🐣 Introduction
Nematode defination, habitat and it's economic relavance in agriculture
Which of the following is correct regarding nematode?
Definition
- Nematology is an important branch of biological science, which deals with a complex, diverse group of round worms known as Nematodes that occur worldwide in essentially all environments.
- A handful of soil from anywhere any part of the world, from mountain top to bottom of ocean, from tropics to arctics, from fresh water to brackish water, from soil to plant tissues and even from blood streams of humans and livestock contain nematodes.
- Therefore, Nematodes are cosmopolitan in nature.
- In light of the high population numbers of nematodes.
N.A. Cobb(1915) who is considered to be the Father of American Nematology, provided a dramatic description of the abundance of nematodes. He stated:
“In short, if all the matter in the universe except the nematodes were swept away, our world would still be dimly recognizable, and if, as disembodied spirits, we could then investigate it, we should find its mountains, hills, vales, rivers, lakes, and oceans represented by a film of nematodes.
- The word Nematode is derived from two Greek words:
- Nema means thread
- Oides means resemblance/like
- The word nema and nematology were coined by N. A. Cobb (1932).
- Commonly nematodes are known as:
- Nema or Eelworms: Because for their serpentine movements.
- Verms: Cylindrical body tapering at both the ends.
- Round Worm: Tubular body or round cross section.
- Nematodes are also known as eelworms in Europe, nemas in the United States and round worms by zoologists.
Habitat
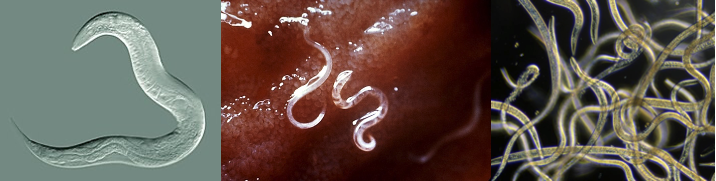
- They are free-living, aquatic, terrestrial or parasitic in plants and animals.
- Belongs to phylum Nematoda, one of the most abundant groups of invertebrates on earth.
- Many species are important parasites of plants and animals, whereas others are beneficial to agriculture and the environment.
- Nematodes that are parasites of man and animals are called
helminthesand the study is known asHelminthology. - The plant parasitic forms are called nematodes and the study is known as
Plant Nematology. Plant Nematologyis a science between zoology and botany now in recent times it is an independent branch in agriculture and horticulture. And a well-established full-fledged discipline of Plant Protection.- Nematodes reside in all kinds of soil.
- Nematodes are found in soil either randomly or uniformly or in clusters.
- In standing crop nematodes are present in clusters.
- The soils in a hectare of all agro ecosystem typically contain billions of plant parasitic as well as beneficial nematodes.
- The damage to plants caused by nematodes is often overlooked because the associated symptoms, including slow growth, stunting and yellowing, can also be attributed to nutritional and water related disorders.
- From one hectare of cultivable land contains 7.5x109 nematodes.
- Nematodes are highly diversified and present in soil, water both fresh and marine water and in different environmental condition.
- About 50% nematodes are marine nematode
- 25% freeliving
- 15% animal parasitic
- Rest
10 %plant parasitic nematode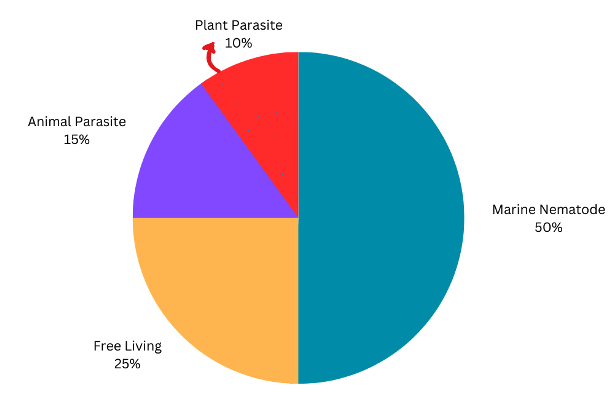
Economic Importance
- Plant-parasitic nematodes are costly burdens of crop production and are associated with nearly every important agricultural crop and represent a significant constraint on global food security.
