🙇♂️ Teaching
Learn teaching and learning process, elements of learning situation, principles of learning.
Which one of the following is not a Principles of learning?
Teaching & Learning in Process
- Extension is an educational process
to bring about desirable changes. - Essential role of an extension worker is to create effective learning situations.
Elements of Learning Situation
- Essential elements of effective learning are five in number.
- Teacher or instructor
- Teaching materials and Plan
- Subject matter
- Learner
- Physical facilities and environment
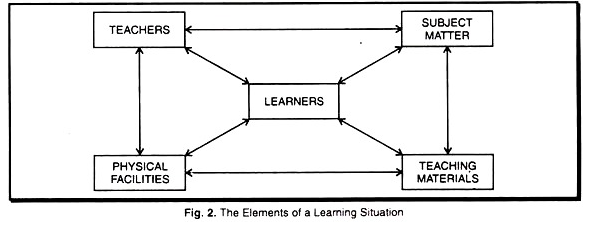
- Out of these 5 elements
learneris the most important element. - The central element in an effective learning situation is
learner. - Out these maximum interaction with the learner is done by
instructor.
Teaching
- The process of arranging situation in which the things to be learned are called to the attention of the learners, there interest developed, desire aroused and action promoted is called teaching.
- In extension teaching the teacher should first know
attitude of the learner. - Effective teaching is not merely to inform people but
to transforming people.
Learning
- The relatively enduring change in overt and covert responses as a result of perceived stimulus is called Learning.
- Learning is the process of acquiring or imparting the ability to perform a behavioural pattern through experience and practice.
- The process by which an individual, through one’s own efforts & abilities change the behaviour is known as learning.
- Learning is an internal process mainly controlled by learner.
- Learning is motivated by self.
- Learning is most rapid by maximizing concentration on one sense at a time.
- Bond theory or Stimulus - Bond or SR theory of learning is advocated by
E.L. Thorndike. - The progressive behaviour adaptation of an individual to a stimulus is called learning.
- Father of learning: Thorndike.
- The learning curve in teaching follows a
S shaped curve.
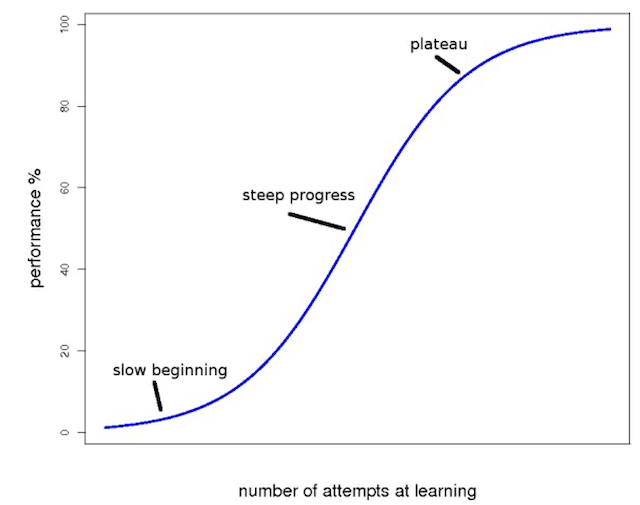
- The experimental technique of learning emphasis on use of
stimulation games. - Experimental learning is learner centred.
- Learning that suddenly appears when a reward or incentive for performance is given is known as
Latent learning. - Learning occurs through various senses shown by Haas & Packer (1964)
- Sight: 87%
- Hear: 7%
- Smell: 3.5%
- Touch: 1.5%
- Taste: 1%
Principles of learning
1. Principle of association
- Learning is growth like and continuous
- New learning may be associated with the previous successful & satisfying responses.
- Example: If the farmers have obtained profitable return by the application of nitrogenous fertilizer, they may be motivated to use balanced fertilizer containing phosphate & potash, for still higher return.
2. Principle of disassociation
- Learning is affected by emotions.
- For effective learning, undesirable responses are to be eliminated. The most effective way of eliminating an undesirable response is to set up a desirable substitute, which must be made more satisfying than the original (undesirable) reaction.
- Ex. Discouraging the application of chemical fertilisers and advocating organic farming.
- Ex. Planting a crop in lines gives better yield, the farmers may be advised not to practice broadcasting.
3. Principle of Clarity of objectives
- The objective of learning should be clear. The ease of learning seems to vary directly with the meaningfulness of the material presented. Meaningful learning is interesting & easier than senseless learning.
- Learning must makes sense to the learner. Learning is purposeful.
- Ex. When farmers use their crop loan only for growing crops, they are clear about the objective of getting loan. This clear understanding enable farmer to learn about proper utilization & repayment of loans & take further loans if necessary, for economic development.
4. Principle of self-activity
- The door to learning is “locked on the inside” and unless the learner opens the door himself, learning cannot take place.
- Conducting demonstration by the farmers in their own field provides opportunity of self-activity i.e.
learning by doing. This makes learning effective & permanent.
5. Principle of Readiness
- Learning must be challenging and satisfying
- Learning takes place more effectively when one is ready to learn.
- Example: When farmers are ready to cooperate, with good guidance, they may be able to form a cooperative society.
