😡 Seed Viability
Viability Test, Isolation Distance
Seed Viability
- Viability of seeds represents the capacity of the seed to germinate.
- Viability is defined as the capacity of the seed to remain capable of germination for some specific period of the time. A Seed vigour is the ability of seed to emerge in varying environments of fields.
Methods for Viability Test of Seeds
1. Electrical Conductance Method
- The seeds are soaked in distilled water and the electrical conductance of the bathing solution is tested, the increase in conductance (Less resistance) is roughly proportional to the percentage of dead tissues.
- The increase in the conductivity is due to leaching of metabolites from dead seeds which become pervious owing to increasing permeability.
2. Potassium Permanganate Method
- The seeds are soaked in a weak solution of potassium permanganate and as the proportion of dead seed increases the discoloration of the solution also increase.
- The dead cells become freely permeable to their contained solutes which leach out easily into bathing solution, whereas leaching from living cells is very less. (More dead part more will be staining)
- Thus, extent of discoloration indicates the proportion of dead seeds into a seed-lot.
3. Indigocarmine Method
- The seeds are soaked in the solution of any aniline dyes such as indigocarmine for few hours, it is observed that the dead seeds or their cells are stained. (More dead part more will be staining)
- Thus, the portion of dead and viable seeds can be determined by counting the number of stained and unstained seeds respectively.
4. Embryo Culture Method
- In this method, the embryo is removed carefully from its cotyledons or endosperm and then it is placed naked on granulated peat mass or on sterilized nutrient agar medium (White’s nutrient medium).
- The method takes about 7 to 10 days to give the viability percentage of the seeds.
- The viability is judged by counting the number of germinated embryos because the viable seeds will germinate and non-viable will fail to do so.
5. Tetrazolium Chloride Test
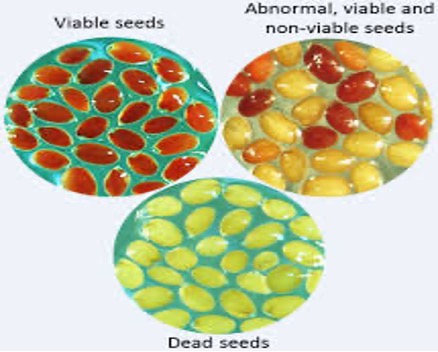
- Given by Lakon.
- The tetrazolium chloride test is also known as “
Biochemical test”. - In this method the seeds are soaked in 0.5 to 2 per cent solution of
tetrazolium chloride(2, 3, 5-triphenyl tetrazolium chloride). - The
viable or living seeds take bright red colorationswhich becomes more intense in the embryo while the dead seeds remain in their original colour. - The method can be used as a guide in blending seeds and their lots under an urgent and immediate demand for seed.
- It can be made quicker by cutting Kernels, using vacuum and maintaining a temperature of 40-45°C, it takes only 4-5 minutes to complete a test of 100 kernels.
6. Grodex Test
- Grodex is a seed germination indicator and is a brand name of
triphenyl tetrazolium bromidein powder form.
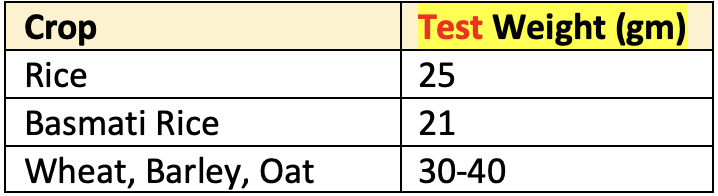
Seed Index
- Weight of
100 seedsof a crop
Test Weight
- Weight of
1000 seedsof a crop.
Pure Live Seed
- Pure Live Seed (PLS) is a measure used by the seed industry to describe the percentage of a quantity of seed that will germinate. (PLS related to germination percentage).
- PLS is obtained by multiplying the purity percentage by the percentage of total viable seed, then dividing by 100.
