🍯 Seed Treatment
Methods, Types, Examples
Seed Treatment
👉🏻 Besides breaking seed dormancy, seed treatment is also done before sowing the seeds for the following purposes:
- To protect from seed borne diseases and insect pests damage
- To promote quick germination by breaking dormancy
- To have convenience in sowing. Ex. removing fuzz in cotton with conc. H2SO4
- To hasten nitrogen fixation capacity in case of pulses. Ex. Rhizobium culture.
- To induce earliness (Vernalization treatment)
Treatment for Diseases and Insects control
(a) Physical treatment
- (i) Hot water treatment: Seeds are kept in hot water at a certain temperature for certain period. Later on, after cooling in cold water such seeds are dried in shade. This method is successful in controlling following diseases:
- Loose smut of Wheat (54°C for 10 minutes)
- Loose smut of Barley (54°C for 13 minutes)
- Alternaria blight of Wheat (38°C for 10 minutes)
- Leaf spot of Til (54°C for one hour)
- (ii) Solar heat treatment: After soaking the seeds in water for some hours, seeds are dried in scorching sun in the month of May-June by keeping on cemented floor or metal-sheet. This method is used to control loose smut of Wheat and Barley. (Loothrs and Satar)
(b) Chemical treatment
- Different fungicides e.g. Agrosan G.N., Ceresan, Captan, Thiram etc. are used for the same.
(B) Seed Inoculations in Legumes
- Before sowing the legumes crops in the new area, the legume seeds are to be inoculated with Rhizobium culture.