- Nematodes are more serious in warmer than cooler areas, more in horticultural crops than field crops.
- Plant-parasitic nematodes the tiny creature are the hidden enemies
- Overall in India, crop loss due to nematodes is 21.3 % amounting to approx. Rs. 10,200 crore i.e. $ 1.2 billion USD annually.
- From around 19 horticultural crops loss is estimated around Rs. 5000 crore. Among fruit crops loss in
- Citrus: Rs. 9,828.22 million
- Banana: Rs. 9,710.46 million
- Tomato: (Rs. 6,035.2 million)
- Brinjal: (Rs. 3,499.12 million)
- Okra: (Rs. 2,480.86 million) among the vegetable crops suffered comparatively more losses.
- Root-knot nematodes (Meloidogyne spp.) cyst nematodes (Heterodera and Globodera spp.) and lesion nematodes (Pratylenchus spp.) rank at the top of list of the most economically and scientifically important species due to their intricate relationship with the host plants, wide host range, and the level of damage ensued by infection.
- In India, the cereal cyst nematode, Heterodera avenae causes the “molya” disease of wheat and barley in Rajasthan, Punjab, Haryana, Himachal Pradesh and Jammu and Kashmir.
- The examples are only a small portion of nematode problem in India. Besides this direct damage, they also associate with bacteria, fungi and viruses to cause complex diseases.
As incitant
- Nematodes acts as incitant. These after feeding the host plant breaks the defence wall system making micropuncture on the cell wall which creates infection or avenue site for other secondary pathogen.
- Eg. Nematode Pratylenchus brachyrus create infection site for fungus Phytopthera parasitica causing “Black Shank Disease of Tobacco”.
As aggravators
- Nematodes when feed the host plant tissues modifies the host substrate making the plant susceptible for other secondary pathogens. It indirectly aggravates the host plant.
- Fusarium wilt was more severe in the presence of root knot nematode (Meloidogyne spp).
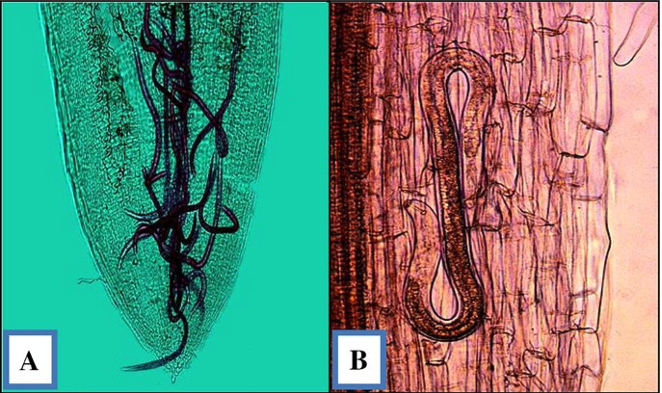
- Eg.:
- Vascular wilt of tomato - Meloidogyne incognita + Fusarium oxysporum f. lycopersici.
- In strawberry by the infestation of Aphelenchoides frageriae (nematode) and Clavibacter fusciens (bacteria) cause “Cauliflower disease”.
As a vector
- In nematode – virus complex, nematode serves as a vector. Nematodes carry other microbes on their surfaces or digestive tract distributes throughout soil and also rhizosphere.
- Nematode transmitted only
RNA viruses. - Hewit, Raski and Goheen (1958) found that Xiphinema index was the vector of
Grapevine Fan Leaf Virus. - Xiphinema spp., Longidorus spp., and Paralongodorus spp. transmit the ring spot viruses which are called
NEPOderived fromNematode transmittedPolyhedral shaped particles. - Teichodorus spp. and Paratrichodorus spp. transmit the rattle viruses and called
NETUderived fromNematode transmittedTubular shaped particles. - All genera of virus vector nematodes belong to order
Dorylaimidaand these haveAuto-parasitic Modeof Feeding.
Helminthology
- Nematodes parasite of animals and humans are known as helminths.