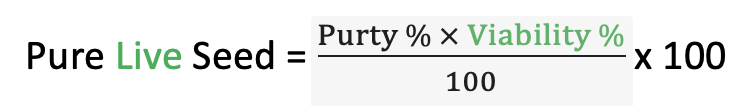
Genetic Purity
- Genetic purity is required 100% as far as impurities by seeds of other varieties of same crop is concerned but in case of Impurity by seeds of other crop species; it is permitted up to 0.1% only.
- Genetic purity is determined by
grow out test.
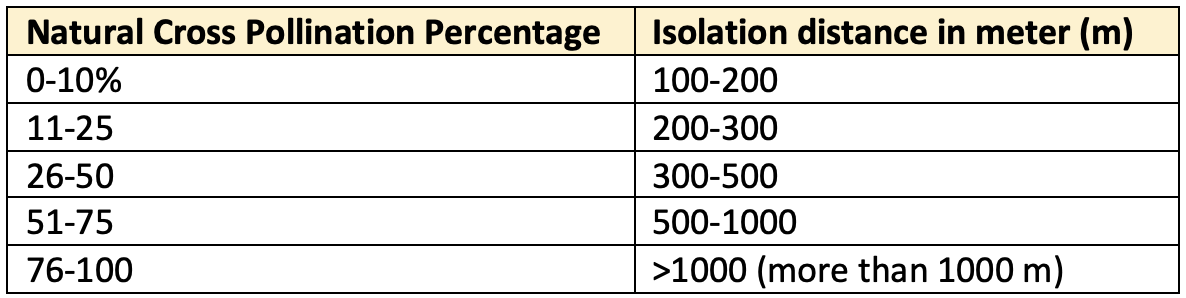
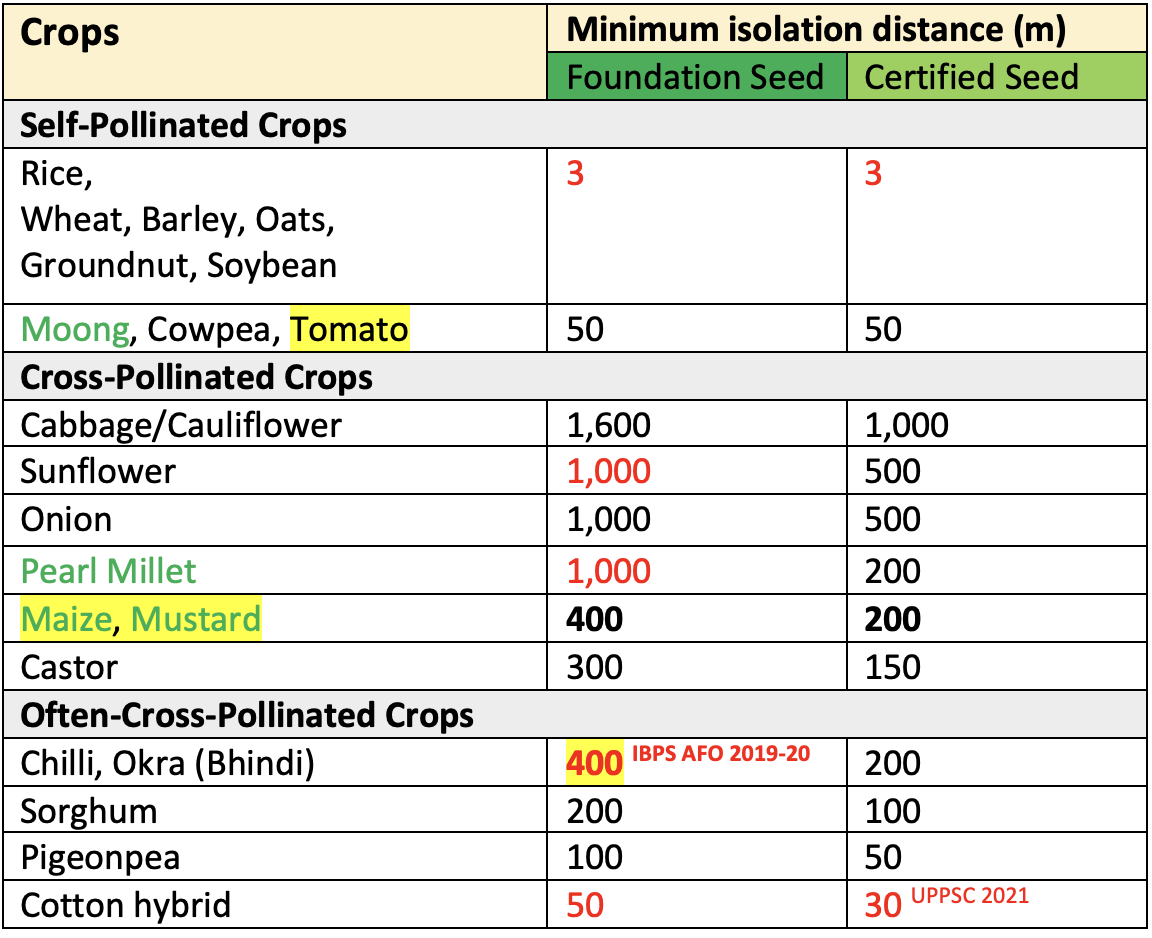
Isolation Distance
- Isolation means to keep apart. Isolation distance is the specified distance from potential contaminants, where an acceptable level of contamination is expected. Isolation of seed crop is essential to avoid genetic & physical impurities.
- Genetic purity i.e. varietal purity may be deteriorated by cross-pollination from the plants of nearby plots.
- Physical impurities may occur due to physical or mechanical admixture with other crop species or other varieties of the same species from the nearby plots.
- Therefore the protection from these sources of contamination is necessary for maintaining genetic and physical purity i.e. good quality of the seed.
- Isolation distance is affected by mode of pollination (i.e. self-pollination or cross pollination), pollination activity as well as direction and velocity of wind.
- Essentially self-pollinated crops like rice, wheat & soybean have only 3 meter as isolation distance. The increase in natural cross pollination percentage requires increasing isolation distance. E.g.
Objectionable Weeds of Seed Crop Plants
👉🏻 The size and shape of their seeds are so similar to that of the crop seed that it is difficult to remove. (Other damages of weeds are same)
- Off types are removed by negative selection.
- Rouging is the removal of plants which are off-type that is phenotypically different from the plants of the variety under production. It is an important aspect of seed production and is necessary to prevent out-crossing and mechanical mixtures. UPPSC 2021
