognized as a separate species – R. citrophilus.
- In India only banana race (R. similis) is present.
Banana
- The disease caused by R. similis on banana is known by different names:
- Banana Blackhead Disease
Banana Decline- Banana Rhizome Rot
- Banana Root Rot
- This nematode also interacts with Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. Cubease and causes panama wilt in banana. The incidence of wilt is doubled and wilting is preponed in plants infected with this nematode.

- It can reduce fruit yield up to 88-95%.
- Above ground symptoms: Yellowing of leaves and followed by withering of foliage and fruit bunches eventually plant dies.
- Below ground symptoms: Reddish elongated lesions that first appear on the roots, gradually enlarge, and coalesce leading to rotting. The root system is devoid of laterals and overall size of the root system is drastically reduced. Rooting extends to rhizomes and plant at bearing stage often ‘topple over’ during high winds due to poor anchorage.

Management
- Use healthy rhizomes for plantation.
Black Pepper
- Rodopholus similies causes ‘yellows’ disease in black pepper.
- Initially yellowing of few leaves start which gradually extend to all over the vine. It leads to complete defoliation. The growth of the vine ceases, berry production reduces drastically and the vines die soon.
Management
- Nematicide Fensulfothion @4-8 kg a.i./ha in nursery stage.
Citrus
- Rodopholus citrophilus – the burrowing nematode of critus is so far found only in Florida and Hawaii (USA).
- It causes
Spreading decline of citrus. - Feeder roots are destroyed, and yield reduction reported.
References
- Dropkin, V.H. 1980. Introduction to plant nematology. John Wiley and sons, INC. New York.
- Singh, R.S and Sitaramaiah, K. 1994. Plant pathogens. The plant parasitic nematodes. Oxford & IBH Pub. Co. Pvt. Ltd. New Delhi.
- Parvata Reddy, P. 1983. Plant nematology. Agricole Pub. Co., New Delhi.
- Southey, J. F. Laboratory methods for work with plant and soil nematodes Tech.
- Bull. Min. Agric. Fish. Food. Her Majesty’s Stationary Office, London.
- Walia, R. K and Bajaj, H. K (2014). Textbook of Introductory Plant Nematology. Directorate of Knowledge Management in Agriculture, ICAR, New Delhi.
- Kumar, V., Khan, M.R. & Walia, R.K. Crop Loss Estimations due to Plant-Parasitic Nematodes in Major Crops in India. Natl. Acad. Sci. Lett. 43, 409–412 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40009-020-00895-2
- Figure 1: Source: A: Maggenti, 1981, B-E: Franklin, 1973
Which of the following is not wrong regarding burrowing nematodes?
- Radopholus similis
- The generic word Radopholus is derived from two Greek words:
- radix: root
- phelien: loving
- Denoting the endoparasitic mode of life.
- The common name “Burrowing Nematode” is coined because it causes extensive cavity formation in the roots due to migratory behaviour.

- The burrowing nematode was first observed by Cobb in 1890-91 while investigating a banana disease in Fiji.
- In India, it is believed to have been introduced into Kerala along with banana suckers from some other country.
- Although the host range of R. similis is very wide, yet it is considered to be a serious problem on banana, pepper, coffee, tea, cocoa, coconut, arcanum, sugarcane, turmeric, ginger etc.
Biology
- Females and all …
Become Successful With AgriDots
Learn the essential skills for getting a seat in the Exam with
🦄 You are a pro member!
Only use this page if purchasing a gift or enterprise account
Plan
Rs
- Unlimited access to PRO courses
- Quizzes with hand-picked meme prizes
- Invite to private Discord chat
- Free Sticker emailed
Lifetime
Rs
1,499
once
- All PRO-tier benefits
- Single payment, lifetime access
- 4,200 bonus xp points
- Next Level
T-shirt shipped worldwide

Yo! You just found a 20% discount using 👉 EASTEREGG

High-quality fitted cotton shirt produced by Next Level Apparel