- Helminths are larger in size and harmful to humans and animals.
- Study of nematodes which are parasitic exclusively on man and animals is known as
Helminthology. - Common nematodes infecting humans and animals are:
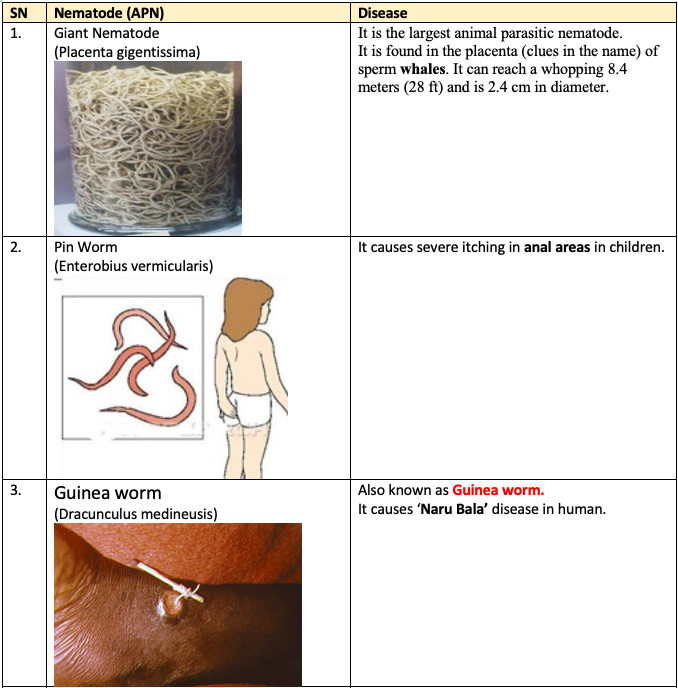

References
- Dropkin, V.H. 1980. Introduction to plant nematology. John Wiley and sons, INC. New York.
- Singh, R.S and Sitaramaiah, K. 1994. Plant pathogens. The plant parasitic nematodes. Oxford & IBH Pub. Co. Pvt. Ltd. New Delhi.
- Parvata Reddy, P. 1983. Plant nematology. Agricole Pub. Co., New Delhi.
- Southey, J. F. Laboratory methods for work with plant and soil nematodes Tech.
- Bull. Min. Agric. Fish. Food. Her Majesty’s Stationary Office, London.
- Walia, R. K and Bajaj, H. K (2014). Textbook of Introductory Plant Nematology. Directorate of Knowledge Management in Agriculture, ICAR, New Delhi.
- Kumar, V., Khan, M.R. & Walia, R.K. Crop Loss Estimations due to Plant-Parasitic Nematodes in Major Crops in India. Natl. Acad. Sci. Lett. 43, 409–412 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40009-020-00895-2
Which of the following is correct regarding nematode?
Definition
- Nematology is an important branch of biological science, which deals with a complex, diverse group of round worms known as Nematodes that occur worldwide in essentially all environments.
- A handful of soil from anywhere any part of the world, from mountain top to bottom of ocean, from tropics to arctics, from fresh water to brackish water, from soil to plant tissues and even from blood streams of humans and livestock contain nematodes.
- Therefore, Nematodes are cosmopolitan in nature.
- In light of the high population numbers of nematodes.
N.A. Cobb(1915) who is considered to be the Father of American Nematology, provided a dramatic description of the abundance of nematodes. He stated:
“In short, if all the matter …
Become Successful With AgriDots
Learn the essential skills for getting a seat in the Exam with
🦄 You are a pro member!
Only use this page if purchasing a gift or enterprise account
Plan
Rs
- Unlimited access to PRO courses
- Quizzes with hand-picked meme prizes
- Invite to private Discord chat
- Free Sticker emailed
Lifetime
Rs
1,499
once
- All PRO-tier benefits
- Single payment, lifetime access
- 4,200 bonus xp points
- Next Level
T-shirt shipped worldwide

Yo! You just found a 20% discount using 👉 EASTEREGG

High-quality fitted cotton shirt produced by Next Level Apparel