🕸 Seed Dormancy
Types, Causes, Seed Storage
Seed Dormancy
- Dormancy is the arrested development and reversible rest period of plant organs either of a seed or of any vegetative part.
Causes of Dormancy
Innate Dormancy (Primary / Endogenous Dormancy)
- This type of dormancy is imposed by factors
insidethe embryo. - It is different from quiescence stage. A seed which is just waiting for favourable environmental condition to germinate is called Quiescent seed.
Enforced Dormancy (Secondary / Exogenous Dormancy)
- This type of dormancy is imposed by factors
outsidethe embryo.
Physiology of Dormancy
- The formation of dormant structures is commonly associated with the suspension of metabolic, synthetic and morphogenetic activities that are associated with the minimum physiological and a minimum moisture content.
- During this period, there is very poor or total suspension of respiration or rather anaerobic respiration with higher respiration quotient (infinite).
- Dormancy is due to lack or inactivity of hydrolytic enzymes.
Gibberellinsare the predominant germination agents found in the germination phase during the food reserve degradation stage.- Cytokinis exert their influence later on the initiation of cell proliferation and expansion.
- Red light (660 μm) promotes and blue especially far-red light (735 μm) inhibits germination.
Causes of Dormancy
- Hard Seed coat
- Seed coats being impermeable to water
- Seed Coat being impermeable to oxygen
- Rudimentary embryo of seeds
- Dormant embryo
- Synthesis and accumulation of germination inhibitors in the seeds.
Methods of Breaking Seed Dormancy
Physical Treatment
- Scarification: Dehusking or removal of seed coats by
rubbingto make it permeable to water.
- Stratification: NABARD 2021
Low temperaturetreatment at 2-8 °C for 12-24 hours but Seeds should be presoaked for 36 hours before they are given the low temperature treatment.
- Heat treatment at 40-45° C for different duration.
- Alternate heating and cooling for several times.
- Alternate drying and wetting for several times.
- Exposure for 24 hours of water-soaked seeds to red light for 1-2 hrs. at 15-25°C temperature.
Chemicals
- Inorganic Chemicals:
- By acid treatment: Dilute solutions of HNO3, HCl or H2SO4 (0.10 - 0.5%) for different durations in minutes.
- Potassium Nitrate (KNO3) @1-3%: Strongest and used for immediate dormancy break after harvesting; NH4NO3 (1-3%), H2O2, H3BO4 etc. Ex. Rice, Tomato, Chilies etc.
- By gases: by increasing O2 concentration.
- Organic Chemicals:
- Non-hormonal: Thiourea, Ascorbic acid.
- Hormonal: GA3 (1-1000 ppm) — Commonly used hormone to break dormancy; Others are Kinetin (1-100pm), Ethylene (Ethrel solution of 100-300 ppm).
Seed Storage
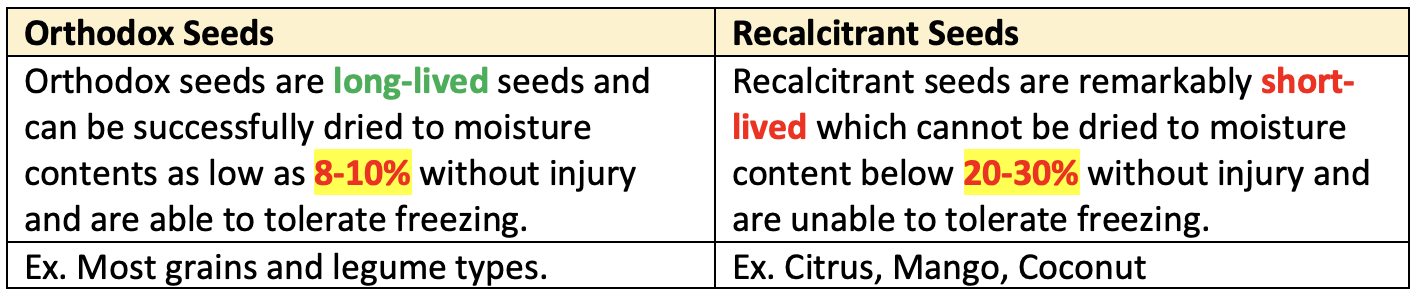
- Cryopreservation: Non-orthodox seeds are stored at
-196°Cthe temperature of liquid nitrogen.

- Dehumidification: Removal of water - vapour from the air in storage.
Silica gelis the most common desiccant used as chemical dehumidifier. - Tempering: Process of bringing grains or other products to a desired moisture or temperature for processing.
- Matrical is the heterogeneity in the quality due to location of the seeds in the inflorescence e.g. difference in flowering pattern.
- Acclimatization: The process that leads to adaptation of a variety, line or population to a new environment is known as Acclimatization.
Seed Dormancy
- Dormancy is the arrested development and reversible rest period of plant organs either of a seed or of any vegetative part.
Causes of Dormancy
Innate Dormancy (Primary / Endogenous Dormancy)
- This type of dormancy is imposed by factors
insidethe embryo. - It is different from quiescence stage. A seed which is just waiting for favourable environmental condition to germinate is called Quiescent seed.
Enforced Dormancy (Secondary / Exogenous Dormancy)
- This type of dormancy is imposed by factors
outsidethe embryo.
Physiology of Dormancy
- The formation of dormant structures is commonly associated with the suspension of metabolic, synthetic and morphogenetic activities that are associated with the minimum physiological and a minimum moisture content.
- During this period, there …
Become Successful With AgriDots
Learn the essential skills for getting a seat in the Exam with
🦄 You are a pro member!
Only use this page if purchasing a gift or enterprise account
Plan
Rs
- Unlimited access to PRO courses
- Quizzes with hand-picked meme prizes
- Invite to private Discord chat
- Free Sticker emailed
Lifetime
Rs
1,499
once
- All PRO-tier benefits
- Single payment, lifetime access
- 4,200 bonus xp points
- Next Level
T-shirt shipped worldwide

Yo! You just found a 20% discount using 👉 EASTEREGG

High-quality fitted cotton shirt produced by Next Level Apparel