🍆 Brinjal
Cultivation, Important Point, Pests
- Botanical Name: Solanum melongena
- Family: Solanaceae
- Bitterness is due to presence of
glycoalkaloids. - Pigment present in brinjal is
Anthocyanin.

- Brinjal fruits are good source of
Vitamin B. - Seed rate:
200 g/hafor nursery sowing
Varieties
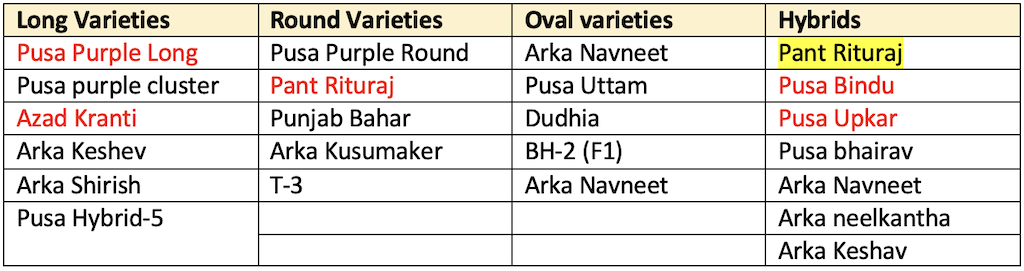
- Pusa purple long (Extra early maturity)
- Pant samrat (Phomopsis blight and bacterial wilt resistant).
- Black beauty (Nematode resistant)
- Arka sheel, Arka nidhi
Hybrid
- Pusa bindu
- Pusa upkar
- Pusa bhairav (Phomopsis blight resistant)
- Arka navneet (Highest yielding)
- Arka neelkantha (Nematode resistant)
- Annamalai: Aphid resistant, recommended for TN
- Arka keshav
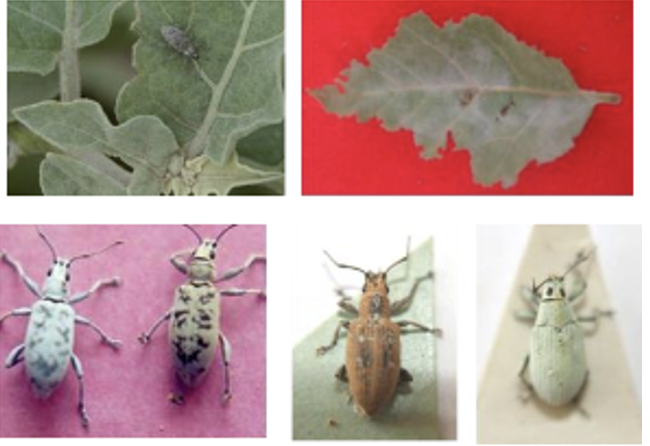
Insect
-
Fruit and shoot borer:
Leucinodes orbonalis, Pyralidae, Lepidoptera (Major pest of brinjal).- Cause ‘dead heart’ in young plants, tender growing shoot is killed by larvae in early stage and later bore into fruits.
- It can be managed by application of Spirotetramat 150 SC @ 75 g a.i. /ha. or Flubendiamide 48 SC @ 60 g a.i. /ha.

-
Hadda beetle:
- Epilachna vignitictopunctata (F. Coccinelidae)

- Epilachna vignitictopunctata (F. Coccinelidae)
-
Brinjal Brown leaf hopper:

- Cestius phycitis (vector of little leaf of brinjal).
- The white flies and jassids/leaf hopper in brinjal can be controlled by application of lmidacloprid 200 SL @ 75 g a.i /ha
- Ash weevils:
- Myllocerus subfasciatus

Diseases:
- Little leaf of brinjal
- Due to
Mycoplama - Transmitted by leaf hoppers:
Cestius phycitis
- Due to
- Botanical Name: Solanum melongena
- Family: Solanaceae
- Bitterness is due to presence of
glycoalkaloids. - Pigment present in brinjal is
Anthocyanin.

- Brinjal fruits are good source of
Vitamin B. - Seed rate:
200 g/hafor nursery sowing
Varieties

- Pusa purple long (Extra early maturity)
- Pant samrat (Phomopsis blight and bacterial wilt resistant).
- Black beauty (Nematode resistant)
- Arka sheel, Arka nidhi
Hybrid
- Pusa bindu
- Pusa upkar
- Pusa bhairav (Phomopsis blight resistant)
- Arka navneet (Highest yielding)
- Arka neelkantha (Nematode resistant)
- Annamalai: Aphid resistant, recommended for TN
- Arka keshav
Insect
-
Fruit and shoot borer:
Leucinodes orbonalis, Pyralidae, Lepidoptera (Major pest of brinjal).- Cause ‘dead heart’ in young plants, tender growing shoot is killed by …
Become Successful With AgriDots
Learn the essential skills for getting a seat in the Exam with
🦄 You are a pro member!
Only use this page if purchasing a gift or enterprise account
Plan
Rs
- Unlimited access to PRO courses
- Quizzes with hand-picked meme prizes
- Invite to private Discord chat
- Free Sticker emailed
Lifetime
Rs
1,499
once
- All PRO-tier benefits
- Single payment, lifetime access
- 4,200 bonus xp points
- Next Level
T-shirt shipped worldwide

Yo! You just found a 20% discount using 👉 EASTEREGG

High-quality fitted cotton shirt produced by Next Level Apparel