🖖🏻 Extension Concept
Learn about concept of Education, Extension Process, Pricipale and Philosophy.
Which of the following statement is wrong about extension education? 📚
Concept of Extension Education
I. The Basic Concept
The basic concept of extension is education.
Education
- Education is essential considered as
production of desirable change in behaviour. - Education causes change in
Knowledge(things known),Skill(things done) andAttitude(things felt). - “Education is the manifestation of perfection already in man” is a said by Swami Vivekananda.
- Education is shaped by
society.
Types
Formal
- Institutionalised, chronologically graded and hierarchically structured education system.
- It’s characteristic feature are Subject and target group specificity.
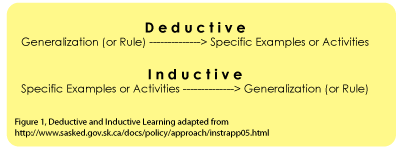
Deductiveapproach.VerticalTeaching.
Non-formal
- It is organised, systematic, educational activity carried on outside framework of the formal system to provide selected type of learning to particular sub-group in the population, adult as well as children according to their needs.
Inductiveapproach. (teacher will explain many examples showing how concept is used)- In non-formal education 6 key elements were identified by Etling, Radhakrishna & Bowen are:
- Its significant aspect is flexible curriculum.
- Teaching is
horizontal. - Learners are
heterogeneous. - Learner centred.
- Less bureaucratic control &
- More decentralization
- Ex. Agricultural Extension.
Informal
Life long processof learning happening through daily experience and exposure.
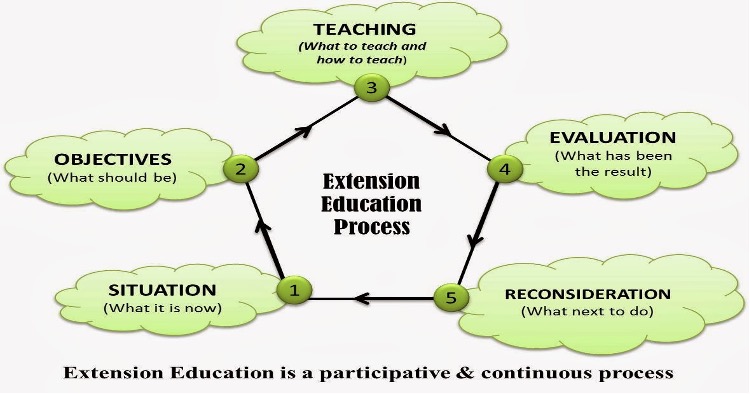
II. The Extension Education Process
- Concept given by
Leagans(1967). - It involves 5 steps:
SOTER.
Meaning of Extension Education
It is an applied science consisting of content derived from research, accumulated field experiences and relevant principles drawn from the behavioural sciences synthesised with useful technology into a body of philosophy, principles, content and methods focused on the problems of out-of-school education for adults and youths.
Agricultural Extension
- Deals with farmer.
- It is a special branch of Extension Education.
- Book entitled “Agricultural Extension” written by
Van den Ban. - Book entitled “Extension Education” written by
Dr. A. Adivi Reddy.
Scope of Extension Education
- Extension Education/Discipline:
- Educational Organisation/ Agency
- Educational Process/ Means
- Educational Job/Work
- Extension Service:
- An organisation or programme for agricultural development & rural welfare, which employs the extension process as a mean of programme implementation.
- Main responsibility of Extension Service is with
Sate Government.
- Extension Process
- Working with the rural people through out of school education along with current interest & needs for getting overall development of rural families.
- Extension Job/Profession
- The job of extension in agriculture & home economics is to assist people engaged in farming & home making to utilize full resources, solving problem and meeting socio-economics condition.
Scope of Agricultural Extension
A/Q Kelsey & Hearne, the scope of agricultural extension identified in 9 areas of programme emphasis.
- Efficiency in agricultural production
- Efficiency in marketing, distribution & utilisation
- Conservation, development and use of natural resources.