6. Principle of Satisfyingness (Reward)
- A satisfying after-effect reinforces learning.
- Example: Crops grown during the rabi-summer season give higher economic return & higher level of satisfaction to the farmers. Farmers learn to invest more & take more care for crops during the season.
7. Principle of transfer
- Application of perceived relationship to another situation in which it is applicable.
- Example: If a farmer has learned the technique of water management in a particular crop, they should be able to use this method in other crop as well. This shall spread the effect of learning.
8. Principle of Motivation
- Motivation or drive means stimulation towards action. Without motivation an organism does not behave & hence does not learn. The practice recommended must be motivating for learning to takes place.
- Example: The favourable experience of planting trees motivates tribal farmers to collect samplings from the forest nursery.
9. Principle of set or attitude
- An unfavourable attitude or set retards learning & a favourable attitude accelerates it. Unless attitude becomes favourable, adoption will not take place.
- Example: When a farmer develops a favourable attitude towards scientific treatment of cattle, they shall learn the importance of this type of treatment for animals.
10. Principle of practice (law of exercise)
- Perfection is seldom achieved without practice. The practice must be correct, otherwise there will be wrong learning. The attainment of perfection demands that undesirable and useless movements are replaced by desired and useful movements.
- Learning must result in functional understanding.
- Example: Learning to use a sprayer correctly requires repeated trying of the instrument.
11. Principle of timing
- Other things being equal, learning takes place more readily when there is introduction of a topic or skill at a time when it can be used in some serviceable manner.
- Example: Issue of advertisement regarding public health and sanitation at the onset of an epidemic outbreak.
- Example: When insects have appeared or are likely to appear in crops, farmers shall learn about plant protection.
- When inspection appeared or is likely to appear in crop, farmers should be ready to learn about plant protection.
12. Principle of Environment
- Learning is affected by physical and social environment.
- Teacher should recognise and utilise the social environment.
- Physical factors where learning is to be done (like seating arrangement).
Steps in Extension Teaching
- Given by
Wilson & Gallup(1955). - Steps shortly called
AIDCAS.
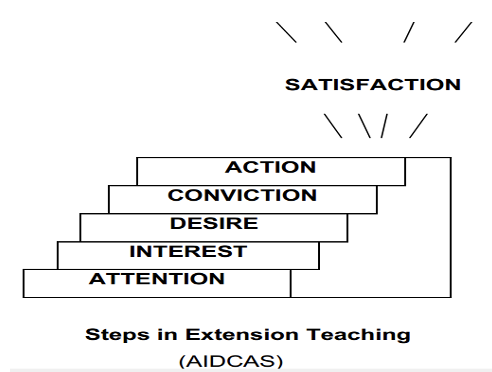
Attention
- The first step in extension teaching which aims to make people aware of new ideas & practices.
Desire
- Unfreezing the existing behaviour & motivating the people for change.
Conviction
- The stage of strong persuasion so as to convince the people about the applicability of the new idea or practice in their own situation.
Action
- It is the stage of putting the ideas or practice into operation.
Which one of the following is not a Principles of learning?
Teaching & Learning in Process
- Extension is an educational process
to bring about desirable changes. - Essential role of an extension worker is to create effective learning situations.
Elements of Learning Situation
- Essential elements of effective learning are five in number.
- Teacher or instructor
- Teaching materials and Plan
- Subject matter
- Learner
- Physical facilities and environment

- Out of these 5 elements
learneris the most important element. - The central element in an effective learning situation is
learner. - Out these maximum interaction with the learner is done by
instructor.
Teaching
- The process of arranging situation in which the things to be learned are called to the attention of the learners, there …
Become Successful With AgriDots
Learn the essential skills for getting a seat in the Exam with
🦄 You are a pro member!
Only use this page if purchasing a gift or enterprise account
Plan
Rs
- Unlimited access to PRO courses
- Quizzes with hand-picked meme prizes
- Invite to private Discord chat
- Free Sticker emailed
Lifetime
Rs
1,499
once
- All PRO-tier benefits
- Single payment, lifetime access
- 4,200 bonus xp points
- Next Level
T-shirt shipped worldwide

Yo! You just found a 20% discount using 👉 EASTEREGG

High-quality fitted cotton shirt produced by Next Level Apparel