Treatment in Important Crops
- Sorghum: Thirum or 300 mesh sulphur: Seed is coated in seed dressing drum or earthen pot @ 3.4 g/kg seed against smut disease.
- Pear Millet: Brine solution treatment is given @ 20 per cent against eargot and to discard light & diseased seed.
- Paddy: Seed is treated with brine solution @ 3 per cent against blast of paddy and to discard unfilled seed.
- Wheat & Oilseed crops: Seed is coated with Thirum or Bavistin @ 5 g/ kg seed against seed borne diseases.
- Cotton: Seed is treated with organo mercurial compound like Ceresan, Agrosan @ 3 g or Thirum @ 5g against seed borne disease like anthracnose.
- Small seeded crops like Sesamum, bajra, tobacco, etc; Seed is mixed with fine sand or soil for even sowing of seed in the field.
- Potato:
- Seed is dipped in 1 per cent
Thioureasolution for breaking the seed dormancy. - Seed is dipped in streptomycin solution @200 g in 100 lit. Water for 1 hour against Ring rots disease.
- Seed is dipped in 1 per cent
- Legume crops like Mung, Urd, Soybean etc.
- Seed is treated with Thirum @3 g/kg seed against seed borne disease.
- Seed is treated with Rhizobium culture @ 250g/10kg seed for ‘N’ fixation & better nodulation.
- Sugarcane:
- Hot water treatment (50°C) or hot air treatment (54°C) is given to sets for 2 hrs. Against grassy shoot & other diseases.
- Sets are treated with OMC 6 per cent @ 500g in 100 lit. Water by dipping for 5 min. against smut & increase germination or Bavistin @ 200g in 100 lit. for 5 min.
Seed Plot technique of Potato
- It was given by
Pushkarnathin 1967. Objective: - To produce seeds
free from virusY, A, X and S. These viruses are transmitted by aphids. - Aphid population is low in hills during April to August while it is low in the plains during October to early January.
- Nucleus seed of potato is produced in the hills during April to August when aphid population is low.
- It is brought to plains and is stored in cold-storage for planting the seed crop in October.
- The seed production practices are:
- Start with disease free seed stock
- Select suitable location i.e. aphids free during crop growth
- Adopt lands isolation and other requirement of certified seed production
- Rogueing and inspection of crops
- Other good crop management
Indian Seed Industry
- Seed is the critical determinant of agricultural production on which depends the performance and efficacy of other inputs.
- Quality seeds appropriate to different agro-climatic conditions and in sufficient quantity at affordable prices are required to raise productivity.
- Quality seed alone increase in the productivity at least 10-15% (ICAR 1993).
- The Indian seed industry is the eighth largest in the world.
- First private seed company:
Sutton and Sons(Existence in 1912 in Kolkata) - Indian seed industry annual growth rate of 12% to 13 %.
- The Planning Commission in its Mid-Term Appraisal of the 10th Five Year Plan (2002-07) has concluded as follows with regard to seeds:
“Despite a huge institutional framework for seed production both in the public and private sector, availability of good quality seeds continues to be a problem for the farmers. As a result, they prefer to rely on farm saved seeds; seed replacement rate continues to remain in the range of 2-10 per cent in certain states for certain crops, which is much below the desired level of 20 per cent for most crops. As is well known, seed replacement rate has a strong positive correlation with the productivity and production of crops. There is a need to rejuvenate the seeds sector through revamping the public sector seed companies, including the State Seed Corporations”.
- The desirable seed replacement rates, without which it is not possible to achieve higher productivity are 25% for self-pollinated crops, 35% for cross pollinated crops and 100% for hybrids.
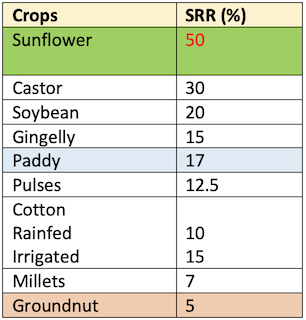
Seed Replacement Rate of Select Crops
- Seed Replacement Ratio denotes how much of the total cropped area was sown with certified seeds in comparison to farm saved seeds.
- It also denotes actual quality seed distributed to farmers vis-a-vis actual seed required for cultivation of crops.
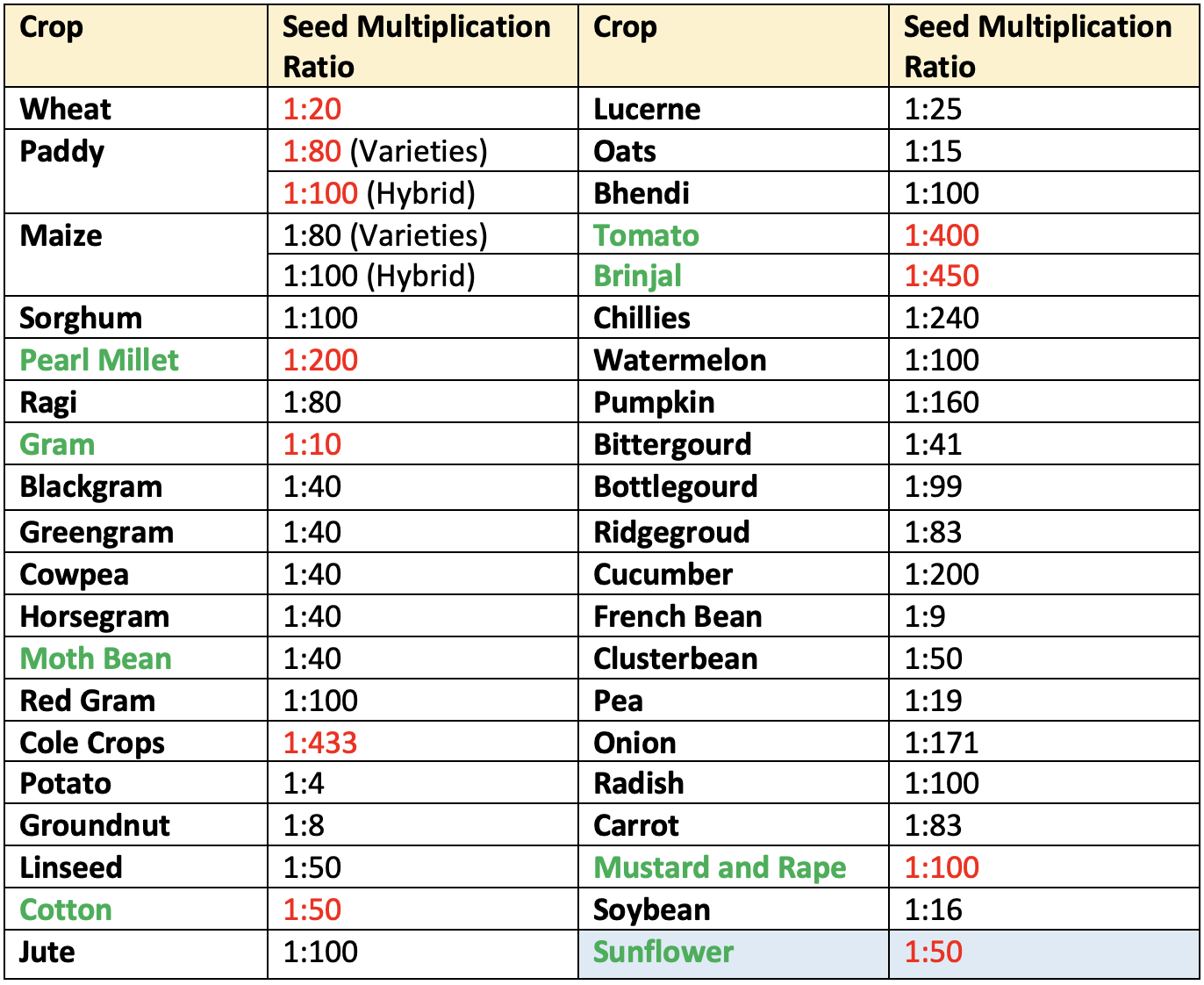
Seed Multiplication Ratio
👉🏻 It is the number of seeds to be produced from a single seed when it is sown and harvested.
Seed Treatment
👉🏻 Besides breaking seed dormancy, seed treatment is also done before sowing the seeds for the following purposes:
- To protect from seed borne diseases and insect pests damage
- To promote quick germination by breaking dormancy
- To have convenience in sowing. Ex. removing fuzz in cotton with conc. H2SO4
- To hasten nitrogen fixation capacity in case of pulses. Ex. Rhizobium culture.
- To induce earliness (Vernalization treatment)
Treatment for Diseases and Insects control
(a) Physical treatment
- (i) Hot water treatment: Seeds are kept in hot water at a certain temperature for certain period. Later on, after cooling in cold water such seeds are dried in shade. This method is successful in controlling following diseases:
- Loose smut of Wheat (54°C for 10 minutes)
- Loose smut of …
Become Successful With AgriDots
Learn the essential skills for getting a seat in the Exam with
🦄 You are a pro member!
Only use this page if purchasing a gift or enterprise account
Plan
- Unlimited access to PRO courses
- Quizzes with hand-picked meme prizes
- Invite to private Discord chat
- Free Sticker emailed
Lifetime
- All PRO-tier benefits
- Single payment, lifetime access
- 4,200 bonus xp points
- Next Level
T-shirt shipped worldwide

Yo! You just found a 20% discount using 👉 EASTEREGG

High-quality fitted cotton shirt produced by Next Level Apparel