👨🏻💻 Extension Programme
Learn about Extension Programme.
Extension Programme
- According to
Kelsey and Hearne(1967), an extension programme is a statement of situation, objectives, problems and solutions (SOPS). It is relatively permanent but requires constant revision.
Situation
A statement of affairs that include the cultural, social, economic & physical conditions in which a particular group of people find themselves at a given period of time.
Problem
- Problem is a condition that the people after study, with or without outside help, have decided needs changing.
- Simple problem: If number of causes are few & easy to identify.
- Complex problem: If the problems are interrelated, causes are many & difficult to identify.
Need
- Concept of need given by
Leagan(1961) - Need implies a gap between what is, the existing situation; and what ought to be, the desired situation.
- The gap between the situation and objective is need.
Sociometric methodis most effective method in identifying real rural needs.- From a psychological standpoint, need may classified into two categories:
1. Felt Need:
- The need of which people are aware of.
- Also called consciously recognised need.
2. Unfelt Need:
- The need of which the people are not aware of at present.
- Also called unrecognized need.
Solution
- Solution is a course of proposed action to change an unsatisfactory condition to one that is more satisfying.
Vision
- Articulation of desired end results.
Aim
- Aim is generalised and broad statement of directions with respect to given activities.
- Ex. Improvement of farmers’ economic condition, increasing the average wheat yield etc.
- Aim includes several objectives & goal is a part of objective.
Objective
- Objectives are expression of the ends towards which our efforts are directed.
- Ex. To increase the average yield of wheat by from 40 quintal to 50 quintal per hectare.
- Three levels of objective:
1. Fundamental or all-inclusive objectives of society
- People’s participation in planning at the grass roots level.
2. General but more definite social objective
- Mandatory creation of Panchayat Raj bodies in the States
3. Working or specific objectives:
- Enactment of suitable laws relating to Panchayats, holding Panchayat elections in time, providing funds and facilities to the Panchayat Raj bodies etc.
- This operates at field extension work.
Goal
- Goal is distance in any direction one expects to go during a given period of time.
- Ex. To raise the yield of wheat by 5 quintals per hectare in the current year.
Principles of Extension Programme Planning
- Extension programme should be based on an analysis of the facts in a situation.
- Extension programme planning selects problems based on people’s interests and needs.
- Extension programme planning determines definite objectives and solution, which offers satisfaction.
- Extension programme planning has permanence with flexibility.
- Extension programme planning has balance with emphasis.
- Extension programme planning has a definite plan of work.
- Extension programme planning is an educational process.
- Extension programme planning is a continuous process.
- Extension programme planning is a co-ordinating process.
- Extension programme planning involves local people and their institutions.
- Extension programme planning provides for evaluation of results.
Steps in Extension Programme Planning
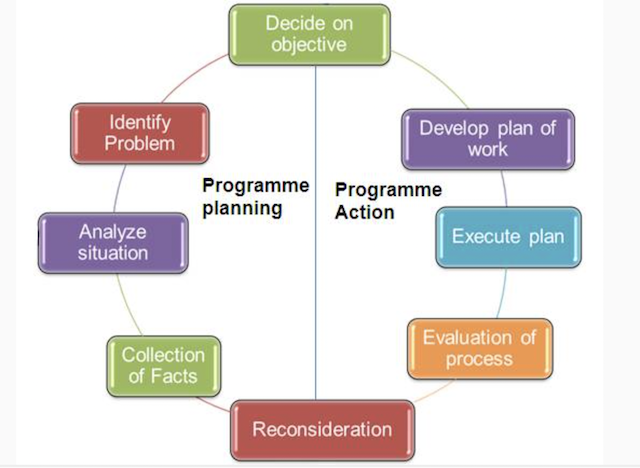
Programme Determination/ Programme Planning
1. Collection of facts
- Local situation acts a bench mark for starting programme planning.
2. Analysis of situation
- The extension work grow out of situation.
3. Identification of problems
4. Determination of objectives and goal
Programme Implementation/Programme action
5. Developing plan of work and calendar of operations
Plan of Work
- An
outline of activitiesso arranged as to enable efficient execution of the programme. - The plan of work indicates:
5Ws & 1Hi.e. what is to be done, who is to do it, how it is to be done, when & where it is to be done, who are to be served or reached and how the results will be evaluated.
Calendar of work
- It is a plan of activities to be undertaken in a
particular time sequence. - When
plan of work arranged chronologicallyis called calendar of work.
6. Follow through plan of work and calendar of work
- Execution of plan should be carried out without change.
7. Evaluation of progress
8. Reconsideration and revision of the programme
Evaluation
- Latin word: ‘valerie’ which means to be strong or valiant.
- It is measuring performance against predetermined goals.
- Evaluation of any programme should be based on objectives of the programme.
- Purpose of evaluation is to identify strong and weak points and to identify gaps and errors.
- The main objective of evaluation in extension is to facilitate effective decision making without jumping to conclusion.
- Evaluation carried during project is known as
process evaluation.
Evaluation of Extension Programmes
- Evaluation is the process by which the effectiveness of extension is assessed. It is more than simply finding out what happened; it involves passing judgement on what happened. Was the outcome of the programme good enough? Was it better or worse than expected? Could more have been achieved?
- The evaluation of agricultural extension programs implies the systematic collection of information about the activities, characteristics, and outcomes of a program to make judgments about the program, improve its effectiveness, and/or inform decisions about future programming.
Objectives of Evaluation
- To know the causes for success or failure of the programme, along with identifying the obstacles for success in the programme
- To inspire the workers for the evaluation of their objectives
- To know the merits and demerits of the programme
- To increase the self-confidence in both the rural people and extension worker
- To unearth the expenses and achievements of a programme
- To find out the usefulness of new experimental teaching methods
Extension Programme
- According to
Kelsey and Hearne(1967), an extension programme is a statement of situation, objectives, problems and solutions (SOPS). It is relatively permanent but requires constant revision.
Situation
A statement of affairs that include the cultural, social, economic & physical conditions in which a particular group of people find themselves at a given period of time.
Problem
- Problem is a condition that the people after study, with or without outside help, have decided needs changing.
- Simple problem: If number of causes are few & easy to identify.
- Complex problem: If the problems are interrelated, causes are many & difficult to identify.
Need
- Concept of need given by
Leagan(1961) - Need implies a gap between what is, the existing situation; and what …
Become Successful With AgriDots
Learn the essential skills for getting a seat in the Exam with
🦄 You are a pro member!
Only use this page if purchasing a gift or enterprise account
Plan
- Unlimited access to PRO courses
- Quizzes with hand-picked meme prizes
- Invite to private Discord chat
- Free Sticker emailed
Lifetime
- All PRO-tier benefits
- Single payment, lifetime access
- 4,200 bonus xp points
- Next Level
T-shirt shipped worldwide

Yo! You just found a 20% discount using 👉 EASTEREGG

High-quality fitted cotton shirt produced by Next Level Apparel