⛲️ Garden Style
Formal, Informal, Free Style
Style of gardening
Formal style
- First plan is made on paper and then land is selected accordingly.
- Land is leveled
Symmetricaldesign- Geometrical: Square, rectangular, circular beds and borders
- Roads and paths cut at right angle
- Balance is symmetrical as same feature replicated on both sides of central axis
- Hedges, edges and topiary are trimmed
- Trees can be selected as individual feature
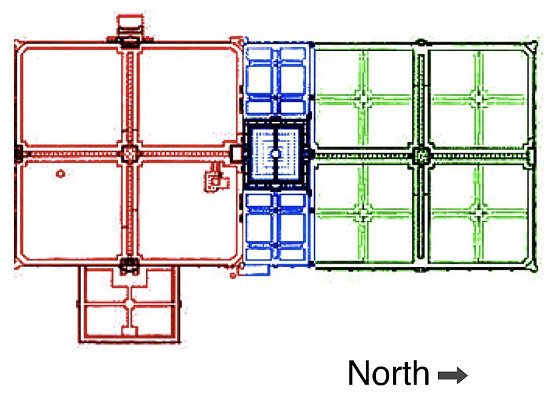
- E.g. Mughal gardens, Persian gardens, Pinjore garden, Italian (Roman), French and American gardens
Informal style
- Plan is forced to fit the land
- It reflects naturalistic effect of total view and represents natural beauty
- Land is not leveled
Asymmetricaldesign- Non-geometrical beds and borders
- Untrimmed hedges, edges and topiary
- Individual plants are not selected as feature
- E.g. Japanese garden, Chinese,
Englishgarden
Freestyle
- Combination of both formal and informal style.
- E.g.
Rose garden of Chandigarh.
Main features of garden
Mughal garden

- Terraces: Terraces are components to maintain the proportion of land for extended view irrespective of topography of the area 7, 8 or 12 terraces symbolize 7 planets, 8 paradise and 12 zodiacal signs. The entrance is located at the lowest terrace.
- Running water: Water is the life and soul of Moghul garden.
- Baradari: It is a canopied building with twelve open doors i.e., three in each direction. From baradari, one can sit and enjoy the fresh breeze and watch dark clouds and birds in the sky. The masonry pillars of baradari were painted with favorite design of bouquets of flowers in vases and the floor was furnished with thick carpets and cushions.
- High protecting wall
- Terminal building
- Scented flowers: The flowers in Moghul gardens are mostly scented in nature and highly colorful
Symbolism in Moghul gardens
- Water: Source of life
- Cross at intersection of water channel meeting humanity with God.
- Eight divisions: Eight divisions of Koran
- Alternate planting of cypress and flowering trees: Immortality and renewal of life.
- Bauhinia alba: Youth and life.
Japanese garden

- Often called as Zen garden.
- Garden lanterns
- Garden pagoda
- Dry landscape
- Wells
- E.g. British garden, Japanese garden, Buddha Jayanti park, New Delhi
English garden

- Herbaceous border
- Rockery
- Lawn
- Cottage garden
- E.g. Persian garden, Rastrapati garden, Tea garden
Lawn
- Regarded as heart of garden
- No garden is complete without lawn
- Planting of grass in lawn by
turf method

- It is best and quickest method for planting of lawn
- In this method turf-piece of earth with grasses are used.
Bonsai
Japaneseart of growing miniature trees and shrubs by extreme dwarfing.- The optimum size of Bonsai is 30-60 cm.
- Aluminium among the following wire is most suitable for making Bonsai.

