📔 Seed Classes
Classes, Improved Seed, Seed Moisture
Seed Classes
👉🏻 There are four generally recognized classes of seeds. They are
- Breeder seed
- Foundation seed
- Registered seed
- Certified seed
- The basis of seed multiplication of all notified varieties/hybrids is the Nucleus seed.
- In India, normally 3 generation system seed are produced.
Definition of seed classes
Nuclear seed
- This is the hundred percent genetically & physical pure seed and produced by the original breeder/Institute/State Agriculture University (SAU) from basic nucleus seed stock.
- Obtained by process of mass selection.
- A
pedigree certificateis issued by the producing breeder.
Breeder seed
- The progeny of nucleus seed multiplied in large area as per indent of Department of Agriculture and Cooperation (DoAC), Ministry of Agriculture, Government of India, under supervision of plant breeder / institute / SAUs and monitored by a committee consisting of the representatives of state seed certification agency, national / state seed corporations, ICAR nominee and concerned breeder.
- This is also hundred percent physical and genetic pure seed for production of foundation seed.
- A
Golden Yellow Colourcertificate is issued for this category of seed by the producing breeder. UPPSC 2021 - Breeder seed is exempted from certification. FCI AGM 2021
- 12 cm x 6 cm

Foundation seed
- Produced from breeder seed and is the source of all other certified seed classes either directly or through registered seed. It is also known as
Mother Seed. - It is always produced by certain organizations viz. National Seeds Corporation (mainly), Tarai Development Corporation (TDC) and State Seed Corporation (SSC).
- lt is produced on Government Farms, at experiment stations, Agriculture Universities or on cultivator’s field under strict supervision of research scientists and experts from NSC or SSC. lt has specific genetic identity and purity.
- A
White Colourcertificate is issued for foundation seed by seed certification agencies. UPPSC 2021 - 15 cm x 7.5 cm

Registered seed
- Produced from FS or Registered seed itself. lt is the parent of certified seed or RS.
- It has satisfactory genetic identity and purity and is usually produced by progressive farmers under technical guidance and supervision from SSC.
- In India, it is often omitted and certified seed is produced directly from FS.
- A
Purple Colourcertificate is issued for this category of seed.
Certified seed
- Progeny of RS, FS or CS itself. lt has satisfactory genetic identity and purity.
- lt is approved and certified by the state seed certifying agency (SSCA), annually produced by progressive farmers according to standard seed production practices.
- lt is available for general distribution to farmers for commercial crop production.
- lt is generally produced by SSC but NSC also undertakes its production, if required.
- This is the commercial seed which is available to the farmers and its genetic purity should be 99 per cent.
- 15 cm x 7.5 cm
- Two classes of CS are produced i.e. F1 and F2.
- Recertification is not permitted form F2 generation (Second) of seeds.
Azure Blue Colourcertificate is issued by seed certification agency for this category of seed. UPPSC 2021

👉🏻 Other types of seeds in Agronomic use are:
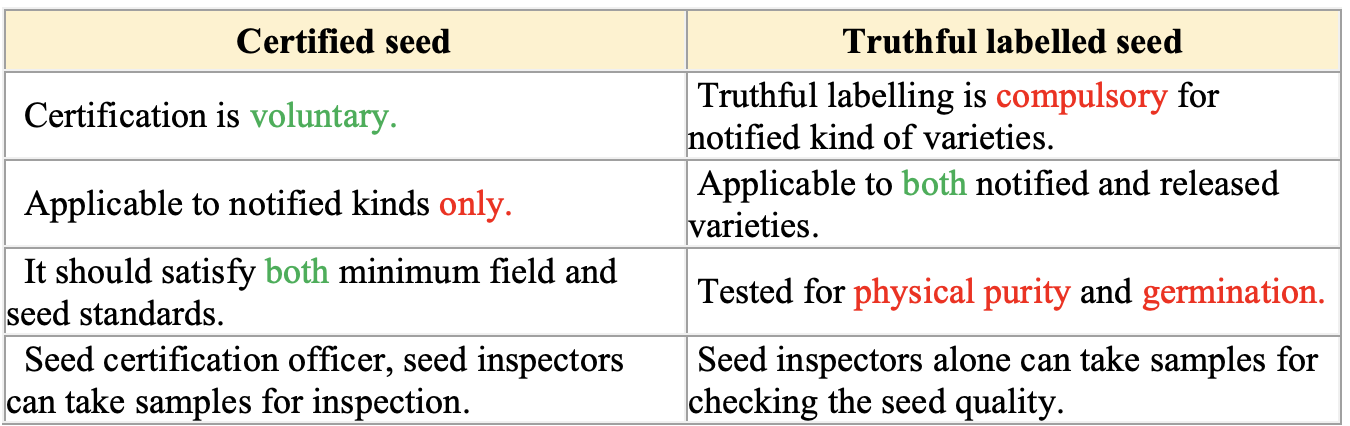
Truthfully Labeled Seed (TFL)
- It is the seed offered for sale after testing germination percentage and physical purity etc.
- It is not a certified seed, as there is no inspection carried out by the certified person.
- There is no colour tag for TFL seed.
Improved seed
- It is a better seed substitute for pure seed but is not so good with respect to genetic and physical factors. It has at least 10-15% more genetic potential than the local seed and are resistant to pest and diseases, well adapted to agro-climatic conditions of the locality, high in response to better condition of growth.
- Hybrid seed
- Composite seeds
- Mutant seeds
Attributes of International Seed Analysis Certification
Seed Moisture
- Germination occurs when seed moisture is above 40-60%.
- The moisture determination in seeds by:
- Traditional bite test
- Electrical moisture meters
- Infra-red moisture meters
- Oil distillation method
- The lab. Oven method
- Karl Fisher reagent method
Seed Classes
👉🏻 There are four generally recognized classes of seeds. They are
- Breeder seed
- Foundation seed
- Registered seed
- Certified seed
- The basis of seed multiplication of all notified varieties/hybrids is the Nucleus seed.
- In India, normally 3 generation system seed are produced.
Definition of seed classes
Nuclear seed
- This is the hundred percent genetically & physical pure seed and produced by the original breeder/Institute/State Agriculture University (SAU) from basic nucleus seed stock.
- Obtained by process of mass selection.
- A
pedigree certificateis issued by the producing breeder.
Breeder seed
- The progeny of nucleus seed multiplied in large area as per indent of Department of Agriculture and Cooperation (DoAC), Ministry of Agriculture, Government of India, under …
Become Successful With AgriDots
Learn the essential skills for getting a seat in the Exam with
🦄 You are a pro member!
Only use this page if purchasing a gift or enterprise account
Plan
Rs
- Unlimited access to PRO courses
- Quizzes with hand-picked meme prizes
- Invite to private Discord chat
- Free Sticker emailed
Lifetime
Rs
1,499
once
- All PRO-tier benefits
- Single payment, lifetime access
- 4,200 bonus xp points
- Next Level
T-shirt shipped worldwide

Yo! You just found a 20% discount using 👉 EASTEREGG

High-quality fitted cotton shirt produced by Next Level Apparel