- Management on the farm & in the home
- Family living
- Youth development
- Leadership development
- Community development & rural area development
- Public affairs.
Need of Extension
To interpret the findings of research to the farmers and to carry the problems of the farmers to research for solution. This gap is filled by the extension.
Objective of Extension
- Expression of ends towards which our efforts are directed or Direction of movement towards a particular activity is known as Objective.
- There are 3 levels of objectives:
1. Fundamental Objective
All-inclusive objectivesof a society are fundamental objective.- Good life, better citizenship, democracy, better prosperity are included in fundamental objective.
- Example: People’s Participation in planning at grass root level.
2. General Objective:
- Objective which is general but more definite social objective are general objective.
- Example: Mandatory creation of Panchayat Raj bodies in the states
3. Working Objective:
-
Also known as specific objective.
-
Working objectives operates at field extension work.
-
Example: Enactment of suitable laws relating to Panchayats, holding election in time, providing funds & facilities
-
Fundamental objective of extension is the overall development of the individual or
Destination Man. -
Major objective categories as:
- Material - Increase production, income.
- Educational – change the outlook of people or develop the individual.
- Social & cultural – development of the community.
-
The ultimate obj. of
ext.is realizing ones fullest potential/change in behaviour. -
The ultimate obj. of
ext. workis the full development of an individual. -
The basic element at the
core of extension educationis man himself. -
The basic objective of
ext. ed.is to create opportunities for effective learning. -
The most important motive for extension work is
influence motivation.
Function of Extension Education:
👉🏻 To bring about desirable changes in human behaviour (KAS) by means of education.
- Change in Knowledge 👉🏻 Change in what people know
- Change in skill 👉🏻 Change in the technique of doing things
- Change in attitude 👉🏻 Change in the feelings or reaction towards certain things
Principal of Motivation in Extension
- A motive is some inner drive, impulse, intention etc. that causes or moves a person to do something or act in a certain way.
- A process of initiating a conscious and purposeful action is called as motivation.
- It is goal seeking or goal directed behaviour or activity.
- Motivation has intrinsic and extrinsic value.
- Intrinsic values are what a learner does for sake of engaging in the activity itself.
Intrinsic motivationis desirable, especially in learning because it contributes in active participation.Extrinsic motivationis an incentive or goal is artificially introduced in the situation to cause or accelerate activity.- Eg. All prize schemes are largely extrinsic in value.
Philosophy of Extension Education
- Philosophy is a body of general principles or laws of a field of knowledge.
- Term philosophy is derived from
Greeklanguage. - The basic philosophy of extension is to teach people
How to donot “What to do”. - To teach people
how to thinknot “what to think”
Which of the following statement is wrong about extension education? 📚
Concept of Extension Education
I. The Basic Concept
The basic concept of extension is education.
Education
- Education is essential considered as
production of desirable change in behaviour. - Education causes change in
Knowledge(things known),Skill(things done) andAttitude(things felt). - “Education is the manifestation of perfection already in man” is a said by Swami Vivekananda.
- Education is shaped by
society.
Types
Formal
- Institutionalised, chronologically graded and hierarchically structured education system.
- It’s characteristic feature are Subject and target group specificity.
Deductiveapproach.VerticalTeaching.
Non-formal
- It is organised, systematic, educational activity carried on outside …
Become Successful With AgriDots
Learn the essential skills for getting a seat in the Exam with
🦄 You are a pro member!
Only use this page if purchasing a gift or enterprise account
Plan
- Unlimited access to PRO courses
- Quizzes with hand-picked meme prizes
- Invite to private Discord chat
- Free Sticker emailed
Lifetime
- All PRO-tier benefits
- Single payment, lifetime access
- 4,200 bonus xp points
- Next Level
T-shirt shipped worldwide

Yo! You just found a 20% discount using 👉 EASTEREGG

High-quality fitted cotton shirt produced by Next Level Apparel