📟 rDNA Technology
PCR-technology, Steps In PCR
Processes of Recombinant DNA Technology
- The DNAs which are to be used as passenger DNA and the vehicle DNA are extracted out of their cells by lysing the cells with the suitable enzyme.
- The extracted DNAs are isolated from other cell contents by ultra-centrifugation and purified.
- Amplification of gene of interest using
PCR.
PCR-technology
- Polymerase chain reaction technology.
- This technique was invented by
Kary Mullis(1933). - In 1993 Karry Mullis got Nobel Prize for PCR (for chemistry).
- PCR is a method for amplifying a specific region of DNA molecule without the requirement for time consuming cloning procedures.
- PCR reaction takes place in
Eppendrof tube.

- Using PCR-technique very low content of DNA available from samples of blood or semen or any other tissue or hair cell can be amplified many times and analysed. In the technique Taq-polymerase is used Taq polymerase enzyme is used in PCR which is a special type of DNA polymerase enzyme which is resistant to high temperature.
Taq Polymeraseis isolated from Thermus aquaticus bacterium- Some other examples of polymerase which are used in PCR are:
- Pflu Polymerase - Isolated from Pyrococus furiosus bacterium
- Vent Polymerase - Isolated from Thermococcus litoralis bacterium
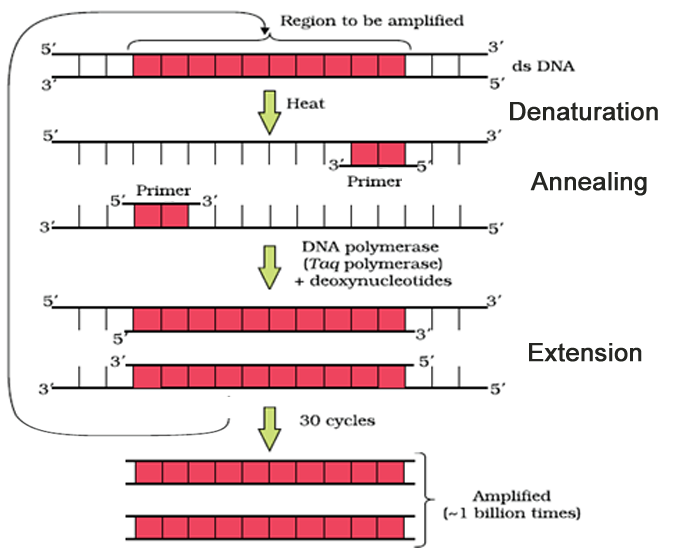
Steps In PCR
- Denaturation: (
94°C) In this step a double stranded DNA molecule is plated at 94°C. So double stranded DNA becomes single stranded & each single stranded DNA functions as a template. - Annealing: (
54°C) In this step two primer DNA are attached at 3’ end of single stranded DNA. - Extension: (
72°C) In this process taq polymerase enzyme synthesize DNA strain over template. PCR is automatic process because taq polymerase enzyme is heat resistant.
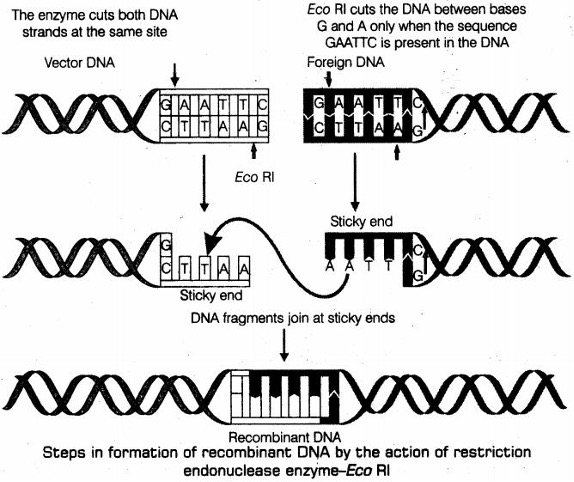
- Both the passenger and vehicle DNAs are then, cleaved by using the same restriction endonuclease so that they have complementary sticky ends.
- The complementary sticky ends of the passenger and vehicle DNAs are joined with ligase enzyme. This gives rise to a
recombinant DNA.
- The recombinant DNA is now inserted into a host cell such as Escherichia coli. The bacteria to be used as hosts should be without plasmids.
- The host cells are treated with calcium chloride or lysozyme. It creates transient (temporary) pores in their wall and makes the latter permeable to recombinant DNA.
- The recombinant DNA is added to the culture in which such bacteria are growing. The recombinant DNA is taken up by the bacteria. It replicates when the host bacteria divide and give rise to multiple copies of recombinant DNA.
Gene Cloning
- Gene cloning is isolating a gene and process of producing identical copies or technique of genetic engineering by which a gene sequence with many identical copies is replicated.
- E. coil is a bacterium used in genetic engineering for its small size.
Recombinant DNA technology
- Technology of DNA molecules means the joining or recombining of two pieces of DNA from two different species. The techniques allow an investigator to biological purify (clone) a gene from one species by inserting it into the DNA of another species, where it is replicated along with the host DNA.
- By using recombinant DNA technology,
Opaque-2 geneis transferred to maize genotype, which is responsible for higher amount of lysine in maize and produce varieties i.e.Ratan,Shakti,Protina. - Gene bank is a group of genes or cloned DNA fragments.
Processes of Recombinant DNA Technology
- The DNAs which are to be used as passenger DNA and the vehicle DNA are extracted out of their cells by lysing the cells with the suitable enzyme.
- The extracted DNAs are isolated from other cell contents by ultra-centrifugation and purified.
- Amplification of gene of interest using
PCR.
PCR-technology
- Polymerase chain reaction technology.
- This technique was invented by
Kary Mullis(1933). - In 1993 Karry Mullis got Nobel Prize for PCR (for chemistry).
- PCR is a method for amplifying a specific region of DNA molecule without the requirement for time consuming cloning procedures.
- PCR reaction takes place in
Eppendrof tube.

- Using PCR-technique very low content of DNA available from samples of blood or semen or any other tissue or hair cell can be …