Characteristics of good quality seed
High genetic purity

Higher physical purity for certification

Optimum moisture content for storage
- Long term storage:
6-8% - Short term storage:
10-13% - Dried to the safe storage moisture level of
10-12%for cereals and7-9 %for oil seeds (on wet basis) for a safe storage period of 6-12 months.
Seed Viability
- Viability of seeds represents the capacity of the seed to germinate.
- Viability is defined as the capacity of the seed to remain capable of germination for some specific period of the time. A Seed vigour is the ability of seed to emerge in varying environments of fields.
Methods for Viability Test of Seeds
1. Electrical Conductance Method
- The seeds are soaked in distilled water and the electrical conductance of the bathing solution is tested, the increase in conductance (Less resistance) is roughly proportional to the percentage of dead tissues.
- The increase in the conductivity is due to leaching of metabolites from dead seeds which become pervious owing to increasing permeability.
2. Potassium Permanganate Method
- The seeds are soaked in a weak solution of potassium …
Become Successful With AgriDots
Learn the essential skills for getting a seat in the Exam with
🦄 You are a pro member!
Only use this page if purchasing a gift or enterprise account
Plan
Rs
- Unlimited access to PRO courses
- Quizzes with hand-picked meme prizes
- Invite to private Discord chat
- Free Sticker emailed
Lifetime
Rs
1,499
once
- All PRO-tier benefits
- Single payment, lifetime access
- 4,200 bonus xp points
- Next Level
T-shirt shipped worldwide

Yo! You just found a 20% discount using 👉 EASTEREGG

High-quality fitted cotton shirt produced by Next Level Apparel