Topiary

- It is an art of training plants in to different shape i.e. shape of animals, birds etc.
- Plants used in topiary are evergreen i.e. Duranta, Minya panniculata.
Edge

- When low growing perennial, annual plants are grown on the border of plots, beds are called edge.
- Ex. Alternanthera, Sunrose.
- Normal height is 30 cm.
Hedges

- When shrubs are planted on boundary for fencing.
- It may be ornamental or protective.
- Ex. Karonda, Bougainvillea, Mehndi, Hibiscus, Clerodendron and Lantana are the best example of hedge.
- Normal height is 1-2 meters.
- Group of shrubs is known as shrubbery.
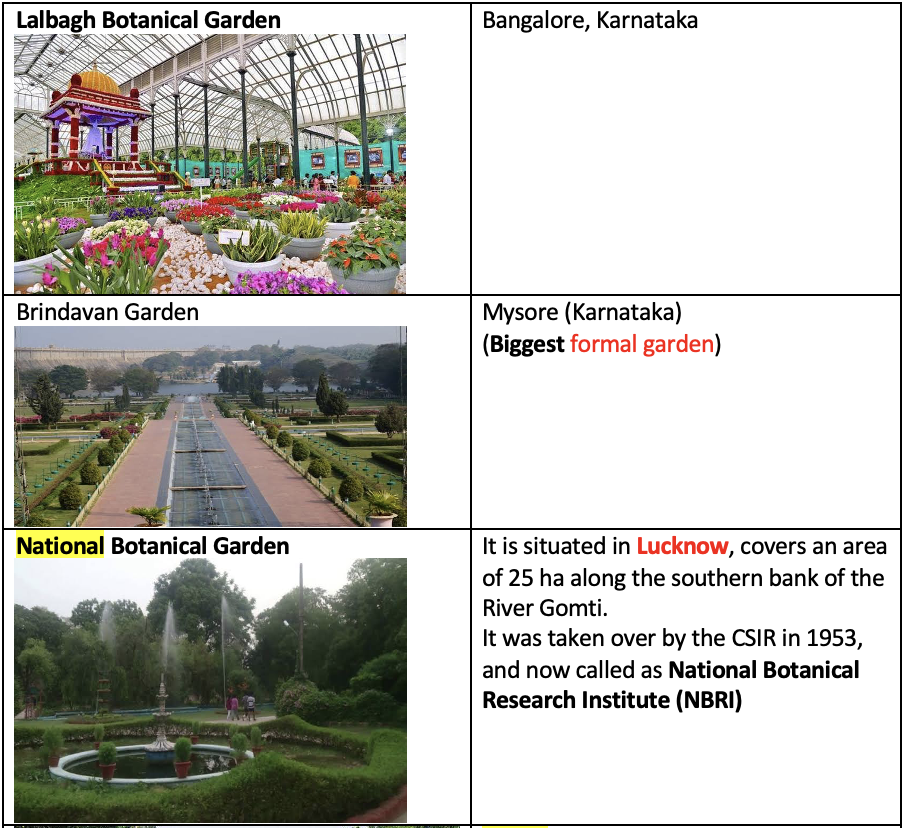
Famous gardens


Types of flowers
Cut flower

- Harvested at full open stage.
Loose flower

Style of gardening
Formal style
- First plan is made on paper and then land is selected accordingly.
- Land is leveled
Symmetricaldesign- Geometrical: Square, rectangular, circular beds and borders
- Roads and paths cut at right angle
- Balance is symmetrical as same feature replicated on both sides of central axis
- Hedges, edges and topiary are trimmed
- Trees can be selected as individual feature

- E.g. Mughal gardens, Persian gardens, Pinjore garden, Italian (Roman), French and American gardens
Informal style
- Plan is forced to fit the land
- It reflects naturalistic effect of total view and represents natural beauty
- Land is not leveled
Asymmetricaldesign- Non-geometrical beds and borders
- Untrimmed hedges, edges and topiary
- Individual plants are not selected as feature
- E.g. Japanese garden, …
Become Successful With AgriDots
Learn the essential skills for getting a seat in the Exam with
🦄 You are a pro member!
Only use this page if purchasing a gift or enterprise account
Plan
Rs
- Unlimited access to PRO courses
- Quizzes with hand-picked meme prizes
- Invite to private Discord chat
- Free Sticker emailed
Lifetime
Rs
1,499
once
- All PRO-tier benefits
- Single payment, lifetime access
- 4,200 bonus xp points
- Next Level
T-shirt shipped worldwide

Yo! You just found a 20% discount using 👉 EASTEREGG

High-quality fitted cotton shirt produced by Next Level Apparel