⨵ Cell Division
Learn about Cell Division.
Cell Division
- Cell is the functional and structural unit of living organism.
- Cell is the basic unit of life.
- All the cell originates by cell division in existing cell. The division of chromosomes and cytoplasm of a cell into daughter cells is called cell division.
- Karyokinesis: Means Division of Nucleus
- Cytokinesis: Means Division of cytoplasm
Cell division cycle
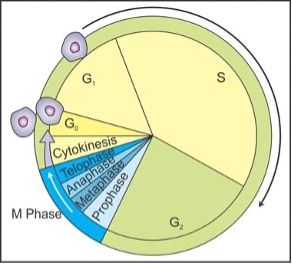
- S-phase: Synthesis phase
Synthesis of DNA/ Replication of DNA/Doubling of DNA occurs.- DNA doubles at Interphase of mitosis & Pre-meiotic interphase.
- G : Means gap
- G1 : Synthesis of RNA & Protein. It is pre DNA phase. It is resting phase.
- G2 : Post DNA synthesis phase. Here planning of cell division occurs.
- Metabolically the most active stage is
Inter phase. - Karyokinesis takes less than one hour in most of the cases.
- There are five types of cell division:
- Amitosis (no - Thread or Chromosome) means chromosome does not appear and cell divides directly i.e. direct nuclear division e.g. Fission (bacteria), budding (yeast)
- Endomitosis or C-mitosis (Colchicine).
- Chromosome doubling is not followed by cell plate formation.
- Colchicine is a chemical which stops the spindle fiber formation & induces
polyploidy. - Colchicine is obtained from Colchicum luteum (family liliaceae)
- Brachymeiosis: Nucleus divides thrice. First and third division are reductional and 2nd is mitosis. Discovered by Claussen e.g. Ascospores formation in Ascomycetes.
Mitosis
- Takes place in
both vegetative and reproductive cells. - Nucleus and cytoplasm divide once.
Twogenetically identical cells are formed.- “Mitosis” was used firstly by
Walter Flemmingin 1882.
Meiosis
- Takes place in
reproductive cells. - Nucleus and Cytoplasm: divide twice.
Fourgenetically but not identical cells are formed.- Meiosis means separation of chromosomes in sex cells.
- Chromosomes split longitudinally only once.
- Chromosome number is
reduced to half. - Discovered by
Strasburger. - The term ‘meiosis’ (reductional division) was given by Farmer & Moore.
- Neurospora: Used in genetic studies because
- All the products of meiosis are within the same sac.
- Neurospora has a short life cycle.
- Asynapsis: Not allow to pair with homologous chromosomes and remain unpaired due to presence of gene.
- Desynapsis: Chromosomes actually paired during diakinesis, chiasma falling apart due to presence of genes.
Cell Division
- Cell is the functional and structural unit of living organism.
- Cell is the basic unit of life.
- All the cell originates by cell division in existing cell. The division of chromosomes and cytoplasm of a cell into daughter cells is called cell division.
- Karyokinesis: Means Division of Nucleus
- Cytokinesis: Means Division of cytoplasm
Cell division cycle

- S-phase: Synthesis phase
Synthesis of DNA/ Replication of DNA/Doubling of DNA occurs.- DNA doubles at Interphase of mitosis & Pre-meiotic interphase.
- G : Means gap
- G1 : Synthesis of RNA & Protein. It is pre DNA phase. It is resting phase.
- G2 : Post DNA synthesis phase. Here planning of cell division occurs.
- Metabolically the most active stage is
Inter phase. - Karyokinesis takes less than one hour in …
Become Successful With AgriDots
Learn the essential skills for getting a seat in the Exam with
🦄 You are a pro member!
Only use this page if purchasing a gift or enterprise account
Plan
Rs
- Unlimited access to PRO courses
- Quizzes with hand-picked meme prizes
- Invite to private Discord chat
- Free Sticker emailed
Lifetime
Rs
1,499
once
- All PRO-tier benefits
- Single payment, lifetime access
- 4,200 bonus xp points
- Next Level
T-shirt shipped worldwide

Yo! You just found a 20% discount using 👉 EASTEREGG

High-quality fitted cotton shirt produced by Next Level Apparel